Chapter 15
... Geologic processes form slowly so Earth was much older than 2,000 years. Lyell – geologist who wrote “Principles of Geology” We must explain past events from what we see today. For example, earthquakes and volcanoes Based on these geologists Darwin asked himself 2 questions. 1. If Earth could ch ...
... Geologic processes form slowly so Earth was much older than 2,000 years. Lyell – geologist who wrote “Principles of Geology” We must explain past events from what we see today. For example, earthquakes and volcanoes Based on these geologists Darwin asked himself 2 questions. 1. If Earth could ch ...
Evolution Reading Updated 2008
... II: Explain the history of life in terms of biodiversity, ancestry, and the rates of evolution The work of Charles Darwin and Gregor Mendel laid a foundation to explain the large diversity of species found today. Adaptive radiation is when species diversity occurs in a relatively short time. It occu ...
... II: Explain the history of life in terms of biodiversity, ancestry, and the rates of evolution The work of Charles Darwin and Gregor Mendel laid a foundation to explain the large diversity of species found today. Adaptive radiation is when species diversity occurs in a relatively short time. It occu ...
Evolution
... specimens that he had never seen and were not documented. Darwin noted the diversity of organisms, how well-suited each organism was to its environment, and new fossils (remains of living things) that were either similar to existing organisms or very unique. ...
... specimens that he had never seen and were not documented. Darwin noted the diversity of organisms, how well-suited each organism was to its environment, and new fossils (remains of living things) that were either similar to existing organisms or very unique. ...
Biology A
... reaching his conclusion that natural selection is the mechanism of evolution. Students know how independent lines of evidence from geology, fossils, and comparative anatomy provide the bases for the theory of evolution. Students know how to construct a simple branching diagram to classify living gro ...
... reaching his conclusion that natural selection is the mechanism of evolution. Students know how independent lines of evidence from geology, fossils, and comparative anatomy provide the bases for the theory of evolution. Students know how to construct a simple branching diagram to classify living gro ...
Evolution Pretest Grading
... because these scientists? a) Explained volcanoes and earthquakes b) Explained all geologic events on Earth c) Suggested that Earth was old enough for evolution to have occurred d) Refuted the work of Lamarck, which was based on misunderstandings ...
... because these scientists? a) Explained volcanoes and earthquakes b) Explained all geologic events on Earth c) Suggested that Earth was old enough for evolution to have occurred d) Refuted the work of Lamarck, which was based on misunderstandings ...
Evolution Notes PPT
... conclusions were based on observations of wildlife in the Galapagos Islands. The Galapagos ...
... conclusions were based on observations of wildlife in the Galapagos Islands. The Galapagos ...
The Modern Synthesis: Evolution and Genetics Charles Darwin
... Observations in the Galapagos Islands • Island chain 1000 km west of Ecuador • Discovered many new species with many similarities to species found on South America • No native amphibians or large land mammals ...
... Observations in the Galapagos Islands • Island chain 1000 km west of Ecuador • Discovered many new species with many similarities to species found on South America • No native amphibians or large land mammals ...
The Nature of Zoology
... This is really the only part of evolutionary theory that gives anyone any trouble – and the truth is, evolution never said that man came from monkeys! It says that man and apes and monkeys all evolved from a common ancestor. ...
... This is really the only part of evolutionary theory that gives anyone any trouble – and the truth is, evolution never said that man came from monkeys! It says that man and apes and monkeys all evolved from a common ancestor. ...
(B) Organisms have and continue to change over time. (C) Evolution
... inevitable, that the watch must have had a maker -- that there must have existed, at some time and at some place or other, an artificer or artificers who formed it for the purpose which we find it actually to answer, who comprehended its construction and designed its use. ...
... inevitable, that the watch must have had a maker -- that there must have existed, at some time and at some place or other, an artificer or artificers who formed it for the purpose which we find it actually to answer, who comprehended its construction and designed its use. ...
Document
... inevitable, that the watch must have had a maker -- that there must have existed, at some time and at some place or other, an artificer or artificers who formed it for the purpose which we find it actually to answer, who comprehended its construction and designed its use. ...
... inevitable, that the watch must have had a maker -- that there must have existed, at some time and at some place or other, an artificer or artificers who formed it for the purpose which we find it actually to answer, who comprehended its construction and designed its use. ...
The Theory of Evolution
... 5. List 3 questions that can be answered by evolution? 6. Lamarck’s theory related to evolution was called Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics. Describe his theory and what he ...
... 5. List 3 questions that can be answered by evolution? 6. Lamarck’s theory related to evolution was called Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics. Describe his theory and what he ...
Evolution – Just A Theory?
... Similar bone structure can reveal evidence of evolutionary relationships. 4. Comparative Embryology • The more similar organisms are in their embryological development, the more closely they are related. ...
... Similar bone structure can reveal evidence of evolutionary relationships. 4. Comparative Embryology • The more similar organisms are in their embryological development, the more closely they are related. ...
Fossils
... – Observation #2: All species can produce more offspring than the environment can support, and many of these offspring fail to survive and reproduce – Inference #2: This unequal ability of individuals to survive and reproduce will lead to the accumulation of favorable traits in the ...
... – Observation #2: All species can produce more offspring than the environment can support, and many of these offspring fail to survive and reproduce – Inference #2: This unequal ability of individuals to survive and reproduce will lead to the accumulation of favorable traits in the ...
File
... fit to reproduce, resulting in adaptation. Wallace was not given credit for the theory because Darwin published first; however, there is a geographical area named for him called the "Wallace Line" which separates Australia and Asia. There are three preconditions for natural selection. 1. The members ...
... fit to reproduce, resulting in adaptation. Wallace was not given credit for the theory because Darwin published first; however, there is a geographical area named for him called the "Wallace Line" which separates Australia and Asia. There are three preconditions for natural selection. 1. The members ...
Biology 300 Ch
... Uncover the lines of evidence that led Darwin & others to suggest evolutionary theory. Demonstrate that the process of natural selection has provided the tremendous diversity of life on earth. Apply your knowledge of genetics to explain how alterations have taken place in living organisms to c ...
... Uncover the lines of evidence that led Darwin & others to suggest evolutionary theory. Demonstrate that the process of natural selection has provided the tremendous diversity of life on earth. Apply your knowledge of genetics to explain how alterations have taken place in living organisms to c ...
Evolution: Exhibition Notes 2
... called stromatolites; and microscopic spheroidal or thread-like structures. These fossils show that life originated within the first 1,000 million years of the Earth’s existence. Primitive cells, complex cells and multicellular organisms The very earliest organisms in the fossil record are cells of ...
... called stromatolites; and microscopic spheroidal or thread-like structures. These fossils show that life originated within the first 1,000 million years of the Earth’s existence. Primitive cells, complex cells and multicellular organisms The very earliest organisms in the fossil record are cells of ...
Unit 6: Evolution
... 12. Identify a couple of factors that could lead to the pattern of evolution we see as divergence? 13. Define each of the following evolutionary trends: a. convergent evolution b. analogous traits c. parallel evolution d. co-evolution CHAPTER 25: PHYLOGENY AND SYSTEMATICS 1. What is phylogeny? 2. H ...
... 12. Identify a couple of factors that could lead to the pattern of evolution we see as divergence? 13. Define each of the following evolutionary trends: a. convergent evolution b. analogous traits c. parallel evolution d. co-evolution CHAPTER 25: PHYLOGENY AND SYSTEMATICS 1. What is phylogeny? 2. H ...
Evolution - Effingham County Schools
... • “Absence of evidence is not evidence of absence.” Charles ...
... • “Absence of evidence is not evidence of absence.” Charles ...
Evolution _2 Relative Dating
... the older rock layers end up at the bottom of the sequence and the newer ones toward the top. The arrow shows the relative order of the rock layers from earliest to most recent. ...
... the older rock layers end up at the bottom of the sequence and the newer ones toward the top. The arrow shows the relative order of the rock layers from earliest to most recent. ...
Evolution
... • For Darwin to hypothesize that the finches had a common ancestor, and have it be supported, two assumptions must be tested: • 1. For beak size to change shape and evolve, there must be the heritable raw genetic material needed for natural ...
... • For Darwin to hypothesize that the finches had a common ancestor, and have it be supported, two assumptions must be tested: • 1. For beak size to change shape and evolve, there must be the heritable raw genetic material needed for natural ...
Evolution PowerPoint
... Ancestry • Explain how the fossil record, anatomical similarities, and/or molecular (DNA) similarities can be used as evidence for the evolutionary development of a given species (e.g., birds, horses, elephants, whales ...
... Ancestry • Explain how the fossil record, anatomical similarities, and/or molecular (DNA) similarities can be used as evidence for the evolutionary development of a given species (e.g., birds, horses, elephants, whales ...
Unit 2 - Todd County Schools
... • Why is radioactive decay used to determine the absolute age of rocks? • a. Radioactive decay cannot be used to determine the age of a rock. • b. Radioactive decay happens very quickly. • c. Radioactive decay does not happen at a ...
... • Why is radioactive decay used to determine the absolute age of rocks? • a. Radioactive decay cannot be used to determine the age of a rock. • b. Radioactive decay happens very quickly. • c. Radioactive decay does not happen at a ...
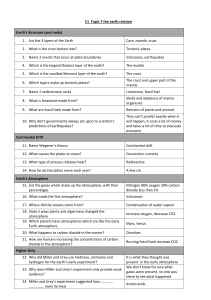
C1 Topic 7 the earth revision Earth`s Structure (and rocks) 1. List the
... They can’t predict exactly when it will happen, it costs a lot of money and takes a lot of time to evacuate everyone ...
... They can’t predict exactly when it will happen, it costs a lot of money and takes a lot of time to evacuate everyone ...
Paleontology

Paleontology or palaeontology (/ˌpeɪlɪɒnˈtɒlədʒi/, /ˌpeɪlɪənˈtɒlədʒi/ or /ˌpælɪɒnˈtɒlədʒi/, /ˌpælɪənˈtɒlədʒi/) is the scientific study of life existent prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene Epoch roughly 11,700 years before present. It includes the study of fossils to determine organisms' evolution and interactions with each other and their environments (their paleoecology). Paleontological observations have been documented as far back as the 5th century BC. The science became established in the 18th century as a result of Georges Cuvier's work on comparative anatomy, and developed rapidly in the 19th century. The term itself originates from Greek παλαιός, palaios, i.e. ""old, ancient"", ὄν, on (gen. ontos), i.e. ""being, creature"" and λόγος, logos, i.e. ""speech, thought, study"".Paleontology lies on the border between biology and geology, but differs from archaeology in that it excludes the study of morphologically modern humans. It now uses techniques drawn from a wide range of sciences, including biochemistry, mathematics and engineering. Use of all these techniques has enabled paleontologists to discover much of the evolutionary history of life, almost all the way back to when Earth became capable of supporting life, about 3,800 million years ago. As knowledge has increased, paleontology has developed specialised sub-divisions, some of which focus on different types of fossil organisms while others study ecology and environmental history, such as ancient climates.Body fossils and trace fossils are the principal types of evidence about ancient life, and geochemical evidence has helped to decipher the evolution of life before there were organisms large enough to leave body fossils. Estimating the dates of these remains is essential but difficult: sometimes adjacent rock layers allow radiometric dating, which provides absolute dates that are accurate to within 0.5%, but more often paleontologists have to rely on relative dating by solving the ""jigsaw puzzles"" of biostratigraphy. Classifying ancient organisms is also difficult, as many do not fit well into the Linnean taxonomy that is commonly used for classifying living organisms, and paleontologists more often use cladistics to draw up evolutionary ""family trees"". The final quarter of the 20th century saw the development of molecular phylogenetics, which investigates how closely organisms are related by measuring how similar the DNA is in their genomes. Molecular phylogenetics has also been used to estimate the dates when species diverged, but there is controversy about the reliability of the molecular clock on which such estimates depend.