WHAT DOES FASD LOOK LIKE?
... What is a mental disorder? •A mental disorder is an illness that affects a person’s thoughts, emotions and behaviors. •Someone with a mental disorder may not feel good about themselves or may have a difficult time developing intimate relationships. •They may have difficulty dealing with everyday ac ...
... What is a mental disorder? •A mental disorder is an illness that affects a person’s thoughts, emotions and behaviors. •Someone with a mental disorder may not feel good about themselves or may have a difficult time developing intimate relationships. •They may have difficulty dealing with everyday ac ...
Chapter 21: Mental Health Diseases and Disorders 1. are those
... some distance, forgetting one’s identity and past, and often changing one’s name. 30. __________________________________________ often occur following severe depression, stress, fatigue, or recovery from a drug addiction. Individuals feel disconnected from mind and body and can feel like they are vi ...
... some distance, forgetting one’s identity and past, and often changing one’s name. 30. __________________________________________ often occur following severe depression, stress, fatigue, or recovery from a drug addiction. Individuals feel disconnected from mind and body and can feel like they are vi ...
Blue and Red Gradient
... her sleep in their bed, allow her to go with dad to work instead of working on class work This pattern of parental accommodation to Susan's avoidance contributes to and maintains her anxious avoidance, which may prevent her from mastering age appropriate developmental challenges ...
... her sleep in their bed, allow her to go with dad to work instead of working on class work This pattern of parental accommodation to Susan's avoidance contributes to and maintains her anxious avoidance, which may prevent her from mastering age appropriate developmental challenges ...
Excessive reassurance
... call its bluff; do not respond and see what occurs. The purpose of exposure and response prevention is to expose one’s self to the anxiety-provoking stimulus, await reduction in anxiety over the short term and in the long term habituate one’s self to that stimulus. ...
... call its bluff; do not respond and see what occurs. The purpose of exposure and response prevention is to expose one’s self to the anxiety-provoking stimulus, await reduction in anxiety over the short term and in the long term habituate one’s self to that stimulus. ...
PSY100-disorders11
... possible evaluation by others • individual fears that he/she may do something humiliating or embarrassing. ...
... possible evaluation by others • individual fears that he/she may do something humiliating or embarrassing. ...
Psychopharmacology in pediatric OCD
... Depression in Adolescents • Irritable or sad mood – More likely to report a sad/depressed mood ...
... Depression in Adolescents • Irritable or sad mood – More likely to report a sad/depressed mood ...
Somatoform and Dissociative Disorders
... Conversion Disorder • Conversion disorder is changing emotional difficulties into a loss of specific body function – No actual physical damage is present – They usually accept the loss with relative calm – They invent physical symptoms to gain freedom from an unbearable conflict ...
... Conversion Disorder • Conversion disorder is changing emotional difficulties into a loss of specific body function – No actual physical damage is present – They usually accept the loss with relative calm – They invent physical symptoms to gain freedom from an unbearable conflict ...
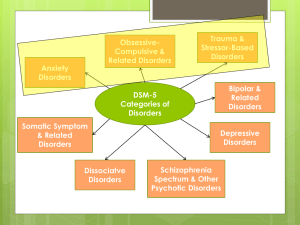
Medical Model - Biloxi Public Schools
... -persistent irrational fears of common events or objects -fear triggered by specific thing or object -intense fear associated w/ public setting -fear of being in open spaces or public places or other places from which escape is perceived to be difficult -anxiety disorder -involuntary, persistent, un ...
... -persistent irrational fears of common events or objects -fear triggered by specific thing or object -intense fear associated w/ public setting -fear of being in open spaces or public places or other places from which escape is perceived to be difficult -anxiety disorder -involuntary, persistent, un ...
正向心理学
... disorders were differentiated Briquet’s syndrome, named for the French physician who initially defined it in 1859 Term “somatization disorder” was first used in DSM-III (1980) ...
... disorders were differentiated Briquet’s syndrome, named for the French physician who initially defined it in 1859 Term “somatization disorder” was first used in DSM-III (1980) ...
Psych B – Module 28
... another experiencing fearfulness--may result in developing fear. • Fear of an object may be reinforced when by avoiding the feared objects. ...
... another experiencing fearfulness--may result in developing fear. • Fear of an object may be reinforced when by avoiding the feared objects. ...
Psychological Disorders
... • A legal, not psychological term • Means an individual is not legally responsible for his/her behavior due to a psychiatric illness or some other temporary or permanent mental condition ...
... • A legal, not psychological term • Means an individual is not legally responsible for his/her behavior due to a psychiatric illness or some other temporary or permanent mental condition ...
Dissociative, Personality, and Somatoform Disorders
... Dissociative Personality Disorders Dissociative Disorder- Occurs when conscious awareness becomes separated (dissociated) from previous memories, thoughts, and feelings. This set of disorders is the most controversial among those who study and treat abnormal behavior. The symptoms must be severe and ...
... Dissociative Personality Disorders Dissociative Disorder- Occurs when conscious awareness becomes separated (dissociated) from previous memories, thoughts, and feelings. This set of disorders is the most controversial among those who study and treat abnormal behavior. The symptoms must be severe and ...
Somatoform, Factitious and Dissociative Disorders
... Selective: unable to recall some, but not all, specific features of a traumatic event Generalized: memory loss covers most of life history Continuous: memory loss from specific time up to the present Systematized: memory loss is specific to category ...
... Selective: unable to recall some, but not all, specific features of a traumatic event Generalized: memory loss covers most of life history Continuous: memory loss from specific time up to the present Systematized: memory loss is specific to category ...
Mental Health Concerns for Educators in Prison - NC-NET
... DX: Hyperactive-impulsive and Inattentive Behaviors ...
... DX: Hyperactive-impulsive and Inattentive Behaviors ...
PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS
... heart would race or pound. And that would make me worry more. I was always imagining things were worse than they really were: when I got a stomachache, I’d think it was an ulcer.” 6.8 million affected F>M ...
... heart would race or pound. And that would make me worry more. I was always imagining things were worse than they really were: when I got a stomachache, I’d think it was an ulcer.” 6.8 million affected F>M ...
Supporting Parents of Anxious Children: Primary
... Over-analyse the meaning of body sensations Often coincides with developmental changes in cognition (awareness of death, end of magical thinking) Over-estimate their role in family for worrying about BIG things ...
... Over-analyse the meaning of body sensations Often coincides with developmental changes in cognition (awareness of death, end of magical thinking) Over-estimate their role in family for worrying about BIG things ...
Anxiety Disorders Overview (CSMH)
... He reports having great difficulty concentrating in his classes because of his increased worrying. He cannot pinpoint his worries; Rather, he reports being nervous about many things in his life, including his relationships with peers, his grades, and even his performance in basketball. His worries a ...
... He reports having great difficulty concentrating in his classes because of his increased worrying. He cannot pinpoint his worries; Rather, he reports being nervous about many things in his life, including his relationships with peers, his grades, and even his performance in basketball. His worries a ...