FREE Sample Here - test bank and solution manual for
... There are two main arguments for relativism. o There are many different moral standards of behavior. o We do not know how to determine the absolute rules. Cultural relativism defines “good” as that which contributes to the health and survival of society. Occupational subcultures also support standar ...
... There are two main arguments for relativism. o There are many different moral standards of behavior. o We do not know how to determine the absolute rules. Cultural relativism defines “good” as that which contributes to the health and survival of society. Occupational subcultures also support standar ...
Chapter 8 Slides
... David Geffen o David Geffen the son of poor Russian immigrants o Geffen was coming of age as an entrepreneur, he still had to face school o Geffen graduated from high school wanting to get rich in show business o From the mailroom a 21-year-old Geffen launched the career that made him “the richest ...
... David Geffen o David Geffen the son of poor Russian immigrants o Geffen was coming of age as an entrepreneur, he still had to face school o Geffen graduated from high school wanting to get rich in show business o From the mailroom a 21-year-old Geffen launched the career that made him “the richest ...
Chapter 2
... judgments about moral matters develops in stages • These stages characterize the way people think about ethical dilemmas ...
... judgments about moral matters develops in stages • These stages characterize the way people think about ethical dilemmas ...
The Ethics Toolkit For Coaches and Mentors
... additional and personal code of ethics that relates to one’s own practice or business. Whether a business consists of a one person entity or a large organisation, a code of conduct is essential for ethical health and wellness. The following are suggested items for inclusion: ...
... additional and personal code of ethics that relates to one’s own practice or business. Whether a business consists of a one person entity or a large organisation, a code of conduct is essential for ethical health and wellness. The following are suggested items for inclusion: ...
James Rachels, “Ethical Egoism”.
... a. Presents “common-sense morality”: although we should look after our own selfinterest, we also have a duty to care for others, especially if it’s at minimum cost to ourselves. b. Presents viewpoint of “Ethical Egoism”: we ought to look out only for what is in our own self-interest (i.e., no “natur ...
... a. Presents “common-sense morality”: although we should look after our own selfinterest, we also have a duty to care for others, especially if it’s at minimum cost to ourselves. b. Presents viewpoint of “Ethical Egoism”: we ought to look out only for what is in our own self-interest (i.e., no “natur ...
Chapter 19 PowerPoint Slides
... • A willingness to seek out and act on reasons having good reasons for the decisions you make. • Requires the decision maker to be impartial. Decision makers will demonstrate a commitment to rationality. The Economic Point of View • Decisions made on a purely economics basis can be unethical. ...
... • A willingness to seek out and act on reasons having good reasons for the decisions you make. • Requires the decision maker to be impartial. Decision makers will demonstrate a commitment to rationality. The Economic Point of View • Decisions made on a purely economics basis can be unethical. ...
6. Why Bother
... ignorance (not knowing what is right) difficulty (the inability to act ethically) ...
... ignorance (not knowing what is right) difficulty (the inability to act ethically) ...
Myths about Business Ethics
... policeperson on the block. • Many believe business ethics is a recent phenomenon because of increased attention to the topic in popular and management literature. • Business ethics was written about even 2,000 years ago -- at least since Cicero wrote about the topic in his On Duties. ...
... policeperson on the block. • Many believe business ethics is a recent phenomenon because of increased attention to the topic in popular and management literature. • Business ethics was written about even 2,000 years ago -- at least since Cicero wrote about the topic in his On Duties. ...
Ethical Behavior - Northwest Missouri State University
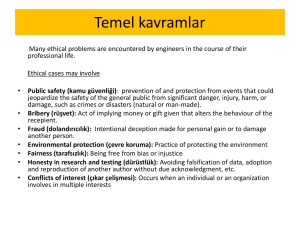
... Why Identifying Ethical Standards is Hard There are two fundamental problems in identifying the ethical standards we are to follow: ...
... Why Identifying Ethical Standards is Hard There are two fundamental problems in identifying the ethical standards we are to follow: ...
Slide 1
... Ie. Perhaps one particular individual or group suffers greatly for the “total benefit” to society. ...
... Ie. Perhaps one particular individual or group suffers greatly for the “total benefit” to society. ...
There Are No Ethical Leaders An Argument for Ethical Individuals Patrick Brousseau
... What is more important, acting ethically or being a leader? Theoretically, there is nothing which prevents both from occurring simultaneously. Yet practically, examples of conflict between the two abound. Imagine for instance an executive who faces the dilemma of either acting unethically or going b ...
... What is more important, acting ethically or being a leader? Theoretically, there is nothing which prevents both from occurring simultaneously. Yet practically, examples of conflict between the two abound. Imagine for instance an executive who faces the dilemma of either acting unethically or going b ...
Integrity and Ethics,Mr.Shiva Hari Adhikari
... Integrity is knowing right things to do and doing the right things. Integrity is not an absolute notion that you either have or totally lack. ...
... Integrity is knowing right things to do and doing the right things. Integrity is not an absolute notion that you either have or totally lack. ...
Performance reviews on business ethics and morals
... potential ethical complications. Managers may intentionally or. Running a Business · Work»; Business Management»; Business Ethics» . 4.1 Business Ethics: Guiding Principles in Selling and in Life based on your personal ethics; your actions reflect your own moral beliefs and moral conduct.. … oversee ...
... potential ethical complications. Managers may intentionally or. Running a Business · Work»; Business Management»; Business Ethics» . 4.1 Business Ethics: Guiding Principles in Selling and in Life based on your personal ethics; your actions reflect your own moral beliefs and moral conduct.. … oversee ...
File - Introduction
... If ethics is defined by the character one holds but can vary greatly with custom, then the same can be said for defining ethical leadership. Merely having ethics does not make a leader, nor does being a leader make someone ethical. These separate concepts, with separate practice, must intently be co ...
... If ethics is defined by the character one holds but can vary greatly with custom, then the same can be said for defining ethical leadership. Merely having ethics does not make a leader, nor does being a leader make someone ethical. These separate concepts, with separate practice, must intently be co ...
Materialy/07/History of Ethics
... can at the same time will that it should become a universal law." "Act as though the maxim of your action were by your will to become a universal law of nature." Act so that you treat humanity, whether in your own person or in that of another, always as an end and never as a means only." ...
... can at the same time will that it should become a universal law." "Act as though the maxim of your action were by your will to become a universal law of nature." Act so that you treat humanity, whether in your own person or in that of another, always as an end and never as a means only." ...
Slide 1 - Faculty Personal Homepage
... that there really are not any justifiable, reliable ethical standards. ...
... that there really are not any justifiable, reliable ethical standards. ...
Duty Ethics
... office” that has the responsibility to ensure that employees have the ability to express their concerns about safety and corporate business practices. These offices also try to foster an ethical culture within the corporate. Students should study ethics because they need to get sensitized to ethical ...
... office” that has the responsibility to ensure that employees have the ability to express their concerns about safety and corporate business practices. These offices also try to foster an ethical culture within the corporate. Students should study ethics because they need to get sensitized to ethical ...
Applying Business Ethics
... the serious consequences that can result from decisions made with a lack of regard to ethics. Even if you believe that good business ethics don't contribute to profit levels, you should be able to recognise that poor ethics can have a detrimental effect on your bottom line in the long term. Poor eth ...
... the serious consequences that can result from decisions made with a lack of regard to ethics. Even if you believe that good business ethics don't contribute to profit levels, you should be able to recognise that poor ethics can have a detrimental effect on your bottom line in the long term. Poor eth ...
Introduction to ethics - U of L Personal Web Sites
... Points out that there are a priori ethical truths, i.e. that some ethical truths, of which there are clear cases, do not derive from a more fundamental principle, but rather that claims to have found a fundamental principle of ethics had better lead to correct conclusions in these cases. ...
... Points out that there are a priori ethical truths, i.e. that some ethical truths, of which there are clear cases, do not derive from a more fundamental principle, but rather that claims to have found a fundamental principle of ethics had better lead to correct conclusions in these cases. ...
Academic Planning & Review
... if you’re slow, and risk missing a deadline, you may chance rather than check. if you fluff the right photo, you might be tempted to do a digital manipulation. if your skills are too to poor find and tell good stories, you will be more prone to hyping a story, or to burning a source. ...
... if you’re slow, and risk missing a deadline, you may chance rather than check. if you fluff the right photo, you might be tempted to do a digital manipulation. if your skills are too to poor find and tell good stories, you will be more prone to hyping a story, or to burning a source. ...
Ethical Decisions: A Foundation for Appropriate Problem
... Is this an ethical dilemma? What is the major ethical issue? How should the problem be resolved? What are the potential consequences? ...
... Is this an ethical dilemma? What is the major ethical issue? How should the problem be resolved? What are the potential consequences? ...
Michael Josephson on Ethical Decision Making
... consciousness, and ethical competency. Ethical Commitment Ethical commitment refers to a strong desire to do the right thing, especially when behaving ethically imposes financial, social or emotional costs. Surveys taken by the Josephson Institute reveal that, regardless of profession, almost all pe ...
... consciousness, and ethical competency. Ethical Commitment Ethical commitment refers to a strong desire to do the right thing, especially when behaving ethically imposes financial, social or emotional costs. Surveys taken by the Josephson Institute reveal that, regardless of profession, almost all pe ...
Ethical Decision Making and Personality Type – Leo Klug
... reasoning, we could profit from intentionally using the four distinct, interrelated steps mentioned earlier. When using this process, most of us will find it easier to focus on some things and neglect others. For example, we may favor phase two (generating possible solutions). We may also find that, ...
... reasoning, we could profit from intentionally using the four distinct, interrelated steps mentioned earlier. When using this process, most of us will find it easier to focus on some things and neglect others. For example, we may favor phase two (generating possible solutions). We may also find that, ...