Unit 4-3 Noteguide Phsyics and Quantem Mechanical
... Classical Mechanics vs. Quantum Mechanics --Classical deals with describing the motion of large bodies and quantum describes the motion of subatomic particles and atoms as waves. --Heisenberg = can’t find the exact velocity and position of a particle at the same time (like electrons) --Why? Because ...
... Classical Mechanics vs. Quantum Mechanics --Classical deals with describing the motion of large bodies and quantum describes the motion of subatomic particles and atoms as waves. --Heisenberg = can’t find the exact velocity and position of a particle at the same time (like electrons) --Why? Because ...
Document
... Q. What is the de Broglie wavelength of an electron that has a kinetic energy of 100 eV? After an electron is accelerated in 100 V potential difference, its kinetic energy is 100 eV. eV unit has to be converted into SI unit, Joule. 1 eV = 1.6 x 10-19 J ...
... Q. What is the de Broglie wavelength of an electron that has a kinetic energy of 100 eV? After an electron is accelerated in 100 V potential difference, its kinetic energy is 100 eV. eV unit has to be converted into SI unit, Joule. 1 eV = 1.6 x 10-19 J ...
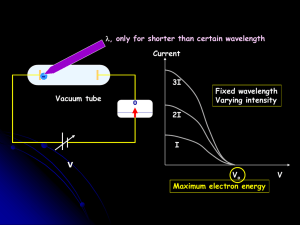
PHY215: Study Guide for Introductory Quantum Mechanics Explain 1. Cathode Ray tubes, Cathode rays, and the generation of X‐rays.
... 1. Cathode Ray tubes, Cathode rays, and the generation of X‐rays. 2. The photoelectric effect, Compton Scattering, Planck’s constant: explain how light behaves as though it is made of particles. 3. The de Broglie wavelength, the Davisson‐Germer experiment: explain how electrons (an ...
... 1. Cathode Ray tubes, Cathode rays, and the generation of X‐rays. 2. The photoelectric effect, Compton Scattering, Planck’s constant: explain how light behaves as though it is made of particles. 3. The de Broglie wavelength, the Davisson‐Germer experiment: explain how electrons (an ...
De Broglie waves
... intensity with angle, distinct maximum and minimum were observed with their positions depending on the electron energy. • The Bragg equation for maxima in the diffraction pattern is: n 2d sin • In a particular case, a beam of 54eV electrons were directed perpendicularly at the nickel target and ...
... intensity with angle, distinct maximum and minimum were observed with their positions depending on the electron energy. • The Bragg equation for maxima in the diffraction pattern is: n 2d sin • In a particular case, a beam of 54eV electrons were directed perpendicularly at the nickel target and ...
Part 1 Electron Arrangement
... electrons could be particles yet they gave off waves of light. • De Broglie suggested that electrons could be considered waves confined to space around a nucleus only at specific frequencies. • Diffraction experiments proved that electron beams can interfere with each other and produce areas of low ...
... electrons could be particles yet they gave off waves of light. • De Broglie suggested that electrons could be considered waves confined to space around a nucleus only at specific frequencies. • Diffraction experiments proved that electron beams can interfere with each other and produce areas of low ...
Lecture XIII_XIV
... introduced in his lifetime. The photoelectric effect pointed to the particle properties of light, which had been considered to be a wave phenomenon. He wondered if electons and other "particles" might exhibit wave properties. The application of these two new ideas to light pointed to an interesting ...
... introduced in his lifetime. The photoelectric effect pointed to the particle properties of light, which had been considered to be a wave phenomenon. He wondered if electons and other "particles" might exhibit wave properties. The application of these two new ideas to light pointed to an interesting ...
You may recall the formula: V = W/q Potential difference between
... Max Planck studied radiation from a hot object explained experimental evidence by saying that radiant energy is absorbed and radiated as multiples of h • f, where h is a constant and f is the frequency energy is absorbed and radiated by matter in "bundles" he called quanta (now ...
... Max Planck studied radiation from a hot object explained experimental evidence by saying that radiant energy is absorbed and radiated as multiples of h • f, where h is a constant and f is the frequency energy is absorbed and radiated by matter in "bundles" he called quanta (now ...