Quantum Phases and Topological States in Optical Lattices
... known as the hopping term which describes the tunneling of atoms between neighboring sites. The strength is characterized by the tunneling matric element J which is generally positive. A single particle state with non-zero components on neighboring sites gives a more negative hopping energy. Hence, ...
... known as the hopping term which describes the tunneling of atoms between neighboring sites. The strength is characterized by the tunneling matric element J which is generally positive. A single particle state with non-zero components on neighboring sites gives a more negative hopping energy. Hence, ...
... the term ‘electron’ in 1899 and identified electrons with cathode rays. He showed how vibrations of electron give rise to Maxwell’s electromagnetic waves. In 1896, Lorentz jointly with Pieter Zeeman (1865-1943) explained the Zeeman effect whereby atomic spectral lines are split in the presence of ma ...
Realization of a Knill-Laflamme-Milburn controlled
... atoms, nuclear spins, quantum dots, superconductor and photons— while photons are indispensable for quantum communication [2, 3] and are particularly promising for quantum metrology [4, 5]. In addition to low-noise quantum systems (typically two-level ‘qubits’) quantum information protocols require ...
... atoms, nuclear spins, quantum dots, superconductor and photons— while photons are indispensable for quantum communication [2, 3] and are particularly promising for quantum metrology [4, 5]. In addition to low-noise quantum systems (typically two-level ‘qubits’) quantum information protocols require ...
Graviton physics - ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst
... The calculation of photon interactions with matter is a staple in an introductory (or advanced) quantum mechanics course. Indeed the evaluation of the Compton scattering cross section is a standard exercise in relativistic quantum mechanics, since gauge invariance together with the masslessness of t ...
... The calculation of photon interactions with matter is a staple in an introductory (or advanced) quantum mechanics course. Indeed the evaluation of the Compton scattering cross section is a standard exercise in relativistic quantum mechanics, since gauge invariance together with the masslessness of t ...
MISiS-02-08-2015
... Lamb shift for artificial macroscopic “atoms” (qubits) is not something illusive. Moreover, strong coupling regime is possible in contrast to natural atoms. ...
... Lamb shift for artificial macroscopic “atoms” (qubits) is not something illusive. Moreover, strong coupling regime is possible in contrast to natural atoms. ...
Staging quantum cryptography with chocolate balls
... present a quantum cryptographic protocol on stage. The audience is actively involved and invited to participate in the dramatic presentation. If at all possible, the event should be moderated by a well-known comedian, or by a physics teacher. The entire process is principally analogous to an experim ...
... present a quantum cryptographic protocol on stage. The audience is actively involved and invited to participate in the dramatic presentation. If at all possible, the event should be moderated by a well-known comedian, or by a physics teacher. The entire process is principally analogous to an experim ...
PDF only - at www.arxiv.org.
... detector D2 with probability R 2 ; (iii) the photon goes to Bob through path b and is detected at detector D3 with probability T . After the detection of a photon is completed, Alice and Bob tell each other whether or not each of the detectors clicked. If D2 or D3 clicks, they also announce both the ...
... detector D2 with probability R 2 ; (iii) the photon goes to Bob through path b and is detected at detector D3 with probability T . After the detection of a photon is completed, Alice and Bob tell each other whether or not each of the detectors clicked. If D2 or D3 clicks, they also announce both the ...
Quantum Brownian motion and the Third Law of thermodynamics
... law of heat) [5, 6]. He took this result even further: He also studied how fast the difference between the changes in the enthalpy ∆H and the Gibbs free energy ∆G, i.e. ∆H − ∆G tends to zero [7]. In fact, this difference vanishes faster than linear in temperature implying that the change of entropy ...
... law of heat) [5, 6]. He took this result even further: He also studied how fast the difference between the changes in the enthalpy ∆H and the Gibbs free energy ∆G, i.e. ∆H − ∆G tends to zero [7]. In fact, this difference vanishes faster than linear in temperature implying that the change of entropy ...
Unitary time evolution
... Exactly what this operator Û is will depend on the particular system and the interactions that it undergoes. It does not, however, depend on the state |ψi. This means that time evolution of quantum systems is linear. Because of this linearity, if a system is in state |ψi or |φi or any linear combin ...
... Exactly what this operator Û is will depend on the particular system and the interactions that it undergoes. It does not, however, depend on the state |ψi. This means that time evolution of quantum systems is linear. Because of this linearity, if a system is in state |ψi or |φi or any linear combin ...
Document
... sense of Sachs, for example), but no information on the dynamical motion. Feynman parton densities give momentum-space distributions of constituents, but no information of the spatial location of the partons. ...
... sense of Sachs, for example), but no information on the dynamical motion. Feynman parton densities give momentum-space distributions of constituents, but no information of the spatial location of the partons. ...
PHYSICS
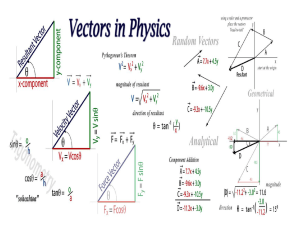
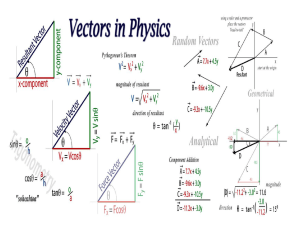
... What is the net velocity? • ex: A plane flies 40 m/s W with a 10 m/s W tailwind. What is the net velocity? ...
... What is the net velocity? • ex: A plane flies 40 m/s W with a 10 m/s W tailwind. What is the net velocity? ...
IB Physics Vector Presentation
... What is the net velocity? • ex: A plane flies 40 m/s W with a 10 m/s W tailwind. What is the net velocity? ...
... What is the net velocity? • ex: A plane flies 40 m/s W with a 10 m/s W tailwind. What is the net velocity? ...
20131018_STEP - University of Birmingham
... Keep existing strategy but select jets up to 100% with J5 Use different minimum bias trigger only (L1_MBTS_2) Unprescaled, fully efficient and has highest trigger rate for all data used Expected time for changes: 1-2 month(s) ...
... Keep existing strategy but select jets up to 100% with J5 Use different minimum bias trigger only (L1_MBTS_2) Unprescaled, fully efficient and has highest trigger rate for all data used Expected time for changes: 1-2 month(s) ...
Probability amplitude

In quantum mechanics, a probability amplitude is a complex number used in describing the behaviour of systems. The modulus squared of this quantity represents a probability or probability density.Probability amplitudes provide a relationship between the wave function (or, more generally, of a quantum state vector) of a system and the results of observations of that system, a link first proposed by Max Born. Interpretation of values of a wave function as the probability amplitude is a pillar of the Copenhagen interpretation of quantum mechanics. In fact, the properties of the space of wave functions were being used to make physical predictions (such as emissions from atoms being at certain discrete energies) before any physical interpretation of a particular function was offered. Born was awarded half of the 1954 Nobel Prize in Physics for this understanding (see #References), and the probability thus calculated is sometimes called the ""Born probability"". These probabilistic concepts, namely the probability density and quantum measurements, were vigorously contested at the time by the original physicists working on the theory, such as Schrödinger and Einstein. It is the source of the mysterious consequences and philosophical difficulties in the interpretations of quantum mechanics—topics that continue to be debated even today.