Astronomy Part 1 - Malvern Troop 7
... a) Identify in the sky at least 10 constellations, at least four of which are in the zodiac. b) Identify at least eight conspicuous stars, five of which are of magnitude 1 or brighter. c) Make two sketches of the Big Dipper. In one sketch, show the Big Dipper's orientation in the early evening sky. ...
... a) Identify in the sky at least 10 constellations, at least four of which are in the zodiac. b) Identify at least eight conspicuous stars, five of which are of magnitude 1 or brighter. c) Make two sketches of the Big Dipper. In one sketch, show the Big Dipper's orientation in the early evening sky. ...
3 - Celestial Sphere
... SCP) and imaginary lines such as the Celestial Equator (CE) positioned on this sphere. Earth is located at the sphere’s center. Currently, the North Celestial Pole is very close to a star called Polaris. 2) The ecliptic is the apparent annual path of the Sun on the Celestial Sphere. Notice that the ...
... SCP) and imaginary lines such as the Celestial Equator (CE) positioned on this sphere. Earth is located at the sphere’s center. Currently, the North Celestial Pole is very close to a star called Polaris. 2) The ecliptic is the apparent annual path of the Sun on the Celestial Sphere. Notice that the ...
Astrology in the field of psychology A study of Jung`s typology
... its being a unique combination of the components of these sequences. Therefore a thorough comprehension of these principles will make the inner meanings of the sign more apparent. It is important to distinguish the zodiacal signs from the constellations associated with them, not only because of thei ...
... its being a unique combination of the components of these sequences. Therefore a thorough comprehension of these principles will make the inner meanings of the sign more apparent. It is important to distinguish the zodiacal signs from the constellations associated with them, not only because of thei ...
Coordinates and Time - University of Florida Astronomy
... Now why on the last slide did I write (J2000.0) after the RA and Dec? What that notation means is that these are the coordinates at which you would find the galactic center on the first day of 2000. This is unfortunately necessary because the equatorial coordinates of objects change with time. ...
... Now why on the last slide did I write (J2000.0) after the RA and Dec? What that notation means is that these are the coordinates at which you would find the galactic center on the first day of 2000. This is unfortunately necessary because the equatorial coordinates of objects change with time. ...
celestial sphere
... distortion inherent in flat star maps is avoided. On the other hand, it forces you to view the constellations from the outside inward rather than from the inside outward. Several hundred stars have been plotted on the globe as well as the great circles representing the hour circles for every hour fr ...
... distortion inherent in flat star maps is avoided. On the other hand, it forces you to view the constellations from the outside inward rather than from the inside outward. Several hundred stars have been plotted on the globe as well as the great circles representing the hour circles for every hour fr ...
To Measure the Sky: An Introduction to Observational Astronomy.
... matched by a similar hemisphere below the horizon, so that we are able to apply a spherical coordinate scheme like the one illustrated. Here, the origin of the system is at O, the location of the observer. The fundamental plane is that of the ‘‘flat’’ Earth (or, to be precise, a plane tangent to the ...
... matched by a similar hemisphere below the horizon, so that we are able to apply a spherical coordinate scheme like the one illustrated. Here, the origin of the system is at O, the location of the observer. The fundamental plane is that of the ‘‘flat’’ Earth (or, to be precise, a plane tangent to the ...
FINAL TEST PART I
... called zodiac. Tropical Zodiac is based on orientation of Earth to Sun. Zodiac measured from point of vernal equinox (apparent position of Sun at the commencement of Spring), which moves in relation to the fixed stars is called movable or Tropical Zodiac. The orientation of equinoxes to the stars ch ...
... called zodiac. Tropical Zodiac is based on orientation of Earth to Sun. Zodiac measured from point of vernal equinox (apparent position of Sun at the commencement of Spring), which moves in relation to the fixed stars is called movable or Tropical Zodiac. The orientation of equinoxes to the stars ch ...
Dignity - Clubs at PSU
... Astrology is an ancient art/science that uses astronomical observations for predictions ...
... Astrology is an ancient art/science that uses astronomical observations for predictions ...
here - Diana`s Fixed Stars
... of Fixed Stars include Uranian Astrology (90 Degree Dial, Planetary Pictures, etc.), Derived Houses, Planetary Nodes, and Solstice Points. Diana has been a resident of New York City her entire life, while my residence in NYC spanned only 7 years, and I moved westwards in the USA in Feb. 1983. Our pa ...
... of Fixed Stars include Uranian Astrology (90 Degree Dial, Planetary Pictures, etc.), Derived Houses, Planetary Nodes, and Solstice Points. Diana has been a resident of New York City her entire life, while my residence in NYC spanned only 7 years, and I moved westwards in the USA in Feb. 1983. Our pa ...
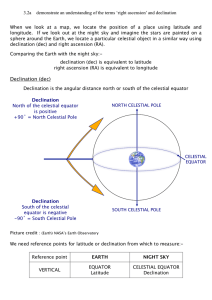
3.2a Right Ascension and Declination
... If a person was able to see the night sky shown above for a full day, the full band of stars would pass in front of them, moving steadily towards the right. The longitude reference point was more difficult. Many countries have laid claim to the Prime Meridian – the Chinese once used a gate from the ...
... If a person was able to see the night sky shown above for a full day, the full band of stars would pass in front of them, moving steadily towards the right. The longitude reference point was more difficult. Many countries have laid claim to the Prime Meridian – the Chinese once used a gate from the ...
History of Astronomy
... sky at its farthest point from the Sun, the planet's angle on the sky away from the Sun, A, can be measured. You can see from the figure that at the same time angle B is 90°. The planet's distance from the Sun can then be calculated with geometry, if one knows the measured value of angle A and the f ...
... sky at its farthest point from the Sun, the planet's angle on the sky away from the Sun, A, can be measured. You can see from the figure that at the same time angle B is 90°. The planet's distance from the Sun can then be calculated with geometry, if one knows the measured value of angle A and the f ...
History
... that keeps the moon in orbit. • Provided the explanation for Kepler’s Laws that Kepler lacked. ...
... that keeps the moon in orbit. • Provided the explanation for Kepler’s Laws that Kepler lacked. ...
© The Dark Pixie Astrology www.thedarkpixieastrology.com 1
... and an R appears halfway down the Mercury column. The R stands for retrograde, which is when a planet appears to be moving backward from our view here on Earth. The planet isn’t actually moving backward, it just appears that way because of the way the planets move in relation to Earth. Since the ...
... and an R appears halfway down the Mercury column. The R stands for retrograde, which is when a planet appears to be moving backward from our view here on Earth. The planet isn’t actually moving backward, it just appears that way because of the way the planets move in relation to Earth. Since the ...
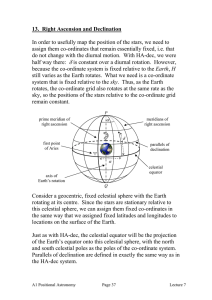
13. Right Ascension and Declination
... time, plus 12 hours), with a 24h day, since human activity is most usefully synchronised with the daily movement of the Sun and the corresponding hours of daylight. Therefore, sidereal time ‘drifts’ relative to solar time: they are synchronised on the day of the vernal equinox (usually on or around ...
... time, plus 12 hours), with a 24h day, since human activity is most usefully synchronised with the daily movement of the Sun and the corresponding hours of daylight. Therefore, sidereal time ‘drifts’ relative to solar time: they are synchronised on the day of the vernal equinox (usually on or around ...
Astrology for Yourself
... astrology is to better know and understand ourselves and our place in the cosmos. In the followin pages, we are going to take you on a journey of self-discovery that only astrology can provide. If someone were to ask you to describe astrology, you would most likely think of the twelve sign of the Zo ...
... astrology is to better know and understand ourselves and our place in the cosmos. In the followin pages, we are going to take you on a journey of self-discovery that only astrology can provide. If someone were to ask you to describe astrology, you would most likely think of the twelve sign of the Zo ...
Saturday, March 16th, 2013: 10 AM
... The Renaissance Physician was a master herbalist and astrologer, heir to traditions evolving from ancient Greece and beyond. The "planetary energetics" mindset of Renaissance doctors demonstrated the essential use of astrology as a preeminent medical model of the period. Astrology was used for diagn ...
... The Renaissance Physician was a master herbalist and astrologer, heir to traditions evolving from ancient Greece and beyond. The "planetary energetics" mindset of Renaissance doctors demonstrated the essential use of astrology as a preeminent medical model of the period. Astrology was used for diagn ...
TIĀN DÌ
... was not just a non-political organisation only interested in abstract ideas. It was actually quite involved in politics at that time and this played a major role in influencing the course of Aristotle's life. After being a student, Aristotle soon became a teacher at the Academy and he ...
... was not just a non-political organisation only interested in abstract ideas. It was actually quite involved in politics at that time and this played a major role in influencing the course of Aristotle's life. After being a student, Aristotle soon became a teacher at the Academy and he ...
Basic Aspects - Astropath Quantum Astrology
... planets constantly form new aspects to each other and we can look at those too and plot them against the natal chart which gives us crucial information about how the transits (the current position of the planets) affects each of us as an individual. You measure an aspect by imagining the astrologica ...
... planets constantly form new aspects to each other and we can look at those too and plot them against the natal chart which gives us crucial information about how the transits (the current position of the planets) affects each of us as an individual. You measure an aspect by imagining the astrologica ...
Observing the Night Sky - Constellations
... Meridian, is fixed relative to any one observer, and the stars pass across the meridian as time progresses. Thus, the sky becomes an enormous clock. Our concept of time is based on the daily motion of the Sun, Moon and stars across the sky. The celestial sphere with the equatorial coordinate system ...
... Meridian, is fixed relative to any one observer, and the stars pass across the meridian as time progresses. Thus, the sky becomes an enormous clock. Our concept of time is based on the daily motion of the Sun, Moon and stars across the sky. The celestial sphere with the equatorial coordinate system ...
Wishonttari Dasha in Vedic Chart Predictions
... although few astrologers use this concept for predicting the time of an event. This article will focus on the 120 year planetary cycles, the Wishonttari Dasha. The basic assumption of the great planetary cycle is that the conventional (astrological) nine planets (Sun, Moon. Mars, Mercury, Jupiter, V ...
... although few astrologers use this concept for predicting the time of an event. This article will focus on the 120 year planetary cycles, the Wishonttari Dasha. The basic assumption of the great planetary cycle is that the conventional (astrological) nine planets (Sun, Moon. Mars, Mercury, Jupiter, V ...
Epoch EclipsE Now
... Christian influence in Western civilization. The precession of zodiacal signs at the equinoxes is the largest cycle known in astrology, 25,800 years, and is the only cycle that moves backwards through the signs. The world is now on the cusp of Aquarius, a fixed sign, fixed air, what can it be? Th ...
... Christian influence in Western civilization. The precession of zodiacal signs at the equinoxes is the largest cycle known in astrology, 25,800 years, and is the only cycle that moves backwards through the signs. The world is now on the cusp of Aquarius, a fixed sign, fixed air, what can it be? Th ...
Week 1
... angular degrees, except at the equator) The sky rotates by at 15 arcseconds per second at the Equator Since lines of RA converge toward the pole – 1 minute of RA spans a different angle depending on Declination – a factor of cos(Dec) comes into ...
... angular degrees, except at the equator) The sky rotates by at 15 arcseconds per second at the Equator Since lines of RA converge toward the pole – 1 minute of RA spans a different angle depending on Declination – a factor of cos(Dec) comes into ...
The celestial sphere
... ASTR211: COORDINATES AND TIME 2. Diurnal motion of celestial bodies Stars, planets, Sun and Moon all exhibit diurnal motion ...
... ASTR211: COORDINATES AND TIME 2. Diurnal motion of celestial bodies Stars, planets, Sun and Moon all exhibit diurnal motion ...
Short Course TIM645: Jyotish (Vedic Astrology)
... Paulo. With his passion for astrology and integrative medicine, Dr. Nair learned Jyotish (Vedic Astrology) with guidance from several reputed astrologers in India (Kerala), and developed his own Vedic Astrology software (JATAKA). Since 1984, he has been practicing professionally, and since 1992, tea ...
... Paulo. With his passion for astrology and integrative medicine, Dr. Nair learned Jyotish (Vedic Astrology) with guidance from several reputed astrologers in India (Kerala), and developed his own Vedic Astrology software (JATAKA). Since 1984, he has been practicing professionally, and since 1992, tea ...
Advanced STARS - WordPress.com
... across the celestial sphere during the year. It crosses the celestial equator twice during the year, once at the Autumnal equinox and once at the Vernal equinox. The Vernal ...
... across the celestial sphere during the year. It crosses the celestial equator twice during the year, once at the Autumnal equinox and once at the Vernal equinox. The Vernal ...
Zodiac

In both astrology and historical astronomy, the zodiac (Greek: ζῳδιακός, zōidiakos) is a circle of twelve 30° divisions of celestial longitude that are centered upon the ecliptic, the apparent path of the Sun across the celestial sphere over the course of the year. The paths of the Moon and visible planets also remain close to the ecliptic, within the belt of the zodiac, which extends 8-9° north or south of the ecliptic, as measured in celestial latitude. Because the divisions are regular, they do not correspond exactly to the twelve constellations after which they are named.Historically, these twelve divisions are called signs. Essentially, the zodiac is a celestial coordinate system, or more specifically an ecliptic coordinate system, which takes the ecliptic as the origin of latitude, and the position of the Sun at vernal equinox as the origin of longitude.