phylum: annelida - Two Oceans Aquarium
... Filter feeders – An animal that uses some body part to strain very small animals or plants (plankton ) from water Herbivore- An animal that eats plants or algae Detritus feeder or detritivore – animal that feeds on dead material (detritus). This is mainly plant material. Carnivores – An animal that ...
... Filter feeders – An animal that uses some body part to strain very small animals or plants (plankton ) from water Herbivore- An animal that eats plants or algae Detritus feeder or detritivore – animal that feeds on dead material (detritus). This is mainly plant material. Carnivores – An animal that ...
Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics
... 1. Label the land masses on each sheet. Color the fossil areas to match the legend below. 2. Cut out each of the continents along the edge of the continental shelf (the outermost dark line). Alfred Wegener's evidence for continental drift is shown on the cut-outs. Wegener used this evidence to recon ...
... 1. Label the land masses on each sheet. Color the fossil areas to match the legend below. 2. Cut out each of the continents along the edge of the continental shelf (the outermost dark line). Alfred Wegener's evidence for continental drift is shown on the cut-outs. Wegener used this evidence to recon ...
Final Exam - Salinella
... 2.18 A closed circulatory system is found in ________ a. insects. ________ b. snails. ________ c. clams. ________ d. earthworms. ________ e. scorpions. 2.19 Most animal species are in which phylum? ________ a. Mollusca ________ b. Arthropoda ________ c. Chordata ________ d. Echinodermata ________ e. ...
... 2.18 A closed circulatory system is found in ________ a. insects. ________ b. snails. ________ c. clams. ________ d. earthworms. ________ e. scorpions. 2.19 Most animal species are in which phylum? ________ a. Mollusca ________ b. Arthropoda ________ c. Chordata ________ d. Echinodermata ________ e. ...
Chapter 5: The Process of Evolution
... Vocabulary evolution naturalist natural selection adaptation ...
... Vocabulary evolution naturalist natural selection adaptation ...
Biology revision notes
... Chemical digestion Chemical digestion involves the use of special chemicals, called enzymes, to breakdown the large food molecules (proteins, fats and carbohydrates) into smaller ones. An enzyme can be defined as a biological catalyst. A catalyst is a chemical which speeds up a chemical reaction wit ...
... Chemical digestion Chemical digestion involves the use of special chemicals, called enzymes, to breakdown the large food molecules (proteins, fats and carbohydrates) into smaller ones. An enzyme can be defined as a biological catalyst. A catalyst is a chemical which speeds up a chemical reaction wit ...
Continental Drift and Seafloor
... Glacial Deposits • Eroded rocks and debris left behind by ancient glaciers can be found in South America, Africa, India, and Australia which all have different climates and are not near the poles. ...
... Glacial Deposits • Eroded rocks and debris left behind by ancient glaciers can be found in South America, Africa, India, and Australia which all have different climates and are not near the poles. ...
a fully formatted pdf version of the note
... -‐Geologists study fossils for paleo ecology where they can find out the pa_erns of life, predict and/or protect future -‐We live in Holocene epoch, Quaternary period and Cenozoic era -‐Major divisions of ...
... -‐Geologists study fossils for paleo ecology where they can find out the pa_erns of life, predict and/or protect future -‐We live in Holocene epoch, Quaternary period and Cenozoic era -‐Major divisions of ...
- Boardworks
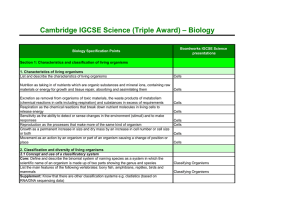
... materials or energy for growth and tissue repair, absorbing and assimilating them Cells Excretion as removal from organisms of toxic materials, the waste products of metabolism (chemical reactions in cells including respiration) and substances in excess of requirements Respiration as the chemical re ...
... materials or energy for growth and tissue repair, absorbing and assimilating them Cells Excretion as removal from organisms of toxic materials, the waste products of metabolism (chemical reactions in cells including respiration) and substances in excess of requirements Respiration as the chemical re ...
Biology End of Course Exam 2012 – Study Guide and... Biological Concept
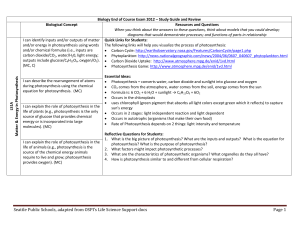
... 3. Explain how enzymes break large food molecules down into smaller molecules and how these molecules become available for the cell to make new molecules. 4. Describe how the new molecules are different than the original large molecules? 5. Describe how a cell can be built from the new molecules men ...
... 3. Explain how enzymes break large food molecules down into smaller molecules and how these molecules become available for the cell to make new molecules. 4. Describe how the new molecules are different than the original large molecules? 5. Describe how a cell can be built from the new molecules men ...
Section 28.1 Summary – pages 741 - 746
... • Movement, sound, and chemicals can be detected with great sensitivity by ______, stalk-like structures that detect changes in the environment. ...
... • Movement, sound, and chemicals can be detected with great sensitivity by ______, stalk-like structures that detect changes in the environment. ...
Biology EOC Study Guide
... 3. Explain how enzymes break large food molecules down into smaller molecules and how these molecules become available for the cell to make new molecules. 4. Describe how the new molecules are different than the original large molecules? 5. Describe how a cell can be built from the new molecules men ...
... 3. Explain how enzymes break large food molecules down into smaller molecules and how these molecules become available for the cell to make new molecules. 4. Describe how the new molecules are different than the original large molecules? 5. Describe how a cell can be built from the new molecules men ...
EOC review guide
... 3. Explain how enzymes break large food molecules down into smaller molecules and how these molecules become available for the cell to make new molecules. 4. Describe how the new molecules are different than the original large molecules? 5. Describe how a cell can be built from the new molecules men ...
... 3. Explain how enzymes break large food molecules down into smaller molecules and how these molecules become available for the cell to make new molecules. 4. Describe how the new molecules are different than the original large molecules? 5. Describe how a cell can be built from the new molecules men ...
big study guide
... 3. Explain how enzymes break large food molecules down into smaller molecules and how these molecules become available for the cell to make new molecules. 4. Describe how the new molecules are different than the original large molecules? 5. Describe how a cell can be built from the new molecules men ...
... 3. Explain how enzymes break large food molecules down into smaller molecules and how these molecules become available for the cell to make new molecules. 4. Describe how the new molecules are different than the original large molecules? 5. Describe how a cell can be built from the new molecules men ...
File
... 3) A lava flow includes fragments of limestone in it. Which rock unit is older, the lava flow or the limestone? ________ 4) The process by which geologists identify and match sedimentary strata and other rocks of the same ages in different areas is ________. 5) The amount of time it takes for half o ...
... 3) A lava flow includes fragments of limestone in it. Which rock unit is older, the lava flow or the limestone? ________ 4) The process by which geologists identify and match sedimentary strata and other rocks of the same ages in different areas is ________. 5) The amount of time it takes for half o ...
Desktop PIA for Kwagga North project, Optimum Colliery, Arnot
... According to Bamford (2011), little data has been published on these potentially fossiliferous deposits. Around the coalmines there is most likely to be good material and yet in other areas the exposures may be too poor to be of interest. When they do occur, fossil plants are usually abundant and it ...
... According to Bamford (2011), little data has been published on these potentially fossiliferous deposits. Around the coalmines there is most likely to be good material and yet in other areas the exposures may be too poor to be of interest. When they do occur, fossil plants are usually abundant and it ...
Extinctions: Georges Cuvier
... abrupt changes. Mountains were built in catastrophic instants, and in the process whole groups of animals became extinct and were replaced by new species. Giant tropical plants, for example, left their fossils in northern Europe during the Carboniferous Period, never to be seen there again. Earth's ...
... abrupt changes. Mountains were built in catastrophic instants, and in the process whole groups of animals became extinct and were replaced by new species. Giant tropical plants, for example, left their fossils in northern Europe during the Carboniferous Period, never to be seen there again. Earth's ...
Chapter 1 Planet Earth
... and scoured by running water, which moves rocks around and changes their appearance. Erosion is the process in which the materials of the Earth’s surface are loosened, dissolved, or worn away and transported form one place to another by a natural agent, such as wind, water, ice or gravity. Erosi ...
... and scoured by running water, which moves rocks around and changes their appearance. Erosion is the process in which the materials of the Earth’s surface are loosened, dissolved, or worn away and transported form one place to another by a natural agent, such as wind, water, ice or gravity. Erosi ...
A is for Acoelomates:
... evolutionary origins. Higher animals can be divided into two groups. Those with fertilized eggs (zygotes) that develop the basic body plan very early and those that develop the basic body plan in stages. The first kind is called a determined or “mosaic” egg. The second kind is called a “regulative” ...
... evolutionary origins. Higher animals can be divided into two groups. Those with fertilized eggs (zygotes) that develop the basic body plan very early and those that develop the basic body plan in stages. The first kind is called a determined or “mosaic” egg. The second kind is called a “regulative” ...
Structure of Fungi - Scienceiskool.com
... that run along the surface of object • Sporangiophores – hyphae that shoot up into the air with zygospores on them ...
... that run along the surface of object • Sporangiophores – hyphae that shoot up into the air with zygospores on them ...
Jigsaw Puzzle Earth
... Paleomagnetism became another theory suggested by scientists during the mid-1960's to explain sea-floor spreading. Paleomagnetism refers to the magnetic properties that rocks acquire during their formation and that become permanent after they harden. Scientists found that as magma cools and solidifi ...
... Paleomagnetism became another theory suggested by scientists during the mid-1960's to explain sea-floor spreading. Paleomagnetism refers to the magnetic properties that rocks acquire during their formation and that become permanent after they harden. Scientists found that as magma cools and solidifi ...
Biology EOC StudyGuide - Edmonds School District
... Understanding of the components of DNA and how the components fit together. DNA codes for genes, which code for specific amino acids needed to make a protein. Proteins are expressed as traits. Reflective Questions for Students: 1. What is the basic structure of DNA (consider a diagram)? 2. Wha ...
... Understanding of the components of DNA and how the components fit together. DNA codes for genes, which code for specific amino acids needed to make a protein. Proteins are expressed as traits. Reflective Questions for Students: 1. What is the basic structure of DNA (consider a diagram)? 2. Wha ...
Biology EOC Review Guide
... Understanding of the components of DNA and how the components fit together. DNA codes for genes, which code for specific amino acids needed to make a protein. Proteins are expressed as traits. Reflective Questions for Students: 1. What is the basic structure of DNA (consider a diagram)? 2. Wha ...
... Understanding of the components of DNA and how the components fit together. DNA codes for genes, which code for specific amino acids needed to make a protein. Proteins are expressed as traits. Reflective Questions for Students: 1. What is the basic structure of DNA (consider a diagram)? 2. Wha ...
Section 2: Rocks and Minerals
... – Kinds of igneous rock are obsidian, basalt, and granite. – Igneous rocks make up ________ of the Earth’s crust. __________________ Rock – They are formed by the __________________ together of smaller particles of rock or the remains of living things. – They take a __________________time to form. ...
... – Kinds of igneous rock are obsidian, basalt, and granite. – Igneous rocks make up ________ of the Earth’s crust. __________________ Rock – They are formed by the __________________ together of smaller particles of rock or the remains of living things. – They take a __________________time to form. ...
STB 111 THEORY - Unesco
... Aristotle’s system distinguished only between plants and animals on the basis of movement, feeding mechanism, and growth patterns. In 1735 the Swedish naturalist Carolus Linnaeus formalized the use of two Latin names to identify each organism, a system called binomial nomenclature. He grouped closel ...
... Aristotle’s system distinguished only between plants and animals on the basis of movement, feeding mechanism, and growth patterns. In 1735 the Swedish naturalist Carolus Linnaeus formalized the use of two Latin names to identify each organism, a system called binomial nomenclature. He grouped closel ...
Evolutionary history of life

The evolutionary history of life on Earth traces the processes by which living and fossil organisms have evolved since life appeared on the planet, until the present day. Earth formed about 4.5 Ga (billion years ago) and life appeared on its surface within 1 billion years. The similarities between all present-day organisms indicate the presence of a common ancestor from which all known species have diverged through the process of evolution. More than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.