Invertebrates
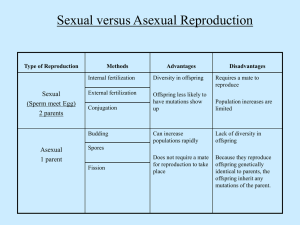
... •Increases population rapidly/no mate needed •What is a disadvantage of asexual reproduction? •Reproduce offspring identical to parents ...
... •Increases population rapidly/no mate needed •What is a disadvantage of asexual reproduction? •Reproduce offspring identical to parents ...
Cell Organelles and Biotechnology
... Most researchers think that eukaryotic cells (such as those in your body) arose from prokaryotic ones (such as bacterial cells). How this happened is a much-discussed topic of interest among biologists. The similarities between the two energy-related organelles of cells, the chloroplast and the mito ...
... Most researchers think that eukaryotic cells (such as those in your body) arose from prokaryotic ones (such as bacterial cells). How this happened is a much-discussed topic of interest among biologists. The similarities between the two energy-related organelles of cells, the chloroplast and the mito ...
The Peppered Moth – A case of Natural Selection and Adaptation
... over the flecked moths. Black soot from factories killed the lichens and covered trees providing an excellent source of camouflage for black moths. Now, the flecked moths were easily seen and eaten. The black moths survived and passed their genes onto their ...
... over the flecked moths. Black soot from factories killed the lichens and covered trees providing an excellent source of camouflage for black moths. Now, the flecked moths were easily seen and eaten. The black moths survived and passed their genes onto their ...
SHS Core Earth Science CG
... protecting the soil for future generations 16. describe how people generate different types of waste (solid, liquid, and gaseous) as they make use of various materials and resources in everyday life 17. explain how different types of waste affect people’s health and the environment 18. cite ways of ...
... protecting the soil for future generations 16. describe how people generate different types of waste (solid, liquid, and gaseous) as they make use of various materials and resources in everyday life 17. explain how different types of waste affect people’s health and the environment 18. cite ways of ...
Flatworms, Nematodes, and Arthropods
... that attaches to a sh to begin transformation to the parasitic adult form. They have only one host during their life, typically of just one species. The worms may produce enzymes that digest the host tissues or graze on surface mucus and skin particles. Most monogeneans are hermaphroditic, but the ...
... that attaches to a sh to begin transformation to the parasitic adult form. They have only one host during their life, typically of just one species. The worms may produce enzymes that digest the host tissues or graze on surface mucus and skin particles. Most monogeneans are hermaphroditic, but the ...
Natural selection
... • Fossils The remains or imprints of once-living organisms found in layers of rock called fossils. ...
... • Fossils The remains or imprints of once-living organisms found in layers of rock called fossils. ...
Chapter Four Notes
... three conditions required for natural selection: evolution: the change in a population's genetic makeup through successive generations. • microevolution: change in gene frequency within a population (short–term evolutionary changes); • macroevolution: the formation of new species from ancestral spec ...
... three conditions required for natural selection: evolution: the change in a population's genetic makeup through successive generations. • microevolution: change in gene frequency within a population (short–term evolutionary changes); • macroevolution: the formation of new species from ancestral spec ...
Text Structure Samples - Utah Education Network
... 1 “The earth’s crust is made up mostly of hard, rocky substances, though some of these substances have crumbled into dirt from years of exposure to wind and rain and roots of plants. That crust is many miles thick (though the part under the ocean is thinner than the part on the land). Underneath the ...
... 1 “The earth’s crust is made up mostly of hard, rocky substances, though some of these substances have crumbled into dirt from years of exposure to wind and rain and roots of plants. That crust is many miles thick (though the part under the ocean is thinner than the part on the land). Underneath the ...
DIVERSITY NOTES
... 2. an example is schistosome, which causes schistosomiasis a. the adult worm enters a person's skin and digests its way into a blood vessel b. eventually, it finds it way to the tiny blood vessels of the intestine and lays its eggs c. the eggs grow and hatch, breaking the blood vessel d. causes coug ...
... 2. an example is schistosome, which causes schistosomiasis a. the adult worm enters a person's skin and digests its way into a blood vessel b. eventually, it finds it way to the tiny blood vessels of the intestine and lays its eggs c. the eggs grow and hatch, breaking the blood vessel d. causes coug ...
Teacher Wrap-Up
... Q1. How are these embryos similar? They have long tails, large heads, eyes, notochord and pharyngeal gill slits. Q2. How do they differ in structure? Some have larger heads and bigger eyes. The bodies are thinner on the A and B embryos. Q3. How are these embryos similar to the other embryos? A and B ...
... Q1. How are these embryos similar? They have long tails, large heads, eyes, notochord and pharyngeal gill slits. Q2. How do they differ in structure? Some have larger heads and bigger eyes. The bodies are thinner on the A and B embryos. Q3. How are these embryos similar to the other embryos? A and B ...
Biology Summary [PDF Document]
... Photosynthesis is the process by which plants make their food. Photosynthesis occurs in the leaves of a plant. The green chemical chlorophyll is needed for photosynthesis. It is found in the chloroplasts in a plant cell. Chlorophyll traps light energy and uses it to combine carbon dioxide and water. ...
... Photosynthesis is the process by which plants make their food. Photosynthesis occurs in the leaves of a plant. The green chemical chlorophyll is needed for photosynthesis. It is found in the chloroplasts in a plant cell. Chlorophyll traps light energy and uses it to combine carbon dioxide and water. ...
Studyguide_PTtest
... ~ The theory Harry Hess put forth – What did he find? What other evidence added to the idea that the seafloor was spreading? (new crust formed at mid-ocean ridge – younger closer to ridge, older farther away; trenches & subduction zones; magnetic striping of seafloor) ~ The 4 basic layers of the Ear ...
... ~ The theory Harry Hess put forth – What did he find? What other evidence added to the idea that the seafloor was spreading? (new crust formed at mid-ocean ridge – younger closer to ridge, older farther away; trenches & subduction zones; magnetic striping of seafloor) ~ The 4 basic layers of the Ear ...
8th Grade Science
... • A force is described by its strength (magnitude) and in what direction it is acting. Many forces can act on a single object simultaneously. The forces acting on an object can be represented by arrows drawn on an isolated picture of the object (a force diagram). ...
... • A force is described by its strength (magnitude) and in what direction it is acting. Many forces can act on a single object simultaneously. The forces acting on an object can be represented by arrows drawn on an isolated picture of the object (a force diagram). ...
Evolution and Taxonomy Outline
... processes and patterns. (DOK 3) c. Research and summarize the contributions of scientists, (including Darwin, Malthus, Wallace, Lamarck, and Lyell) whose work led to the development of the theory of evolution. (DOK 2) d. Analyze and explain the roles of natural selection, including the mechanisms of ...
... processes and patterns. (DOK 3) c. Research and summarize the contributions of scientists, (including Darwin, Malthus, Wallace, Lamarck, and Lyell) whose work led to the development of the theory of evolution. (DOK 2) d. Analyze and explain the roles of natural selection, including the mechanisms of ...
Plate Tectonics Layered Earth Unit B Worksheet Key
... then slowly carried away by seafloor spreading. A magnetic reversal of the poles would show up as band of reversed polarity in the seafloor. The symmetric banding was the result of seafloor spreading on both sides of the mid-ocean ridge. 2. Why was the Vine and Matthews explanation of magnetic strip ...
... then slowly carried away by seafloor spreading. A magnetic reversal of the poles would show up as band of reversed polarity in the seafloor. The symmetric banding was the result of seafloor spreading on both sides of the mid-ocean ridge. 2. Why was the Vine and Matthews explanation of magnetic strip ...
Course Outline and General Information
... Lecture Outline: (order of topics may change) Introduction to the course An overview of physical geology: Important concepts and its place among Earth sciences. Earth’s structure. Geologic time. Why is geology important? From atoms to minerals Atoms, elements and isotopes. Crystal structures. Minera ...
... Lecture Outline: (order of topics may change) Introduction to the course An overview of physical geology: Important concepts and its place among Earth sciences. Earth’s structure. Geologic time. Why is geology important? From atoms to minerals Atoms, elements and isotopes. Crystal structures. Minera ...
6_GC1_AtmosOceanCon..
... How long have we had Oceans? Oceans: formed soon after Earth’s temperature fell to levels where liquid water was stable • Oceans may have condensed and then been vaporized many times as impacts bombarded early Earth • Size of impactor matters - Diameter of ~100km will vaporize photic zone (upper 10 ...
... How long have we had Oceans? Oceans: formed soon after Earth’s temperature fell to levels where liquid water was stable • Oceans may have condensed and then been vaporized many times as impacts bombarded early Earth • Size of impactor matters - Diameter of ~100km will vaporize photic zone (upper 10 ...
English
... Cell Specialization An organ is a group of tissues that work together to perform specific functions. Each tissue job varies, but by working together the organ carries out its function. Examples of organs include the heart, lungs, and liver. ...
... Cell Specialization An organ is a group of tissues that work together to perform specific functions. Each tissue job varies, but by working together the organ carries out its function. Examples of organs include the heart, lungs, and liver. ...
AnatomyPhysiology-English
... Cell Specialization Cells are the building blocks of organisms. A cell is the basic structure of life. Cells have important structures that allow them to function. Protoplasm within a cell carries out important chemical activities. Multi-cellular organisms have many cells. These cells for ...
... Cell Specialization Cells are the building blocks of organisms. A cell is the basic structure of life. Cells have important structures that allow them to function. Protoplasm within a cell carries out important chemical activities. Multi-cellular organisms have many cells. These cells for ...
INSIDE THE EARTH
... the rocks get older as you move further from the ridge. EQ6: What happens at deep-ocean trenches? Subduction occurs at deep-ocean trenches. This is where the sea floor goes back into the mantle. ...
... the rocks get older as you move further from the ridge. EQ6: What happens at deep-ocean trenches? Subduction occurs at deep-ocean trenches. This is where the sea floor goes back into the mantle. ...
Evidence for Common Descent
... Cross-generational change in a population of organisms that involves changes in gene frequency . In science, labeling something a theory does not mean that it is a conjecture or hypothesis. It means a well-supported, testable framework to explain or predict some natural phenomenon. What we call the ...
... Cross-generational change in a population of organisms that involves changes in gene frequency . In science, labeling something a theory does not mean that it is a conjecture or hypothesis. It means a well-supported, testable framework to explain or predict some natural phenomenon. What we call the ...
Feature Summary
... p. 000). The bacteria are usually sheltered in special light-producing organs, or photophores. These deep-sea animals, which live in darkness, use light to communicate with other members of their species, lure prey, blend with the light that filters from the surface, and perform other functions. Fla ...
... p. 000). The bacteria are usually sheltered in special light-producing organs, or photophores. These deep-sea animals, which live in darkness, use light to communicate with other members of their species, lure prey, blend with the light that filters from the surface, and perform other functions. Fla ...
Evolutionary history of life

The evolutionary history of life on Earth traces the processes by which living and fossil organisms have evolved since life appeared on the planet, until the present day. Earth formed about 4.5 Ga (billion years ago) and life appeared on its surface within 1 billion years. The similarities between all present-day organisms indicate the presence of a common ancestor from which all known species have diverged through the process of evolution. More than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.











![Biology Summary [PDF Document]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015201071_1-645f2d1eb761f177f20a3a1ed550cdc7-300x300.png)











