Unit 7 Study Guide
... Mountains are created and eroded, The sea floor spreads as new rock pushes up to create ocean ridges. Layers of rock are disturbed causing them to be tilted, folded, eroded to form uncomformities, broken to form faults, and intrusions where magma pushes upwards and cuts through layers of rock. E ...
... Mountains are created and eroded, The sea floor spreads as new rock pushes up to create ocean ridges. Layers of rock are disturbed causing them to be tilted, folded, eroded to form uncomformities, broken to form faults, and intrusions where magma pushes upwards and cuts through layers of rock. E ...
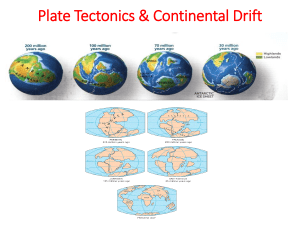
ALFRED WEGENER THEORY OF CONTINENTAL
... 6. What happens when plates pull apart? 7. Define Pangea ...
... 6. What happens when plates pull apart? 7. Define Pangea ...
Chapter 16 Darwin and Natural Selection
... Summary of Darwin’s Theory • Because more organisms are produce than can survive, each species must struggle for resources • Each organism is unique, each has advantages and disadvantages in the struggle for existence ...
... Summary of Darwin’s Theory • Because more organisms are produce than can survive, each species must struggle for resources • Each organism is unique, each has advantages and disadvantages in the struggle for existence ...
study guide for evolution test – friday june 3rd
... 1) The answers to the frequently asked questions (FAQs) in the first lecture about evolution such as: a. Can creationism legally be taught in the public schools of the United States? b. Are humans descendents of apes? c. Are there any religions which accept the teaching of modern evolutionary theory ...
... 1) The answers to the frequently asked questions (FAQs) in the first lecture about evolution such as: a. Can creationism legally be taught in the public schools of the United States? b. Are humans descendents of apes? c. Are there any religions which accept the teaching of modern evolutionary theory ...
Intro to Evolution with HOMEWORK
... Individual organisms differ and some of these variations are heritable (passed on) Organisms produce more offspring than can survive and many that do survive do not reproduce Because more organisms are produce than can survive, they must compete for limited resources (food, shelter, etc) Eac ...
... Individual organisms differ and some of these variations are heritable (passed on) Organisms produce more offspring than can survive and many that do survive do not reproduce Because more organisms are produce than can survive, they must compete for limited resources (food, shelter, etc) Eac ...
abiotic nonliving, physical features of the environment, including air
... compound, such as ethanol, that is formed when 2OH groups replace one or more hydrogen atoms in a hydrocarbon. chlorophyll-containing, plantlike protists that produce oxygen as a result of photosynthesis. an alternate form that a gene may have for a single trait; can be dominant or recessive. substa ...
... compound, such as ethanol, that is formed when 2OH groups replace one or more hydrogen atoms in a hydrocarbon. chlorophyll-containing, plantlike protists that produce oxygen as a result of photosynthesis. an alternate form that a gene may have for a single trait; can be dominant or recessive. substa ...
The Theory of Evolution
... inherited changes within populations over time. – group of individuals of one species that live in the same area i.e. all organisms have descended from common ancestors with modifications, over long periods of time Population ...
... inherited changes within populations over time. – group of individuals of one species that live in the same area i.e. all organisms have descended from common ancestors with modifications, over long periods of time Population ...
100 living environment regents facts
... 48. When small group of individuals is separated from the main population, they may evolve into a new species specialized for a different environment, or may become extinct. 49. Changes in genes (gene mutations) result in variation leading to new species. 50. Changes in genes make evolution possible ...
... 48. When small group of individuals is separated from the main population, they may evolve into a new species specialized for a different environment, or may become extinct. 49. Changes in genes (gene mutations) result in variation leading to new species. 50. Changes in genes make evolution possible ...
Name - Humble ISD
... V. MACROEVOLUTION- refers to large-scale evolutionary pattern and processes that occur over long periods of time. A. Extinction-More than 99 % of all species that have ever lived are now extinct, which means the species has died out. Darwin proposed possible reasons with competition for resources an ...
... V. MACROEVOLUTION- refers to large-scale evolutionary pattern and processes that occur over long periods of time. A. Extinction-More than 99 % of all species that have ever lived are now extinct, which means the species has died out. Darwin proposed possible reasons with competition for resources an ...
Biology Final Review
... 63. A nucleotide of DNA would contain what pieces? 64. If the code for an amino acid is ATG on the DNA molecule, this code on the tRNA molecule would be written as __________. 65. The decoding of mRNA message into a protein is known as _____________. 66. Each combination of three mucleotides on the ...
... 63. A nucleotide of DNA would contain what pieces? 64. If the code for an amino acid is ATG on the DNA molecule, this code on the tRNA molecule would be written as __________. 65. The decoding of mRNA message into a protein is known as _____________. 66. Each combination of three mucleotides on the ...
FRQs (will be Evolution Only)
... b. For each process of phenomenon you selected in (a), discuss its impact on the diversity of life on Earth. FRQ #2 Charles Darwin proposed that evolution by natural selection was the basis for the difference that he saw in similar organisms as he traveled and collected specimen in South America and ...
... b. For each process of phenomenon you selected in (a), discuss its impact on the diversity of life on Earth. FRQ #2 Charles Darwin proposed that evolution by natural selection was the basis for the difference that he saw in similar organisms as he traveled and collected specimen in South America and ...
Unit 2 - Notes
... this field is a taxonomist. A classification system is a way to identify an organism and place it into the correct group with related organisms. It is also a way of referring to an organism by name so that scientists in each part of the world can understand each other regardless of language (ie.) a ...
... this field is a taxonomist. A classification system is a way to identify an organism and place it into the correct group with related organisms. It is also a way of referring to an organism by name so that scientists in each part of the world can understand each other regardless of language (ie.) a ...
Intro Stream Processes
... What might best explain homologous structures between the fins of whales and wings of bats? ...
... What might best explain homologous structures between the fins of whales and wings of bats? ...
Galapagos Islands
... theories of evolution and natural selection. • Like several scientists before him, Darwin believed all the life on earth evolved (developed gradually) over millions of years from a few common ancestors. • In 1831, Darwin took a trip around the world on the ship, the M.S. Beagle, where he collected e ...
... theories of evolution and natural selection. • Like several scientists before him, Darwin believed all the life on earth evolved (developed gradually) over millions of years from a few common ancestors. • In 1831, Darwin took a trip around the world on the ship, the M.S. Beagle, where he collected e ...
Life Science Final Review
... 5. For a science project Susie wants to compare the densities of different types of wood. She gets a block of pine and the same size block of oak. She finds two of the same sized nails, (but one is made of steel and the other is made of aluminum). She finds two of the same hammers. Then she recruit ...
... 5. For a science project Susie wants to compare the densities of different types of wood. She gets a block of pine and the same size block of oak. She finds two of the same sized nails, (but one is made of steel and the other is made of aluminum). She finds two of the same hammers. Then she recruit ...
More Than An EyeWitness
... well documented THEORY uniting all of biology. • Modern evolutionary theory uses ideas of genetics, particularly mutations, to help explain how evolution may occur. (Darwin didn’t know ...
... well documented THEORY uniting all of biology. • Modern evolutionary theory uses ideas of genetics, particularly mutations, to help explain how evolution may occur. (Darwin didn’t know ...
Chapter Seven: Evolution of Living Things
... 18. Read page 181 and explain why insects quickly build up a resistance to pesticides. Insect populations change quickly because they have a short generation time. The insects that are resistant to pesticides survive and reproduce insects that have this same trait. ...
... 18. Read page 181 and explain why insects quickly build up a resistance to pesticides. Insect populations change quickly because they have a short generation time. The insects that are resistant to pesticides survive and reproduce insects that have this same trait. ...
•The Earth has millions of organisms that display different
... suited to survive and flourish according to the conditions on that specific island. Some animals were similar, but they occupied different habitats on one island. ...
... suited to survive and flourish according to the conditions on that specific island. Some animals were similar, but they occupied different habitats on one island. ...
Natural Selection - wvhs.wlwv.k12.or.us
... • (1798) Thomas Malthus: Reasoned that if the human population grew unchecked, their wouldn’t be enough space and food for everyone. • (1830) Charles Lyell: Argued for uniformitarianism, which holds that the geological processes we see today must be the same ones that occurred long ago. ...
... • (1798) Thomas Malthus: Reasoned that if the human population grew unchecked, their wouldn’t be enough space and food for everyone. • (1830) Charles Lyell: Argued for uniformitarianism, which holds that the geological processes we see today must be the same ones that occurred long ago. ...
Darwinian Evolution
... • Helps to explain how change has occurred over time • Nothing magical about how it occurs ...
... • Helps to explain how change has occurred over time • Nothing magical about how it occurs ...
EVOLUTION Biogenesis Define biogenesis. What is spontaneous
... b. Use a science dictionary to look up and explain relative dating of fossils. ...
... b. Use a science dictionary to look up and explain relative dating of fossils. ...
Kiosk 8th Period - Solon City Schools
... • He was amazed by the diversity of all the different animals • There were many of the same species of animals with diff. characteristics than the other organism that are the same species but have ...
... • He was amazed by the diversity of all the different animals • There were many of the same species of animals with diff. characteristics than the other organism that are the same species but have ...
Evolutionary history of life

The evolutionary history of life on Earth traces the processes by which living and fossil organisms have evolved since life appeared on the planet, until the present day. Earth formed about 4.5 Ga (billion years ago) and life appeared on its surface within 1 billion years. The similarities between all present-day organisms indicate the presence of a common ancestor from which all known species have diverged through the process of evolution. More than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.