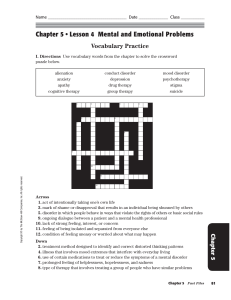
Ch. 5 Vocab
... Everybody feels sad from time to time. However, the 1. of sad feelings for weeks or months is a sign of depression. This mental disorder is fairly common 15 percent of all teens. Anxiety disduring adolescence, affecting 2. orders are also quite common in teens. Other types of mental disorders includ ...
... Everybody feels sad from time to time. However, the 1. of sad feelings for weeks or months is a sign of depression. This mental disorder is fairly common 15 percent of all teens. Anxiety disduring adolescence, affecting 2. orders are also quite common in teens. Other types of mental disorders includ ...
Document
... spectrum of symptoms (MDD, Panic) • Symptom focus as opposed to disorder focus • Use Balint Agreement ...
... spectrum of symptoms (MDD, Panic) • Symptom focus as opposed to disorder focus • Use Balint Agreement ...
The Anxiety Disorders Some Practical Questions & Answers
... let me know whether I’ve succeeded and how I could improve on your evaluation form and Facebook. ...
... let me know whether I’ve succeeded and how I could improve on your evaluation form and Facebook. ...
Psychological Disorders Defining Abnormal Behavior
... – Individual has a pervasive fear of illness and disease • Conversion disorder – individual experiences specific physical symptoms event though no physiological problems can be found ...
... – Individual has a pervasive fear of illness and disease • Conversion disorder – individual experiences specific physical symptoms event though no physiological problems can be found ...
Abnormal Behavior
... Panic Disorder - Anxiety that strikes suddenly wreaks havoc and then disappears - a panic attack is a minutes long episode that includes the belief that something terrible is going to happen - Can cause heart palpitations, shortness of breath, trembling or dizziness - 1 in 75 people has this disord ...
... Panic Disorder - Anxiety that strikes suddenly wreaks havoc and then disappears - a panic attack is a minutes long episode that includes the belief that something terrible is going to happen - Can cause heart palpitations, shortness of breath, trembling or dizziness - 1 in 75 people has this disord ...
Detailed notes to help with LOQ`s
... Key Facts About DID: • This disorder is RARE • Each personality may have it’s own name, memories, traits, and physical mannerisms. • May also be different in age, race, gender, and sexual orientation. • Alters are commonly quite different from one another. • The alters can come on suddenly ...
... Key Facts About DID: • This disorder is RARE • Each personality may have it’s own name, memories, traits, and physical mannerisms. • May also be different in age, race, gender, and sexual orientation. • Alters are commonly quite different from one another. • The alters can come on suddenly ...
Personality Disorders - American Psychiatric Association
... DSM is the manual used by clinicians and researchers to diagnose and classify mental disorders. The American Psychiatric Association (APA) will publish DSM-5 in 2013, culminating a 14-year revision process. APA is a national medical specialty society whose more than 37,000 physician members speciali ...
... DSM is the manual used by clinicians and researchers to diagnose and classify mental disorders. The American Psychiatric Association (APA) will publish DSM-5 in 2013, culminating a 14-year revision process. APA is a national medical specialty society whose more than 37,000 physician members speciali ...
Personality Disorders - DSM-5
... DSM is the manual used by clinicians and researchers to diagnose and classify mental disorders. The American Psychiatric Association (APA) will publish DSM-5 in 2013, culminating a 14-year revision process. For more information, go to www. DSM5.org. APA is a national medical specialty society whose ...
... DSM is the manual used by clinicians and researchers to diagnose and classify mental disorders. The American Psychiatric Association (APA) will publish DSM-5 in 2013, culminating a 14-year revision process. For more information, go to www. DSM5.org. APA is a national medical specialty society whose ...
Intro1
... impairment in one or more important areas of functioning) or with a significantly increased risk of suffering death, pain, disability, or an important loss of freedom” ...
... impairment in one or more important areas of functioning) or with a significantly increased risk of suffering death, pain, disability, or an important loss of freedom” ...
314.9 Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Not
... Examples include 1. Individuals whose symptoms and impainnent meet the criteria for AttentionDeficit/Hyperactivity Disorder, Predominantly Inattentive Type but whose age at onset is 7 years or after 2. Individuals with clinically significant impairment who present with inattention and whose symptom ...
... Examples include 1. Individuals whose symptoms and impainnent meet the criteria for AttentionDeficit/Hyperactivity Disorder, Predominantly Inattentive Type but whose age at onset is 7 years or after 2. Individuals with clinically significant impairment who present with inattention and whose symptom ...
SECTION 7: MENTAL HEALTH Summary: This table is based on the
... violence committed. ASPD was present in 0.3% of adults aged 18 or over (0.6% of men and 0.1% of women). BPD is characterised by high levels of personal and emotional instability associated with significant impairment. People with BPD have severe difficulties with sustaining relationships, and self-h ...
... violence committed. ASPD was present in 0.3% of adults aged 18 or over (0.6% of men and 0.1% of women). BPD is characterised by high levels of personal and emotional instability associated with significant impairment. People with BPD have severe difficulties with sustaining relationships, and self-h ...
Chapter 16 Test Review - DeForest Area School District
... • When people’s symptoms of psychological distress are at their worst, whatever they do to try to alleviate the condition is likely to be followed by improvement rather than further deterioration. This is best explained in terms of: a. systematic desensitization. b. the therapeutic alliance. c. coun ...
... • When people’s symptoms of psychological distress are at their worst, whatever they do to try to alleviate the condition is likely to be followed by improvement rather than further deterioration. This is best explained in terms of: a. systematic desensitization. b. the therapeutic alliance. c. coun ...
Class 8: Mental Illness and Diagnosis
... symptom severity and level of functioning. If it is, the appropriate range has been reached (continue with step 4). If not, go back to step 2 and continue moving down the scale 4. To determine the specific GAF rating within the selected 10-point range, consider whether the individual is functioning ...
... symptom severity and level of functioning. If it is, the appropriate range has been reached (continue with step 4). If not, go back to step 2 and continue moving down the scale 4. To determine the specific GAF rating within the selected 10-point range, consider whether the individual is functioning ...
Psychology - Beal City Schools
... Advantages and disadvantages of I.Q. testing (IVE-4.2) Multiple Intelligences (IVE-3.2) Motivation/Emotion (3 weeks) (IIC-1/IIC-6) Theories of Emotion (IIC-6.1) Hunger motivation (IIC-2) Maslow's hierarchy (IIC-3) Achievement motivation (IIC-4.1) Cultural standards of emotion (IIC-4.1) Physical attr ...
... Advantages and disadvantages of I.Q. testing (IVE-4.2) Multiple Intelligences (IVE-3.2) Motivation/Emotion (3 weeks) (IIC-1/IIC-6) Theories of Emotion (IIC-6.1) Hunger motivation (IIC-2) Maslow's hierarchy (IIC-3) Achievement motivation (IIC-4.1) Cultural standards of emotion (IIC-4.1) Physical attr ...
Posttraumatic Stress Disorder - DSM-5
... Negative cognitions and mood represents myriad feelings, from a persistent and distorted sense of blame of self or others, to estrangement from others or markedly diminished interest in activities, to an inability to remember key aspects of the event. Finally, arousal is marked by aggressive, reckle ...
... Negative cognitions and mood represents myriad feelings, from a persistent and distorted sense of blame of self or others, to estrangement from others or markedly diminished interest in activities, to an inability to remember key aspects of the event. Finally, arousal is marked by aggressive, reckle ...
WHAT DOES FASD LOOK LIKE?
... What is a mental disorder? •A mental disorder is an illness that affects a person’s thoughts, emotions and behaviors. •Someone with a mental disorder may not feel good about themselves or may have a difficult time developing intimate relationships. •They may have difficulty dealing with everyday ac ...
... What is a mental disorder? •A mental disorder is an illness that affects a person’s thoughts, emotions and behaviors. •Someone with a mental disorder may not feel good about themselves or may have a difficult time developing intimate relationships. •They may have difficulty dealing with everyday ac ...
AD/HD, bipolar Disorder, and Effective treatment
... disorders, AD/HD being at the lower end and bipolar disorder at the higher end? No, they are two separate disorders, though they share some of the same symptoms. An individual can have both disorders, which will require complex treatment. We have talked a lot about recognizing symptoms in children. ...
... disorders, AD/HD being at the lower end and bipolar disorder at the higher end? No, they are two separate disorders, though they share some of the same symptoms. An individual can have both disorders, which will require complex treatment. We have talked a lot about recognizing symptoms in children. ...
Disorders First Apparent in Childhood
... seat Leaves seat when it is inappropriate Runs or climbs excessively Difficulty playing quietly Is often “on the go” or acts as if “driven by a motor” ...
... seat Leaves seat when it is inappropriate Runs or climbs excessively Difficulty playing quietly Is often “on the go” or acts as if “driven by a motor” ...
Abnormal Psychology - Solon City Schools
... Dissociative Identity Disorder • Dissociative Identity Disorder (DID) - 2 or more distinct personalities control a person’s behavior – Used to be known as Multiple Personality Disorder. – Patients commonly have a history of childhood abuse or trauma. ...
... Dissociative Identity Disorder • Dissociative Identity Disorder (DID) - 2 or more distinct personalities control a person’s behavior – Used to be known as Multiple Personality Disorder. – Patients commonly have a history of childhood abuse or trauma. ...
Mods 40 – 42 Therapy Unit Essay Question Options
... Causes- chemical imbalance, bad brain structure Treatments- Drugs, surgery C. Cognitive Causes- clients views of them self Treatment- therapists telling the patient their statements don’t match 3. Describe the therapeutic procedure called systematic desensitization. Select a specific disorder for wh ...
... Causes- chemical imbalance, bad brain structure Treatments- Drugs, surgery C. Cognitive Causes- clients views of them self Treatment- therapists telling the patient their statements don’t match 3. Describe the therapeutic procedure called systematic desensitization. Select a specific disorder for wh ...
DSM-5: A First Look - Mental Health Heroes
... criteria for DSM-5 has included careful consideration of how gender, race and ethnicity may affect the diagnosis of mental illness. ...
... criteria for DSM-5 has included careful consideration of how gender, race and ethnicity may affect the diagnosis of mental illness. ...
Electrode Placement for Chest Leads, V1 to V6
... • The clinical exercise physiologist should recognize that the depressed person who exercises is at risk for nonadherence, that depression is common in patients with CHD and other chronic diseases, and that depressive symptoms may interfere with the enjoyment of exercise and motivation to fully enga ...
... • The clinical exercise physiologist should recognize that the depressed person who exercises is at risk for nonadherence, that depression is common in patients with CHD and other chronic diseases, and that depressive symptoms may interfere with the enjoyment of exercise and motivation to fully enga ...
Dissociative identity disorder

Dissociative identity disorder (DID), previously known as multiple personality disorder (MPD), is a mental disorder on the dissociative spectrum characterized by the appearance of at least two distinct and relatively enduring identities or dissociated personality states that alternately control a person's behavior, accompanied by memory impairment for important information not explained by ordinary forgetfulness. These symptoms are not accounted for by substance abuse, seizures, other medical conditions, nor by imaginative play in children. Diagnosis is often difficult as there is considerable comorbidity with other mental disorders. Malingering should be considered if there is possible financial or forensic gain, as well as factitious disorder if help-seeking behavior is prominent.DID is one of the most controversial psychiatric disorders, with no clear consensus on diagnostic criteria or treatment. Research on treatment efficacy has been concerned primarily with clinical approaches and case studies. Dissociative symptoms range from common lapses in attention, becoming distracted by something else, and daydreaming, to pathological dissociative disorders. No systematic, empirically-supported definition of ""dissociation"" exists. It is not the same as schizophrenia.Although neither epidemiological surveys nor longitudinal studies have been conducted, it is generally believed that DID rarely resolves spontaneously. Symptoms are said to vary over time. In general, the prognosis is poor, especially for those with comorbid disorders. There are few systematic data on the prevalence of DID. The International Society for the Study of Trauma and Dissociation states that the prevalence is between 1 and 3% in the general population, and between 1 and 5% in inpatient groups in Europe and North America. DID is diagnosed more frequently in North America than in the rest of the world, and is diagnosed three to nine times more often in females than in males. The prevalence of DID diagnoses increased greatly in the latter half of the 20th century, along with the number of identities (often referred to as ""alters"") claimed by patients (increasing from an average of two or three to approximately 16). DID is also controversial within the legal system, where it has been used as a rarely successful form of the insanity defense. The 1990s showed a parallel increase in the number of court cases involving the diagnosis.Dissociative disorders including DID have been attributed to disruptions in memory caused by trauma and other forms of stress, but research on this hypothesis has been characterized by poor methodology. So far, scientific studies, usually focusing on memory, have been few and the results have been inconclusive. An alternative hypothesis for the etiology of DID is as a by-product of techniques employed by some therapists, especially those using hypnosis, and disagreement between the two positions is characterized by intense debate. DID became a popular diagnosis in the 1970s, 80s and 90s, but it is unclear if the actual rate of the disorder increased, if it was more recognized by health care providers, or if sociocultural factors caused an increase in therapy-induced (iatrogenic) presentations. The unusual number of diagnoses after 1980, clustered around a small number of clinicians and the suggestibility characteristic of those with DID, support the hypothesis that DID is therapist-induced. The unusual clustering of diagnoses has also been explained as due to a lack of awareness and training among clinicians to recognize cases of DID.























