“hot” and “cold” cognition - Evidence
... Objectives: The central role of cognitive deficits in depression is well established and represents a primary mediator of the negative consequences of this disorder in both human and economic terms. The aim of the present review is to provide an up-to-date overview of current knowledge on the cognit ...
... Objectives: The central role of cognitive deficits in depression is well established and represents a primary mediator of the negative consequences of this disorder in both human and economic terms. The aim of the present review is to provide an up-to-date overview of current knowledge on the cognit ...
THE DIFFERENTIATION OF PATIENTS WITH MPD OR DDNOS
... difference in the description of amnesia between groups III and IV. Memory problems in group IV were associated also with episodes of depersonalization, or sometimes with childhood experiences. Patients in group III, however, differed significantly from patients in group IV in the prevalence and sev ...
... difference in the description of amnesia between groups III and IV. Memory problems in group IV were associated also with episodes of depersonalization, or sometimes with childhood experiences. Patients in group III, however, differed significantly from patients in group IV in the prevalence and sev ...
systematic assessment of dissociative identity
... caseworker, who offered her 24-hour (telephone) access to crisis assistance should she feel unsafe. In the absence of recent physical abuse, Melissa felt that she would be safe. However, her meeting with the protective services caseworker precipitated a family crisis. Melissa's mother phoned the tre ...
... caseworker, who offered her 24-hour (telephone) access to crisis assistance should she feel unsafe. In the absence of recent physical abuse, Melissa felt that she would be safe. However, her meeting with the protective services caseworker precipitated a family crisis. Melissa's mother phoned the tre ...
PREDISPOSED BORDERLINE PERSONALITY DISORDER (PreBPD)
... 6. Affective instability due to a marked reactivity of mood (e.g., intense episodic dysphoria, irritability or anxiety usually lasting a few hours and only rarely more than a few days). 7. Chronic feelings of emptiness and boredom. 8. Inappropriate anger or difficulty controlling anger (e.g., freque ...
... 6. Affective instability due to a marked reactivity of mood (e.g., intense episodic dysphoria, irritability or anxiety usually lasting a few hours and only rarely more than a few days). 7. Chronic feelings of emptiness and boredom. 8. Inappropriate anger or difficulty controlling anger (e.g., freque ...
trauma. - Mindful Ohio
... traumatic event(s), beginning or worsening after the traumatic event(s) occurred, as evidenced by two (or more) of the following: 1. Inability to remember an important aspect of the traumatic event(s) (typically due to dissociative amnesia and not to other factors such as head injury, alcohol, or dr ...
... traumatic event(s), beginning or worsening after the traumatic event(s) occurred, as evidenced by two (or more) of the following: 1. Inability to remember an important aspect of the traumatic event(s) (typically due to dissociative amnesia and not to other factors such as head injury, alcohol, or dr ...
Relationship-related obsessive- compulsive phenomena: The case
... The cognitive substrate of relationship-related OC phenomena Cognitive behavioural models stipulate the central role of dysfunctional appraisals of internal or external stimuli in the development and maintenance of OCD related disorders. According to such models (e.g., Rachman, 1997; Storch, Abramow ...
... The cognitive substrate of relationship-related OC phenomena Cognitive behavioural models stipulate the central role of dysfunctional appraisals of internal or external stimuli in the development and maintenance of OCD related disorders. According to such models (e.g., Rachman, 1997; Storch, Abramow ...
Cluster A Personality Disorders 301.0 Paranoid Personality Disorder
... Paranoid Personality Disorder must be distinguished from Personality Change Due to a General Medical Condition, in which the traits emerge due to the direct effects of a general medical condition on the central nervous system. It must also be distinguished from symptoms that may develop in associati ...
... Paranoid Personality Disorder must be distinguished from Personality Change Due to a General Medical Condition, in which the traits emerge due to the direct effects of a general medical condition on the central nervous system. It must also be distinguished from symptoms that may develop in associati ...
10461_2012_212_MOESM1_ESM
... MVA: Depression treatment (antidepressants and/or psychotherapy use) significantly increased the likelihood to be adherent to cART (AOR = 2.52, 95% CI 1.40, 4.53). Antidepressant MPR of >80% were significantly more likely to be adherent to cART than those with poor antidepressant adherence (AOR = 2. ...
... MVA: Depression treatment (antidepressants and/or psychotherapy use) significantly increased the likelihood to be adherent to cART (AOR = 2.52, 95% CI 1.40, 4.53). Antidepressant MPR of >80% were significantly more likely to be adherent to cART than those with poor antidepressant adherence (AOR = 2. ...
Mental Disorders in Litigation - The Continuing Legal Education
... The DSM-IV is purely a clinical tool to assist physicians communicating with each other. DSM-IV was not devised for use in forensic settings. Legal criteria for “mental disorder” or similar terms such as “nervous shock” are very different from medical criteria and should not be confused. As an examp ...
... The DSM-IV is purely a clinical tool to assist physicians communicating with each other. DSM-IV was not devised for use in forensic settings. Legal criteria for “mental disorder” or similar terms such as “nervous shock” are very different from medical criteria and should not be confused. As an examp ...
Kliiniline küsimus nr 1 Kas kõigil ärevushäire kahtlusega
... depressed mood, and (or) sleep difficulties. Diagnosis for these patients can easily be confused with hypochondriasis or major depression if one fails to ask about worries other than those about healt Table 7.2 Interview questions to screen for GAD such as your family, health, work, or finances? muc ...
... depressed mood, and (or) sleep difficulties. Diagnosis for these patients can easily be confused with hypochondriasis or major depression if one fails to ask about worries other than those about healt Table 7.2 Interview questions to screen for GAD such as your family, health, work, or finances? muc ...
Atypical Antipsychotics Induced Chronic Akathisia: A Case Report
... follows: acute, tardive, withdrawal and chronic akathisia. Standardized titration and use of second generation antipsychotics are successful approaches of prevention from drug-induced akathisia. On the other hand, it is possible that atypic antipsychotics-induced akathisia may emerge and there may b ...
... follows: acute, tardive, withdrawal and chronic akathisia. Standardized titration and use of second generation antipsychotics are successful approaches of prevention from drug-induced akathisia. On the other hand, it is possible that atypic antipsychotics-induced akathisia may emerge and there may b ...
psychological disorders
... argued that “mental illness is a myth” and that “mental disorders” are nothing more than conditions that society dislikes. He even proposed that psychologists and psychiatrists use diagnoses as weapons of control: By attaching negative labels to people whose behaviours they find objectionable, they’ ...
... argued that “mental illness is a myth” and that “mental disorders” are nothing more than conditions that society dislikes. He even proposed that psychologists and psychiatrists use diagnoses as weapons of control: By attaching negative labels to people whose behaviours they find objectionable, they’ ...
Melancholia and the probability and lethality of suicide attempts
... lethality of future suicide attempts. Melancholia did not predict lethality prospectively, perhaps owing to a lack of statistical power. Global depression severity, as measured by the HRSD and BDI, is not consistently associated with suicide attempt lethality (Malone et al, al, 1996). Defining depre ...
... lethality of future suicide attempts. Melancholia did not predict lethality prospectively, perhaps owing to a lack of statistical power. Global depression severity, as measured by the HRSD and BDI, is not consistently associated with suicide attempt lethality (Malone et al, al, 1996). Defining depre ...
Other Personality Disorders
... substance/medication related disorder is accompanied by a non-substancerelated diagnosis such as major depression since both may have contributed equally to the need for admission or treatment. Principal diagnosis is listed first and the term "Principal diagnosis" follows the diagnosis name Rema ...
... substance/medication related disorder is accompanied by a non-substancerelated diagnosis such as major depression since both may have contributed equally to the need for admission or treatment. Principal diagnosis is listed first and the term "Principal diagnosis" follows the diagnosis name Rema ...
Expression and Treatment of Depression among Haitian Immigrant
... meet their basic needs. In fact, clients rarely report having a decrease in appetite or sex drive. It is important to note that although some of the symptoms of this type of depression (i.e., crying spells and sleep difficulties) may resemble that of major depression, clients would not meet the diag ...
... meet their basic needs. In fact, clients rarely report having a decrease in appetite or sex drive. It is important to note that although some of the symptoms of this type of depression (i.e., crying spells and sleep difficulties) may resemble that of major depression, clients would not meet the diag ...
Document - New Directions Support Group
... hypomania the individual experiences heightened energy, an enhanced ability to do work and less need for sleep. He may also become irritable and annoyed at the least little thing. The quandary about hypomania is that it is often a welcome feeling due to one’s productivity. However, it is usually acc ...
... hypomania the individual experiences heightened energy, an enhanced ability to do work and less need for sleep. He may also become irritable and annoyed at the least little thing. The quandary about hypomania is that it is often a welcome feeling due to one’s productivity. However, it is usually acc ...
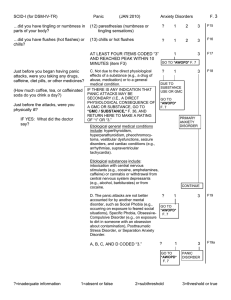
SCID-I (for DSM-IV-TR) Panic (JAN 2010) Anxiety Disorders F. 3
... 4 - In Partial Remission: The full criteria for the disorder were previously met but currently only some of the symptoms or signs of the disorder remain. 5 - In Full Remission: There are no longer any symptoms or signs of the disorder, but it Is still clinically relevant to note the disorder--for ex ...
... 4 - In Partial Remission: The full criteria for the disorder were previously met but currently only some of the symptoms or signs of the disorder remain. 5 - In Full Remission: There are no longer any symptoms or signs of the disorder, but it Is still clinically relevant to note the disorder--for ex ...
Meta-analysis of the SLC6A3/DAT1 VNTR haplotype in
... Patients (n=275) had been referred for assessment of ADHD to the outpatient clinic of GGZ Delfland in Delft, to Parnassia, psycho-medical centre in The Hague, or to the department of Psychiatry at the Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Centre in Nijmegen, the Netherlands. Most of the patients have ...
... Patients (n=275) had been referred for assessment of ADHD to the outpatient clinic of GGZ Delfland in Delft, to Parnassia, psycho-medical centre in The Hague, or to the department of Psychiatry at the Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Centre in Nijmegen, the Netherlands. Most of the patients have ...
Axis-I comorbidity is linked to prospective Open Access
... major depression in body weight instability and abnormal food intake has been evidenced [18]. Tozzi et al. reported that crossover between AN and BN is significantly correlated with the personality factor of self-directedness [8]. Because recent studies reported that high harm avoidance and low self ...
... major depression in body weight instability and abnormal food intake has been evidenced [18]. Tozzi et al. reported that crossover between AN and BN is significantly correlated with the personality factor of self-directedness [8]. Because recent studies reported that high harm avoidance and low self ...
overview of depression - Innovative Educational Services
... with bipolar disorder typically reflect the extreme mood state at the time (e.g., grandiosity during mania, worthlessness during depression). Rapid Cycling Bipolar disorder with rapid cycling is defined as four or more episodes of illness within a 12-month period. This form of the illness tends to b ...
... with bipolar disorder typically reflect the extreme mood state at the time (e.g., grandiosity during mania, worthlessness during depression). Rapid Cycling Bipolar disorder with rapid cycling is defined as four or more episodes of illness within a 12-month period. This form of the illness tends to b ...
Chapter 15: Mood Disorders
... • True • Anhedonia refers to the loss of any sense of pleasure from activities that a person formerly enjoyed. This is a manifestation of ...
... • True • Anhedonia refers to the loss of any sense of pleasure from activities that a person formerly enjoyed. This is a manifestation of ...
Participant Program Manual
... • The symptoms last at least two weeks without a break • There is a clear change from the adolescent’s normal mood or behavior • The symptoms are observed in several different contexts — at home, at school or work, with friends — suggesting they are not just a reaction to a specific problem Studi ...
... • The symptoms last at least two weeks without a break • There is a clear change from the adolescent’s normal mood or behavior • The symptoms are observed in several different contexts — at home, at school or work, with friends — suggesting they are not just a reaction to a specific problem Studi ...
Trastornos de la salud mental más comunes en la práctica de
... numerals are especially limiting. • Research advances will continue to require text revisions to DSM, and a TR designation, as was done with DSM-IVTR, can only be appended once. • After DSM-5 is published in may 2013, future changes prior to the manual's next complete revision will be signified as D ...
... numerals are especially limiting. • Research advances will continue to require text revisions to DSM, and a TR designation, as was done with DSM-IVTR, can only be appended once. • After DSM-5 is published in may 2013, future changes prior to the manual's next complete revision will be signified as D ...
manic depression - Geisel School of Medicine
... With manic depression, periods of normal mood usually occur between the periods of extreme highs and lows.The lengths of episodes vary from person to person and can change over time. If you or someone you know has experienced cycles of the following behaviors, professional help should be considered: ...
... With manic depression, periods of normal mood usually occur between the periods of extreme highs and lows.The lengths of episodes vary from person to person and can change over time. If you or someone you know has experienced cycles of the following behaviors, professional help should be considered: ...