Chapter 9 Mood Disorders: Depressive Disorders
... thoughts of death and dying – Somatic complaints are also common – Associated with increased suicide risk ...
... thoughts of death and dying – Somatic complaints are also common – Associated with increased suicide risk ...
Mental Health Nursing II NURS 2310
... and into a fantasy world of one’s own creation Development in social interaction and communication is markedly abnormal or impaired Activities and interests are restricted; may be considered bizarre Prevalence of approximately 1 in 150 children in the U.S. Onset occurs before age 3 ...
... and into a fantasy world of one’s own creation Development in social interaction and communication is markedly abnormal or impaired Activities and interests are restricted; may be considered bizarre Prevalence of approximately 1 in 150 children in the U.S. Onset occurs before age 3 ...
Chapter 5
... Signs should be taken seriously. The more signs exhibited, the more likely it is that the person is thinking about suicide Recognizing these signs may help prevent `````````````````````a SUICIDE``````````````````````` Direct statements “I wish I were dead” Deterioration of schoolwork Indirect ...
... Signs should be taken seriously. The more signs exhibited, the more likely it is that the person is thinking about suicide Recognizing these signs may help prevent `````````````````````a SUICIDE``````````````````````` Direct statements “I wish I were dead” Deterioration of schoolwork Indirect ...
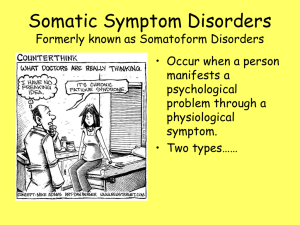
somatoform disorders
... her seat belt. Three days later she began to complain of a stiff neck and sharp pains radiating down both arms, her spine to the small of her back, and both legs. Because an orthopedic consultation failed to uncover the cause of the pain, she was referred to the neurology clinic. The patient was an ...
... her seat belt. Three days later she began to complain of a stiff neck and sharp pains radiating down both arms, her spine to the small of her back, and both legs. Because an orthopedic consultation failed to uncover the cause of the pain, she was referred to the neurology clinic. The patient was an ...
Slide 1
... 1) Somatization Disorder: when an individual presents a long history of medically unexplained physical complaints over many years. 2) Hypochondriasis: when one has a belief or fear that one has a serious disease when one is only experiencing normal bodily reactions. 3) Conversion Disorder: when one ...
... 1) Somatization Disorder: when an individual presents a long history of medically unexplained physical complaints over many years. 2) Hypochondriasis: when one has a belief or fear that one has a serious disease when one is only experiencing normal bodily reactions. 3) Conversion Disorder: when one ...
Intro
... • Epidemiology is the study of diseases in populations of humans or other animals, specifically how, when and where they occur. – Epidemiological studies can never prove causation – Incidence = new cases of a condition which occur during a specified period – Prevalence = cases (both new and existing ...
... • Epidemiology is the study of diseases in populations of humans or other animals, specifically how, when and where they occur. – Epidemiological studies can never prove causation – Incidence = new cases of a condition which occur during a specified period – Prevalence = cases (both new and existing ...
Somatoform Illness and Malingering
... Responsibility: to actively try to get well; comply with recommendations; respond to treatment ...
... Responsibility: to actively try to get well; comply with recommendations; respond to treatment ...
Psychological Disorders
... • Localized amnesia is present in an individual who has no memory of specific events that took place, usually traumatic. The loss of memory is localized with a specific window of time. For example, a survivor of a car wreck who has no memory of the experience until two days later is experiencing loc ...
... • Localized amnesia is present in an individual who has no memory of specific events that took place, usually traumatic. The loss of memory is localized with a specific window of time. For example, a survivor of a car wreck who has no memory of the experience until two days later is experiencing loc ...
DSM5 Diagnostic Criteria
... C. Symptoms must be present in the early developmental period (but may not become fully manifest until social demands exceed limited capacities, or may be masked by learned strategies in later life). ...
... C. Symptoms must be present in the early developmental period (but may not become fully manifest until social demands exceed limited capacities, or may be masked by learned strategies in later life). ...
Methods of carrying out research: • case study, experiment
... o Anxiety disorders, generalised anxiety disorder, panic disorder, specific phobia, social phobia, obsessive-‐compulsive disorder, post-‐traumatic stress disorder o Anorexia nervosa, eating disorder, risk factors ...
... o Anxiety disorders, generalised anxiety disorder, panic disorder, specific phobia, social phobia, obsessive-‐compulsive disorder, post-‐traumatic stress disorder o Anorexia nervosa, eating disorder, risk factors ...
Part VII. Schizophrenia
... • Most severe and debilitating of the psychological disorders. • Strikes at young adulthood • Psychotic disorder – marked by irrationality and lost contact with reality. ...
... • Most severe and debilitating of the psychological disorders. • Strikes at young adulthood • Psychotic disorder – marked by irrationality and lost contact with reality. ...
Ch12worksheetAPpsyMentalDisorders
... 17. Define Personality disorders: Cluster A of personality disorders-Odd-Eccentric: I am a hermit, _____________; I am violent but not psychotic ______________; I have odd thoughts and emotions ______________ Cluster B of personality disorders-Dramatic-erratic: Look at me, I am better than you, I am ...
... 17. Define Personality disorders: Cluster A of personality disorders-Odd-Eccentric: I am a hermit, _____________; I am violent but not psychotic ______________; I have odd thoughts and emotions ______________ Cluster B of personality disorders-Dramatic-erratic: Look at me, I am better than you, I am ...
Practice Questions
... month she was suffering from migraines, the next month it was severe stomach cramps, and the following month it was arthritic pain. While her symptoms are real, doctors have found no physiological reason for them. It is possible that Tamara has a. conversion disorder b. dependent personality c. bord ...
... month she was suffering from migraines, the next month it was severe stomach cramps, and the following month it was arthritic pain. While her symptoms are real, doctors have found no physiological reason for them. It is possible that Tamara has a. conversion disorder b. dependent personality c. bord ...
Section III - American Psychiatric Association
... base that warranted their progression into Section II for widespread clinical use, however, other conditions were dropped from the manual altogether failing to have garnered utility or empirical evidence since the prior manual was published. It is anticipated that the conditions included in Section ...
... base that warranted their progression into Section II for widespread clinical use, however, other conditions were dropped from the manual altogether failing to have garnered utility or empirical evidence since the prior manual was published. It is anticipated that the conditions included in Section ...
Narcissistic Personality Disorder
... but is easily hurt and rejected. This often happens because their expectations are so high. Their relationships with other people tend to be very poor. Other possible causes may include genetics, environment, and trauma or abuse in childhood. Most people diagnosed with this disorder are men, but it ...
... but is easily hurt and rejected. This often happens because their expectations are so high. Their relationships with other people tend to be very poor. Other possible causes may include genetics, environment, and trauma or abuse in childhood. Most people diagnosed with this disorder are men, but it ...
View Presentation
... • Diagnosed in school-aged children, mostly male • 15 percent of school-aged population in the United States have been diagnosed • Increasing numbers of children diagnosed with ADHD may be a reflection of changing social expectations, rather than an increase in the frequency of this neurological con ...
... • Diagnosed in school-aged children, mostly male • 15 percent of school-aged population in the United States have been diagnosed • Increasing numbers of children diagnosed with ADHD may be a reflection of changing social expectations, rather than an increase in the frequency of this neurological con ...
DSM guide - Staff Portal Camas School District
... the event is happening again; psychological and physical reactivity to reminders of the traumatic event, such as an anniversary Avoidant symptoms describe ways that someone may try to avoid any memory of the event, and must include one of the following: Avoiding thoughts, feelings, people, or situ ...
... the event is happening again; psychological and physical reactivity to reminders of the traumatic event, such as an anniversary Avoidant symptoms describe ways that someone may try to avoid any memory of the event, and must include one of the following: Avoiding thoughts, feelings, people, or situ ...
Neurotic disorders - Farrell`s Class Page
... Dissociative Amnesia • The main feature is loss of memory, usually of important recent event, which is not due to organic mental disorder and is too extensive to be explained by ordinary forgetfulness or fatigue. • The amnesia is usually centered on traumatic events, such as accidents, combat exper ...
... Dissociative Amnesia • The main feature is loss of memory, usually of important recent event, which is not due to organic mental disorder and is too extensive to be explained by ordinary forgetfulness or fatigue. • The amnesia is usually centered on traumatic events, such as accidents, combat exper ...
Schizophrenia - issues surrounding diagnosis L1
... The NHS is a wonderful thing! • There is limited time and resources available of many professionals working in the National Health Service. • Diagnoses can be made by professionals that are rushed, and preoccupied with only admitting the most serious cases in order to safeguard the resources of the ...
... The NHS is a wonderful thing! • There is limited time and resources available of many professionals working in the National Health Service. • Diagnoses can be made by professionals that are rushed, and preoccupied with only admitting the most serious cases in order to safeguard the resources of the ...
Unit 6: Psychopathology Name: I. Defining Psychological Disorders
... • B. Becomes harmful when behavior is… • C. Standards of this harmful behavior … II. Medical Model • A. The idea that diseases have… ...
... • B. Becomes harmful when behavior is… • C. Standards of this harmful behavior … II. Medical Model • A. The idea that diseases have… ...
Conversion disorder: the modern hysteria References
... (Couprie et al, 1995; Mace & Trimble, 1996). Others, however, have failed to show this relationship. Crimlisk et al (1998), for example, investigated the psychiatric and neurological morbidity, diagnostic stability and indicators of prognosis in patients identified 6 years previously as having medic ...
... (Couprie et al, 1995; Mace & Trimble, 1996). Others, however, have failed to show this relationship. Crimlisk et al (1998), for example, investigated the psychiatric and neurological morbidity, diagnostic stability and indicators of prognosis in patients identified 6 years previously as having medic ...
ho-2301-chap14powerpoint
... Personality Disorders • DSM-IV--10 personality disorders, grouped in 3 basic clusters – The odd, eccentric includes paranoid, schizoid, and schizotypal personality disorders – The dramatic, emotional, or erratic cluster consists of antisocial, borderline, histrionic, and narcissistic personality di ...
... Personality Disorders • DSM-IV--10 personality disorders, grouped in 3 basic clusters – The odd, eccentric includes paranoid, schizoid, and schizotypal personality disorders – The dramatic, emotional, or erratic cluster consists of antisocial, borderline, histrionic, and narcissistic personality di ...
Chapter 14 Powerpoint
... • Phobias – irrational, persistent fear of an abject, situation, or social activity • Social Phobias – fear of interacting with others or social situations • Specific Phobias – fear of objects or specific situations or events • Agoraphobia – fear of being in a place or situation ...
... • Phobias – irrational, persistent fear of an abject, situation, or social activity • Social Phobias – fear of interacting with others or social situations • Specific Phobias – fear of objects or specific situations or events • Agoraphobia – fear of being in a place or situation ...
Mental Illness
... Persistent recurring thoughts accompanied with the need to repeatedly perform some action, such as washing one’s hands Panic Intense feelings of terror that occur suddenly PostTraumatic Stress Disorder ...
... Persistent recurring thoughts accompanied with the need to repeatedly perform some action, such as washing one’s hands Panic Intense feelings of terror that occur suddenly PostTraumatic Stress Disorder ...