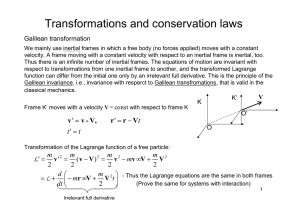
Document
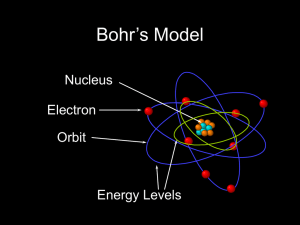
... Generally symbolized by n, it denotes the shell (energy level) in which the electron is located. ...
... Generally symbolized by n, it denotes the shell (energy level) in which the electron is located. ...
Phys202_Final_Exam_Spr2007.doc
... 54. If a clock that flashes an alarm every 7 hours, on the object in the last problem moves at the same velocity, then at what interval will that flash be seen to the observer that sees it moving? a. 783 b. 238 c. 832 d. ~ 495 ...
... 54. If a clock that flashes an alarm every 7 hours, on the object in the last problem moves at the same velocity, then at what interval will that flash be seen to the observer that sees it moving? a. 783 b. 238 c. 832 d. ~ 495 ...
ProblemSet3 ProblemSet3
... a) Find the transmitted and reflected waves in terms of the amplitude of the incident wave. b) Write the total electric field E and magnetic field B in the half–space z < 0. Find the position (expressed in terms of the wavelength λ of the wave) of the nodal planes, where E and B are zero, and justif ...
... a) Find the transmitted and reflected waves in terms of the amplitude of the incident wave. b) Write the total electric field E and magnetic field B in the half–space z < 0. Find the position (expressed in terms of the wavelength λ of the wave) of the nodal planes, where E and B are zero, and justif ...
Homework 9
... *1. (II) At a given instant, a 1.8-A current flows in the wires connected to a parallelplate capacitor. What is the rate at which the electric field is changing between the plates if the square plates are 1.60 cm on a side? Solution The current in the wires must also be the displacement current in t ...
... *1. (II) At a given instant, a 1.8-A current flows in the wires connected to a parallelplate capacitor. What is the rate at which the electric field is changing between the plates if the square plates are 1.60 cm on a side? Solution The current in the wires must also be the displacement current in t ...
Document
... BUT: photons tend to be detected “together”! How can they be correlated at detection? ...
... BUT: photons tend to be detected “together”! How can they be correlated at detection? ...
Document
... oscillation in matter or in a physical field. Light is an electromagnetic wave, consisting of oscillations in electric and magnetic fields traveling through space. ...
... oscillation in matter or in a physical field. Light is an electromagnetic wave, consisting of oscillations in electric and magnetic fields traveling through space. ...
divinity - Particle Theory Group
... Institute for Advanced Study, a photomicrograph of a nuclear emulsion event, showing what is now known a a K-meson decaying into three pions. We all saw it. No doubt that something interesting was going on, very different from what was then known, but it was hardly discussed because no one knew what ...
... Institute for Advanced Study, a photomicrograph of a nuclear emulsion event, showing what is now known a a K-meson decaying into three pions. We all saw it. No doubt that something interesting was going on, very different from what was then known, but it was hardly discussed because no one knew what ...
Chapter 5
... position and the speed of the electron at the same time. • This became known as the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle. • It simply means that the electron is so small and moving so fast, that the simple act of trying to measure its speed or position would change either quantity. ...
... position and the speed of the electron at the same time. • This became known as the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle. • It simply means that the electron is so small and moving so fast, that the simple act of trying to measure its speed or position would change either quantity. ...
PART 1 Identical particles, fermions and bosons. Pauli exclusion
... the wave equation for a particle with spin 1/2 is of the first order in time derivative (see discussion of the Dirac equation later in the course). At the same time the wave equation for a particle with integer spin is of the second order in time derivative. An example: The vector potential in elect ...
... the wave equation for a particle with spin 1/2 is of the first order in time derivative (see discussion of the Dirac equation later in the course). At the same time the wave equation for a particle with integer spin is of the second order in time derivative. An example: The vector potential in elect ...
First lecture, 7.10.03
... But in real life, don’t I know something about each? Don’t I also know that if a car left this morning and is already in Budapest, it’s going faster than if it’s still on Währingerstr.? Wigner function: W(x,p) is like the probability for a particle to be at x and have momentum p. Its integrals corre ...
... But in real life, don’t I know something about each? Don’t I also know that if a car left this morning and is already in Budapest, it’s going faster than if it’s still on Währingerstr.? Wigner function: W(x,p) is like the probability for a particle to be at x and have momentum p. Its integrals corre ...