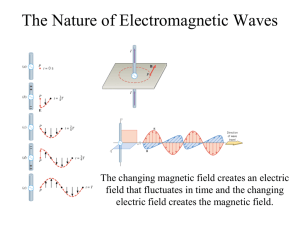
PSC1341 Chapter 4 Waves Waves • A wave is a repeating
... • A wave is a repeating disturbance or movement that transfers energy through matter or space • Waves can be mechanical and electromagnetic • Waves can be Transverse and Longitudinal • A wave is characterized by its wavelength, frequency, and amplitude Mechanical vs. Electromagnetic • Mechanical – E ...
... • A wave is a repeating disturbance or movement that transfers energy through matter or space • Waves can be mechanical and electromagnetic • Waves can be Transverse and Longitudinal • A wave is characterized by its wavelength, frequency, and amplitude Mechanical vs. Electromagnetic • Mechanical – E ...
Rusov-Presentation-Sofia-Mateev-NuclearFission
... N.G. Chetaev, Motion stability. Resear. on the analyt. mechanics, Nauka, Moscow 1962. ...
... N.G. Chetaev, Motion stability. Resear. on the analyt. mechanics, Nauka, Moscow 1962. ...
Lecture 1 - Particle Physics Group
... Given the list of particles and vertices which exist in a certain theory, (e.g. the SM) we can use FDs to find out all the processes which are allowed by the theory, and make rough estimates of their relative probability. Every vertex and particle corresponds to a term in the Lagrangian (the formula ...
... Given the list of particles and vertices which exist in a certain theory, (e.g. the SM) we can use FDs to find out all the processes which are allowed by the theory, and make rough estimates of their relative probability. Every vertex and particle corresponds to a term in the Lagrangian (the formula ...
Modern physics
... to the frequency of the light, but does not depend on its intensity Compton effect was of great historical importance because it confirmed that photons are real particles with momentum as well as energy. Collisions between the energetic quanta of radiation and electrons obey relativistic energy and ...
... to the frequency of the light, but does not depend on its intensity Compton effect was of great historical importance because it confirmed that photons are real particles with momentum as well as energy. Collisions between the energetic quanta of radiation and electrons obey relativistic energy and ...
6.5
... ψ ( r , t ) is the wavefunction, which is the amplitude for the particle to have a given position r at any given time t. m is the mass of the particle. ...
... ψ ( r , t ) is the wavefunction, which is the amplitude for the particle to have a given position r at any given time t. m is the mass of the particle. ...
Bonding 1 - Department of Chemistry
... The eight orbitals can be classified by symmetry into two sets: 4 s and 4 orbitals. The four orbitals from one doubly degenerate pair of bonding orbitals and one doubly degenerate pair of antibonding orbitals. The four s orbitals span a range of energies, one being strongly bonding and another s ...
... The eight orbitals can be classified by symmetry into two sets: 4 s and 4 orbitals. The four orbitals from one doubly degenerate pair of bonding orbitals and one doubly degenerate pair of antibonding orbitals. The four s orbitals span a range of energies, one being strongly bonding and another s ...
Document
... Free particle When E>V (everywhere) you have a free particle. We deal with the case of V=0 but it can be applied to other cases as well. Free particles have oscillating solutions or y ( x) A cos(kx) B sin( kx) y (x) Ceikx De ikx To get the full wave function we multiply by the time depende ...
... Free particle When E>V (everywhere) you have a free particle. We deal with the case of V=0 but it can be applied to other cases as well. Free particles have oscillating solutions or y ( x) A cos(kx) B sin( kx) y (x) Ceikx De ikx To get the full wave function we multiply by the time depende ...
High Energy Astrophysics - Mullard Space Science Laboratory
... • Photons and nuclei have a similar crosssection, and the g-ray does not differentiate much between another photon or a nucleus. • Then we must compare the photon density with the particle density in space. ...
... • Photons and nuclei have a similar crosssection, and the g-ray does not differentiate much between another photon or a nucleus. • Then we must compare the photon density with the particle density in space. ...