Hypothalamus
... The hypothalamus regulates these basic life processes by recourse to 3 main mechanisms • Receiving sensory information from virtually the entire body. Direct inputs from the retina, olfactory system and visceral sensory system. Inputs from the circumventricular organs. Internal sensory neurons resp ...
... The hypothalamus regulates these basic life processes by recourse to 3 main mechanisms • Receiving sensory information from virtually the entire body. Direct inputs from the retina, olfactory system and visceral sensory system. Inputs from the circumventricular organs. Internal sensory neurons resp ...
Central nervous system practical block
... A schwannoma. typically has dense areas called Antoni A (black arrow) and looser areas called Antoni B (blue arrows). The cells are elongated (spindle shaped) and the nuclei have a tendency to line up as seen here in the Antoni A area. ...
... A schwannoma. typically has dense areas called Antoni A (black arrow) and looser areas called Antoni B (blue arrows). The cells are elongated (spindle shaped) and the nuclei have a tendency to line up as seen here in the Antoni A area. ...
The Central Nervous System
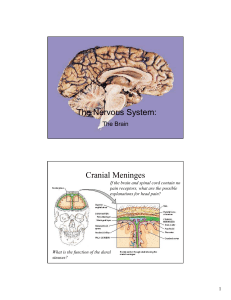
... Between the dura mater and the arachnoid membrane Contains a small amount of lubricating fluid ...
... Between the dura mater and the arachnoid membrane Contains a small amount of lubricating fluid ...
Objectives 49
... - Subcortical dementia due to damage to subcortical structures, such as basal ganglia (Parkinson’s disease); cognitive slowing and memory retrieval problems - Vascular disorders (strokes) cause damage to both cortical and subcortical structures Clinical course - some dementias are reversible (brain ...
... - Subcortical dementia due to damage to subcortical structures, such as basal ganglia (Parkinson’s disease); cognitive slowing and memory retrieval problems - Vascular disorders (strokes) cause damage to both cortical and subcortical structures Clinical course - some dementias are reversible (brain ...
The Nervous System: Cranial Meninges
... Which ventricle is found in the diencephalon? Describe the structure and function of the reticular formation (RAS). ...
... Which ventricle is found in the diencephalon? Describe the structure and function of the reticular formation (RAS). ...
Cognitive Disorders
... Dementia of the Alzheimer’s Type • Most common form of dementia • results not only in physical, but social, death • Video (Larry Gorrell, Ab Psy #10 or from Faces) ...
... Dementia of the Alzheimer’s Type • Most common form of dementia • results not only in physical, but social, death • Video (Larry Gorrell, Ab Psy #10 or from Faces) ...
PATHOLOGY/HISTOLOGY TEST KIT 6C: MORE BRAIN (26 vials)
... The space between the arachnoid membrane and pia mater that is occupied by spongy tissue consisting of trabeculae (delicate connective tissue filaments) and intercommunicating channels in which the cerebrospinal fluid is contained. The superior parietal lobule is involved with spatial orientation, r ...
... The space between the arachnoid membrane and pia mater that is occupied by spongy tissue consisting of trabeculae (delicate connective tissue filaments) and intercommunicating channels in which the cerebrospinal fluid is contained. The superior parietal lobule is involved with spatial orientation, r ...
Cerebrospinal Fluid
... formed around blood vessels and along ventricular walls. It circulates from the lateral ventricles to the foramen of Monro , third ventricle, aqueduct of Sylvius , fourth ventricle, foramina of Magendie and foramina of Luschka ;subarachnoid space over brain and spinal cord; re absorption into venous ...
... formed around blood vessels and along ventricular walls. It circulates from the lateral ventricles to the foramen of Monro , third ventricle, aqueduct of Sylvius , fourth ventricle, foramina of Magendie and foramina of Luschka ;subarachnoid space over brain and spinal cord; re absorption into venous ...
List 10-1
... primary motor area of the cerebral cortex? Where is the primary somatic sensory area? 2. What does the reticular activating system have to do with alertness? 3.What is the function of the limbic system? 4.What kind of information can be gained from an EEG? ...
... primary motor area of the cerebral cortex? Where is the primary somatic sensory area? 2. What does the reticular activating system have to do with alertness? 3.What is the function of the limbic system? 4.What kind of information can be gained from an EEG? ...
different types of dementia
... to the cortex—the area associated with learning, memory and language. Mini-strokes are sometimes referred to as TIAs (transient ischemic attacks). TIAs cause temporary, partial blockages of blood supply and brief impairments in consciousness or sight. However, over time the damage caused to brain ti ...
... to the cortex—the area associated with learning, memory and language. Mini-strokes are sometimes referred to as TIAs (transient ischemic attacks). TIAs cause temporary, partial blockages of blood supply and brief impairments in consciousness or sight. However, over time the damage caused to brain ti ...
the brain: anatomical regions
... Can be caused from virus (not that bad) or bacteria (can be fatal). ...
... Can be caused from virus (not that bad) or bacteria (can be fatal). ...
AChE inhibitor
... •Turns performed en bloc With Parkinson’s, there is also: •Rigidity •Tremors (at rest) •Akinesia (loss of power of movement) •Bradykinesia (slowed movement) Pathology of Parkinson’s entails: •Presence of Lewy bodies •Loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra ...
... •Turns performed en bloc With Parkinson’s, there is also: •Rigidity •Tremors (at rest) •Akinesia (loss of power of movement) •Bradykinesia (slowed movement) Pathology of Parkinson’s entails: •Presence of Lewy bodies •Loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra ...