Chapter 1
... Positron Emission Tomography (PET). Example below shows subjects learning a new language (left) and performing language task after it was learned (right) ...
... Positron Emission Tomography (PET). Example below shows subjects learning a new language (left) and performing language task after it was learned (right) ...
Psychotherapy - Mansfield University
... focus selectively on negative, ignore the positive. pessimistic about future. negative conclusions about personal worth based on insignificant events. ...
... focus selectively on negative, ignore the positive. pessimistic about future. negative conclusions about personal worth based on insignificant events. ...
Psychopathology Psychopathology is a term which refers to either
... Mental distress is a term used, both by some mental health practitioners and users of mental health services, to describe a range of symptoms and experiences of a person's internal life that are commonly held to be troubling, confusing or out of the ordinary. Mental distress has a wider scope than t ...
... Mental distress is a term used, both by some mental health practitioners and users of mental health services, to describe a range of symptoms and experiences of a person's internal life that are commonly held to be troubling, confusing or out of the ordinary. Mental distress has a wider scope than t ...
Aging Well
... behavior. Usually occurs in young adulthood (18-24) Can occur later in life, usually women where paranoia is prominent Delusions, hallucinations, “word salad” speech, behaviors common, sitting for hours ...
... behavior. Usually occurs in young adulthood (18-24) Can occur later in life, usually women where paranoia is prominent Delusions, hallucinations, “word salad” speech, behaviors common, sitting for hours ...
Psychological Disorders
... Medical Model - the concept that diseases have physical causes that can be diagnosed, treated, and in most cases, cured. When applied to psychological disorders, the medical model assumes that these “mental” illnesses can be diagnosed on the basis of their symptoms and cured through therapy, which m ...
... Medical Model - the concept that diseases have physical causes that can be diagnosed, treated, and in most cases, cured. When applied to psychological disorders, the medical model assumes that these “mental” illnesses can be diagnosed on the basis of their symptoms and cured through therapy, which m ...
Psych Disorder Notes
... Medical Model - the concept that diseases have physical causes that can be diagnosed, treated, and in most cases, cured. When applied to psychological disorders, the medical model assumes that these “mental” illnesses can be diagnosed on the basis of their symptoms and cured through therapy, which m ...
... Medical Model - the concept that diseases have physical causes that can be diagnosed, treated, and in most cases, cured. When applied to psychological disorders, the medical model assumes that these “mental” illnesses can be diagnosed on the basis of their symptoms and cured through therapy, which m ...
Ch. 19 S. 5 Biological Therapy
... the availability of antipsychotic drugs, lobotomies are now performed only rarely. Drug therapies, and to a limited extent ECT, seem to be effective for some psychological disorders that do no respond to psychotherapy. It is important to realize, however, that medications and electric shocks cannot ...
... the availability of antipsychotic drugs, lobotomies are now performed only rarely. Drug therapies, and to a limited extent ECT, seem to be effective for some psychological disorders that do no respond to psychotherapy. It is important to realize, however, that medications and electric shocks cannot ...
Students with Emotional and Behavioral Disorders
... • An inability to learn that cannot be explained by intellectual, sensory, or health factors An inability to build or maintain satisfactory interpersonal relationships with peers and teachers Inappropriate types of behavior or feelings under normal circumstances A general pervasive mood of unha ...
... • An inability to learn that cannot be explained by intellectual, sensory, or health factors An inability to build or maintain satisfactory interpersonal relationships with peers and teachers Inappropriate types of behavior or feelings under normal circumstances A general pervasive mood of unha ...
Chapter 1 What is Psychology? Philosophical Developments
... Modern Psychology • Separated from philosophy in 19th century – influences from physiology remain ...
... Modern Psychology • Separated from philosophy in 19th century – influences from physiology remain ...
Concepts of Normality and Abnormality Part II
... the woman was African American and nondepressed, in another condition she was a white American and nondepressed. In the other two conditions she was each of these races but depressed. Although the therapists rated the nondepressed African American and the white American in much the same way, their r ...
... the woman was African American and nondepressed, in another condition she was a white American and nondepressed. In the other two conditions she was each of these races but depressed. Although the therapists rated the nondepressed African American and the white American in much the same way, their r ...
Schizoid Personality Disorder
... The exact cause of this disorder is not known. Experts think it may be caused by differences in the brain or nervous system. It might also be related to problems in the family such as financial stresses, death of loved ones, mental illness, or abuse. For example, people who were often rejected or ab ...
... The exact cause of this disorder is not known. Experts think it may be caused by differences in the brain or nervous system. It might also be related to problems in the family such as financial stresses, death of loved ones, mental illness, or abuse. For example, people who were often rejected or ab ...
Module 24 - Doral Academy Preparatory
... • patients could be helped to function better by providing humane treatment in a relaxed and decent environment; late 1800s, it was abandoned • 1930s, Sigmund Freud developed psychoanalysis • early 1950s, wretched conditions and inhumane treatment of patients persisted • mid 1950s, two dramatic chan ...
... • patients could be helped to function better by providing humane treatment in a relaxed and decent environment; late 1800s, it was abandoned • 1930s, Sigmund Freud developed psychoanalysis • early 1950s, wretched conditions and inhumane treatment of patients persisted • mid 1950s, two dramatic chan ...
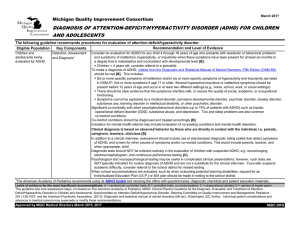
diagnosis of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (adhd)
... Consider an evaluation for ADHD for any child 4 through 18 years of age who presents with academic or behavioral problems and symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, or impulsivity when these symptoms have been present for at least six months to a degree that is maladaptive and inconsistent with dev ...
... Consider an evaluation for ADHD for any child 4 through 18 years of age who presents with academic or behavioral problems and symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, or impulsivity when these symptoms have been present for at least six months to a degree that is maladaptive and inconsistent with dev ...
Somatoform disorders - Salisbury University
... • How do we define “abnormality”? • Medical model “disease” view, biological causes • Psychological models Psychogenic – Caused by psychological factors (thoughts, beliefs, childhood, experiences) ...
... • How do we define “abnormality”? • Medical model “disease” view, biological causes • Psychological models Psychogenic – Caused by psychological factors (thoughts, beliefs, childhood, experiences) ...
Section III - American Psychiatric Association
... and perceived causes. To help clinicians gauge such factors, a cultural formulation interview guide is provided with questions about patients’ history in terms of their race, ethnicity, language, religion, social culture or customs, and geographical origin. The interview provides an opportunity for ...
... and perceived causes. To help clinicians gauge such factors, a cultural formulation interview guide is provided with questions about patients’ history in terms of their race, ethnicity, language, religion, social culture or customs, and geographical origin. The interview provides an opportunity for ...
Schizophrenia & Other Psychotic Disorders
... C H I L D & A D O L E S C E N T P S Y C H I AT R I S T COLLEGE OF MEDICINE, KSU ...
... C H I L D & A D O L E S C E N T P S Y C H I AT R I S T COLLEGE OF MEDICINE, KSU ...
learning objectives chapter 13
... Define and describe systematic desensitization therapy, modeling, assertiveness training, positive reinforcement, token economy program, extinction, flooding, implosive therapy, aversion conditioning, and punishment. Give an example of each. (see “Techniques for Modifying Behavior”) ...
... Define and describe systematic desensitization therapy, modeling, assertiveness training, positive reinforcement, token economy program, extinction, flooding, implosive therapy, aversion conditioning, and punishment. Give an example of each. (see “Techniques for Modifying Behavior”) ...
Affective and Personality Disorders
... “Every great movement begins with one man, and that’s me.” [Did you get out of control?] “Well yeah! I don’t have another gear!” ...
... “Every great movement begins with one man, and that’s me.” [Did you get out of control?] “Well yeah! I don’t have another gear!” ...
Reactive Attachment Disorder
... have RAD, neither do traditional therapies, especially since most therapies are based on the child/youth’s ability to form a trusting relationship with the therapist. Natural consequences seem to work better than behavioral methods, such as lectures or charts. Structure is important, but only when c ...
... have RAD, neither do traditional therapies, especially since most therapies are based on the child/youth’s ability to form a trusting relationship with the therapist. Natural consequences seem to work better than behavioral methods, such as lectures or charts. Structure is important, but only when c ...
What is Psychology? - Tipp City Exempted Village Schools
... • Aristotle, a student of Plato, outlined many laws of associationism – experiences often remind us of similar experiences in the past – Used scientific approach ...
... • Aristotle, a student of Plato, outlined many laws of associationism – experiences often remind us of similar experiences in the past – Used scientific approach ...
IGDA. 4: Evaluation of symptoms and mental state
... a chief complaint and history, and specific questioning in suspected problem areas. Evidence of signs and symptoms may also come from ancillary information sources, such as records of prior treatment and the reports of relatives, friends, representatives of social agencies, and other professionals. ...
... a chief complaint and history, and specific questioning in suspected problem areas. Evidence of signs and symptoms may also come from ancillary information sources, such as records of prior treatment and the reports of relatives, friends, representatives of social agencies, and other professionals. ...
A1985AGF6400001
... book. John Davis also suggested this call pharmacological dissection, has and pointed out that he could do the been widely adopted and widely critiextensive, detailed, critical review of cized. Of late, attempts to consider psythe treatment literature for which he chopharmacological effects in terms ...
... book. John Davis also suggested this call pharmacological dissection, has and pointed out that he could do the been widely adopted and widely critiextensive, detailed, critical review of cized. Of late, attempts to consider psythe treatment literature for which he chopharmacological effects in terms ...
Success Through Change Camps - Keystone Behavioral Pediatrics
... child given a comprehensive evaluation by gathering information from multiple sources including the child, parents and teachers. This is important in order to determine the severity of the behavioral difficulties and to develop appropriate treatment goals for your child. Therapy: Therapists use seve ...
... child given a comprehensive evaluation by gathering information from multiple sources including the child, parents and teachers. This is important in order to determine the severity of the behavioral difficulties and to develop appropriate treatment goals for your child. Therapy: Therapists use seve ...