adenoids - ENT Lectures
... subluxation can occur in patients with Down syndrome. Atlantoaxial joint laxity because of Grisel’s syndrome. This is vertebral body decalcification and laxity of the anterior transverse ligament between the atlas and the axis from inflammation or infection in the nasopharynx. Spontaneous sublux ...
... subluxation can occur in patients with Down syndrome. Atlantoaxial joint laxity because of Grisel’s syndrome. This is vertebral body decalcification and laxity of the anterior transverse ligament between the atlas and the axis from inflammation or infection in the nasopharynx. Spontaneous sublux ...
Abdominal Exam
... most examiners use the diaphragm. You should listen for at least 10-15 seconds and note the pitch and frequency of bowel sounds. If you do not hear any bowel sounds, you should listen for a full two minutes before you can state that the patient does not have any bowel sounds. Bowel sounds should occ ...
... most examiners use the diaphragm. You should listen for at least 10-15 seconds and note the pitch and frequency of bowel sounds. If you do not hear any bowel sounds, you should listen for a full two minutes before you can state that the patient does not have any bowel sounds. Bowel sounds should occ ...
File - Sheffield Peer Teaching Society
... Hepatic Artery, Hepatic Portal Vein and Bile Ductule Note: inside area surrounding central hepatic venule more likely to become damaged either congestion or low oxygen ...
... Hepatic Artery, Hepatic Portal Vein and Bile Ductule Note: inside area surrounding central hepatic venule more likely to become damaged either congestion or low oxygen ...
Pediatric Laproscopic Nissen Fundoplication
... portion of the esophagus passes through a small tunnel of stomach muscle This strengthens the lower esophageal sphincter which prevents acid from retreating into the esophagus (when the stomach contracts, it closes off the sphincter) ...
... portion of the esophagus passes through a small tunnel of stomach muscle This strengthens the lower esophageal sphincter which prevents acid from retreating into the esophagus (when the stomach contracts, it closes off the sphincter) ...
35616680
... Liver has a dual blood supply; portal vein(75%) & hepatic artery (25%),The hepatic veins are responsible for drainage of filtered blood from the liver into the IVC. ...
... Liver has a dual blood supply; portal vein(75%) & hepatic artery (25%),The hepatic veins are responsible for drainage of filtered blood from the liver into the IVC. ...
Acute Myocardial Infarction
... Majority of ST-segment elevation will develop Q waves. Those w/o ST elevation will be diagnosed with unstable angina or NQWMI on the basis of the presence of cardiac enzymes. ...
... Majority of ST-segment elevation will develop Q waves. Those w/o ST elevation will be diagnosed with unstable angina or NQWMI on the basis of the presence of cardiac enzymes. ...
Anatomy and Physiology of the Liver
... The combination of hypothermia and the use of an adequate preservation solution prevent hypothermic and preservation-induced injury, and make it possible to keep the liver for a limited amount of time outside its physiologic environment. Cold storage allows preservation for 12-15 hours in the clinic ...
... The combination of hypothermia and the use of an adequate preservation solution prevent hypothermic and preservation-induced injury, and make it possible to keep the liver for a limited amount of time outside its physiologic environment. Cold storage allows preservation for 12-15 hours in the clinic ...
Abdominal Examination
... Cushing’s), spider naevi, movement with respiration (absent in peritonitis), obvious pulsations, distended portal-systemic anastomoses (portal hypertension) Palpation: ask if any pain (start away from painful areas) o Superficial palpation: crouch to patient’s level and roll fingers of one hand over ...
... Cushing’s), spider naevi, movement with respiration (absent in peritonitis), obvious pulsations, distended portal-systemic anastomoses (portal hypertension) Palpation: ask if any pain (start away from painful areas) o Superficial palpation: crouch to patient’s level and roll fingers of one hand over ...
high CRP
... conversion of atrial flutter; it may however prolong the QT interval and promote torsades ...
... conversion of atrial flutter; it may however prolong the QT interval and promote torsades ...
Abdomen Part 2
... Each segment is functionally independent with its own artery, portal vein and bile duct ...
... Each segment is functionally independent with its own artery, portal vein and bile duct ...
An Overview - Association of Surgical Technologists
... via a portal vein entrance and a hepatic vein exit. Cirrhosis causes blockage of the portal vein system. In the normal liver, total blood volume is 450 ml, equaling 10% of the total blood volume in the body. High pressure in the heart's right atrium causes backup ptessure in the liver, which can exp ...
... via a portal vein entrance and a hepatic vein exit. Cirrhosis causes blockage of the portal vein system. In the normal liver, total blood volume is 450 ml, equaling 10% of the total blood volume in the body. High pressure in the heart's right atrium causes backup ptessure in the liver, which can exp ...
가로막, 간, 쓸개
... - The liver has functionally independent right and left parts (portal lobes) that are approximately equal in size. Each part has its own blood supply from the hepatic artery and portal vein and its own venous and biliary drainage. On the visceral surface, the right (part of the) liver is demarcated ...
... - The liver has functionally independent right and left parts (portal lobes) that are approximately equal in size. Each part has its own blood supply from the hepatic artery and portal vein and its own venous and biliary drainage. On the visceral surface, the right (part of the) liver is demarcated ...
Anatomy
... lobes. The middle hepatic vein also demarcates the true right and left lobes. The right lobe is further divided into an anterior and posterior segment by the right hepatic vein. The left lobe is divided into the medial and lateral segments by the left hepatic vein. The fissure for the ligamentum ter ...
... lobes. The middle hepatic vein also demarcates the true right and left lobes. The right lobe is further divided into an anterior and posterior segment by the right hepatic vein. The left lobe is divided into the medial and lateral segments by the left hepatic vein. The fissure for the ligamentum ter ...
Anatomy of liver
... posterior surface of the liver Formed by: bare area, groove for IVC, caudate lobe, fissure for ligamentum venosum and oesophageal notch. Bare area of liver: a triangular area related directely to the diaphragm , its base is formed by the groove for IVC, its apex is formed by right triangular ligame ...
... posterior surface of the liver Formed by: bare area, groove for IVC, caudate lobe, fissure for ligamentum venosum and oesophageal notch. Bare area of liver: a triangular area related directely to the diaphragm , its base is formed by the groove for IVC, its apex is formed by right triangular ligame ...
Liver Function Test
... days. Several days later, the prothrombin time may be measured. If the prothrombin time becomes normal, then hepatic synthetic function is intact. This test does not indicate that there is no liver disease, but is suggestive that malnutrition may coexist with (or without) liver disease. ...
... days. Several days later, the prothrombin time may be measured. If the prothrombin time becomes normal, then hepatic synthetic function is intact. This test does not indicate that there is no liver disease, but is suggestive that malnutrition may coexist with (or without) liver disease. ...
Anatomy
... fissure for the ligamentum teres also separates the medial and lateral segments. The medial segment is also called the quadrate lobe. In the widely used Couinaud (or "French") system, the functional lobes are further divided into a total of eight subsegments based on a transverse plane through the ...
... fissure for the ligamentum teres also separates the medial and lateral segments. The medial segment is also called the quadrate lobe. In the widely used Couinaud (or "French") system, the functional lobes are further divided into a total of eight subsegments based on a transverse plane through the ...
Abdomen
... LT/RT perirenal space areas directly around kidney This space contains the kidneys, adrenal glands, ...
... LT/RT perirenal space areas directly around kidney This space contains the kidneys, adrenal glands, ...
Distinguishing Characteristics of Hepatic and Portal Veins
... The Liver occupies all of the right hypochondrium, the greater part of the epigastrium, and left hypochondrium. The ribs cover the greater part of the right lobe .In the epigastric region, the liver extends several centimeters below the xiphoid process. Most of the left lobe of the liver is covered ...
... The Liver occupies all of the right hypochondrium, the greater part of the epigastrium, and left hypochondrium. The ribs cover the greater part of the right lobe .In the epigastric region, the liver extends several centimeters below the xiphoid process. Most of the left lobe of the liver is covered ...
Materials covered in lecture
... Gallstone = cholelithiasis- 10% prevalence Stone impaction and obstruction cystic duct Pain with contraction after fatty meal 20-30 minutes Adult 40+- female more common ...
... Gallstone = cholelithiasis- 10% prevalence Stone impaction and obstruction cystic duct Pain with contraction after fatty meal 20-30 minutes Adult 40+- female more common ...
Liver and Gall Bladder
... Bile canaliculi. The bile created from the hepatocytes is collect by small channel, or duct called bile canaliculi. The bile then moves from the bile canaliculi, to the bile ductules and then eventually the bile ducts. The bile next enters the small intestines. Hepatic sinusoids. Blood capillaries ...
... Bile canaliculi. The bile created from the hepatocytes is collect by small channel, or duct called bile canaliculi. The bile then moves from the bile canaliculi, to the bile ductules and then eventually the bile ducts. The bile next enters the small intestines. Hepatic sinusoids. Blood capillaries ...
cross-sectional-anatomy-liver-part-1
... patients part of the left love extends into the LUQ. The liver is displaced inferiorly with inspiration. Except for several ligament attachments, there is a large potential space for the accumulation of fluids between the liver and diaphragm known as the right and left subphrenic or sub-diaphragmati ...
... patients part of the left love extends into the LUQ. The liver is displaced inferiorly with inspiration. Except for several ligament attachments, there is a large potential space for the accumulation of fluids between the liver and diaphragm known as the right and left subphrenic or sub-diaphragmati ...
XCA LIVER - WordPress.com
... patients part of the left love extends into the LUQ. The liver is displaced inferiorly with inspiration. Except for several ligament attachments, there is a large potential space for the accumulation of fluids between the liver and diaphragm known as the right and left subphrenic or sub-diaphragmati ...
... patients part of the left love extends into the LUQ. The liver is displaced inferiorly with inspiration. Except for several ligament attachments, there is a large potential space for the accumulation of fluids between the liver and diaphragm known as the right and left subphrenic or sub-diaphragmati ...
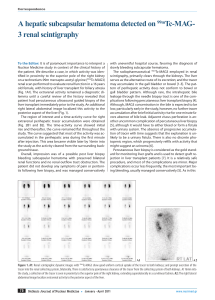
A hepatic subcapsular hematoma detected on 99mTc-MAG
... [5], although it would have to either bleed or form a fistula with urinary system. The absence of progressive accumulation of tracer with time suggests that the explanation is unlikely to be a urinary fistula. There is also no discrete photopenic region, which progressively refills with activity tha ...
... [5], although it would have to either bleed or form a fistula with urinary system. The absence of progressive accumulation of tracer with time suggests that the explanation is unlikely to be a urinary fistula. There is also no discrete photopenic region, which progressively refills with activity tha ...
The Liver and Oxidative Stress
... own body’s production of antioxidants, such as coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10). Oxidative stress occurs when our own supply of antioxidants is unable to keep up with the numbers of free radicals being produced. Oxidative stress is associated with a number of different degenerative disease states, including live ...
... own body’s production of antioxidants, such as coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10). Oxidative stress occurs when our own supply of antioxidants is unable to keep up with the numbers of free radicals being produced. Oxidative stress is associated with a number of different degenerative disease states, including live ...
Acute liver failure

Acute liver failure is the appearance of severe complications rapidly after the first signs of liver disease (such as jaundice), and indicates that the liver has sustained severe damage (loss of function of 80–90% of liver cells). The complications are hepatic encephalopathy and impaired protein synthesis (as measured by the levels of serum albumin and the prothrombin time in the blood). The 1993 classification defines hyperacute as within 1 week, acute as 8–28 days and subacute as 4–12 weeks. It reflects the fact that the pace of disease evolution strongly influences prognosis. Underlying etiology is the other significant determinant of outcome.