here - Persona Counselling
... significance of practical, material, interpersonal and social aspects of their experiences, which only constitute subsidiary or ‘trigger’ factors in the current system of classification ...
... significance of practical, material, interpersonal and social aspects of their experiences, which only constitute subsidiary or ‘trigger’ factors in the current system of classification ...
short version
... Brief Psychotic Disorder It is called a psychotic episode with symptoms alike to schizophrenia’s that is manifested abruptly and lasts less than a month. It is a rare disorder mainly manifested to adolescents and very young persons. The treatment includes antipsychotic medication and supportin ...
... Brief Psychotic Disorder It is called a psychotic episode with symptoms alike to schizophrenia’s that is manifested abruptly and lasts less than a month. It is a rare disorder mainly manifested to adolescents and very young persons. The treatment includes antipsychotic medication and supportin ...
Depression - Helsenorge.no
... are nausea, dizziness, and other kinds of pain. Many lose their desire for sex. A depression will manifest as a combination of the symptoms described above, with variations in scope and intensity. Some people experience one isolated depressive episode, while it may recur for others. Depression can s ...
... are nausea, dizziness, and other kinds of pain. Many lose their desire for sex. A depression will manifest as a combination of the symptoms described above, with variations in scope and intensity. Some people experience one isolated depressive episode, while it may recur for others. Depression can s ...
No Slide Title
... or indecisiveness • Recurrent thoughts of death, suicidal ideation, or suicide attempt ...
... or indecisiveness • Recurrent thoughts of death, suicidal ideation, or suicide attempt ...
Slide 1
... • Mood disorders include: – Major Depressive disorders (MDD) – Bipolar disorders • Mood disorders are characterized by persistent disturbances, either highs or lows, in mood (emotions / affect). • Everyone experiences ups and downs in response to events (good or bad) in their lives. Short-term ups a ...
... • Mood disorders include: – Major Depressive disorders (MDD) – Bipolar disorders • Mood disorders are characterized by persistent disturbances, either highs or lows, in mood (emotions / affect). • Everyone experiences ups and downs in response to events (good or bad) in their lives. Short-term ups a ...
Impulse Control Disorders Not Elsewhere Classified
... Apparently rare (information is lacking) ...
... Apparently rare (information is lacking) ...
Impulse Control Disorders Not Elsewhere Classified
... Apparently rare (information is lacking) ...
... Apparently rare (information is lacking) ...
Schizophrenia
... A false belief that cannot be explained by the individual’s culture or education. The individual cannot be persuaded that the belief is incorrect, despite evidence to the contrary or weight of opinion Types of delusions: grandeur, guilt, ill health, jealousy, passivity, persecution, poverty, r ...
... A false belief that cannot be explained by the individual’s culture or education. The individual cannot be persuaded that the belief is incorrect, despite evidence to the contrary or weight of opinion Types of delusions: grandeur, guilt, ill health, jealousy, passivity, persecution, poverty, r ...
anxiety and mood disorders lecture
... Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) Follows traumatic event or events such as war, rape, or assault Symptoms include: nightmares flashbacks sleeplessness easily startled depression irritability ...
... Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) Follows traumatic event or events such as war, rape, or assault Symptoms include: nightmares flashbacks sleeplessness easily startled depression irritability ...
Date - Psychology
... 3. One distinction that DSM-IV-TR makes between acute stress disorder and posttraumatic stress disorder is based on: A) how intense the anxiety-linked symptoms are. B) what the cause of the anxiety-linked symptoms was. C) how long the anxiety symptoms last*. D) what sort of treatment is contemplated ...
... 3. One distinction that DSM-IV-TR makes between acute stress disorder and posttraumatic stress disorder is based on: A) how intense the anxiety-linked symptoms are. B) what the cause of the anxiety-linked symptoms was. C) how long the anxiety symptoms last*. D) what sort of treatment is contemplated ...
Anxiety Disorders
... (6 Mos.) & are not tied to any specific event. Aware of unusually high anxiety, but can’t shake it off or pinpoint the cause. Usually sets in during Childhood or adolescence. ...
... (6 Mos.) & are not tied to any specific event. Aware of unusually high anxiety, but can’t shake it off or pinpoint the cause. Usually sets in during Childhood or adolescence. ...
Abnormal Psychology
... Mood Disorders • Experience extreme or inappropriate emotion. • Females are twice as likely as men to suffer from these – why do you think this is? ...
... Mood Disorders • Experience extreme or inappropriate emotion. • Females are twice as likely as men to suffer from these – why do you think this is? ...
OCD introduction
... recheck things. They often visualize horrific catastrophes in which they are to blame for a lack of responsibility. Checkers often develop elaborate checking rituals that make it difficult for them complete daily tasks. ...
... recheck things. They often visualize horrific catastrophes in which they are to blame for a lack of responsibility. Checkers often develop elaborate checking rituals that make it difficult for them complete daily tasks. ...
MyersExpPsych7e_IM_Module 38 garber edits
... Major Depressive Disorder Depression is the “common cold” of psychological disorders. In a year, 5.8% of men and 9.5% of women report depression worldwide (WHO, 2002). ...
... Major Depressive Disorder Depression is the “common cold” of psychological disorders. In a year, 5.8% of men and 9.5% of women report depression worldwide (WHO, 2002). ...
PSYCHOLOGY (9th Edition) David Myers
... Formerly called manic-depressive disorder. An alternation between depression and mania signals bipolar disorder. Depressive Symptoms ...
... Formerly called manic-depressive disorder. An alternation between depression and mania signals bipolar disorder. Depressive Symptoms ...
PowerPoint
... Later when reviewing the admitting lab work, the attending MD noted Gary had an elevated white blood cell count indicating an infection. This coupled with Gary being non-responsive to the anti-psychotic medications led the MD to run further tests. He was diagnosed with meningitis and aggressively tr ...
... Later when reviewing the admitting lab work, the attending MD noted Gary had an elevated white blood cell count indicating an infection. This coupled with Gary being non-responsive to the anti-psychotic medications led the MD to run further tests. He was diagnosed with meningitis and aggressively tr ...
DSM-IV-TR/DSM-5, AN EVIDENCE-BASED COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS
... attempts to address some of the concerns regarding the lack of a contextual assessment process regarding the role of culture within the lives of clients (Warren, ...
... attempts to address some of the concerns regarding the lack of a contextual assessment process regarding the role of culture within the lives of clients (Warren, ...
Signs of Mental Illness and Suicide Prevention
... What causes these conditions? It can be difficult to pinpoint the cause of a mental health condition. Things that could contribute to the presence of these conditions: ...
... What causes these conditions? It can be difficult to pinpoint the cause of a mental health condition. Things that could contribute to the presence of these conditions: ...
Dissociative Disorders - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
... – questioner must be careful to phrase questions (as not to suggest existence of event and risk creating false memory). – accuracy of memories recovered with such strategies can only be determined by external corroboration. ...
... – questioner must be careful to phrase questions (as not to suggest existence of event and risk creating false memory). – accuracy of memories recovered with such strategies can only be determined by external corroboration. ...
Psychopharmacology and Other Biologic Treatments
... – Progressive, recurrent illness – Over time, episodes are more frequent, severe and longer in duration. – Mean age of onset is about 40 years of age. – An untreated episode lasts six to 13 months. – Suicide is the most serious complication (10 to ...
... – Progressive, recurrent illness – Over time, episodes are more frequent, severe and longer in duration. – Mean age of onset is about 40 years of age. – An untreated episode lasts six to 13 months. – Suicide is the most serious complication (10 to ...
File
... male and 2 are female. Far more teens attempt to kill themselves but fail. Only accidents and homicides kill more teens than suicides do. ...
... male and 2 are female. Far more teens attempt to kill themselves but fail. Only accidents and homicides kill more teens than suicides do. ...
Cross-cultural adjustment & mental illness
... Major Depressive Disorder Intervention • When symptom last for at least 6 weeks. • Interfere with functioning, i.e. school, work and relationships • Difficult to resolve with social support, rest, exercise, leisure or diet change. • When there is suicidal ideation/plans ...
... Major Depressive Disorder Intervention • When symptom last for at least 6 weeks. • Interfere with functioning, i.e. school, work and relationships • Difficult to resolve with social support, rest, exercise, leisure or diet change. • When there is suicidal ideation/plans ...
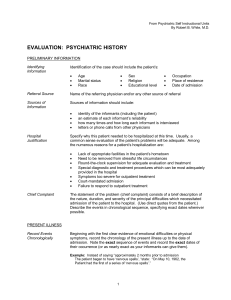
evaluation: psychiatric history
... rarely remember events before the third or fourth year and often relate what they have learned from parents; the source of information should be indicated. An informative question is, What is the first thing in your life that you remember?’ The answer, even though it may represent a “screen memo ...
... rarely remember events before the third or fourth year and often relate what they have learned from parents; the source of information should be indicated. An informative question is, What is the first thing in your life that you remember?’ The answer, even though it may represent a “screen memo ...
Mental Health Services
... Personality, health status, financial situation, social support and ability to cope with stress all affect adjustment The emotional health of the elder is important The elder’s perception of their own health is a factor Even though elders have so many changes, they report less stress than any other ...
... Personality, health status, financial situation, social support and ability to cope with stress all affect adjustment The emotional health of the elder is important The elder’s perception of their own health is a factor Even though elders have so many changes, they report less stress than any other ...
Insight therapies
... ○ Reflection of feelings: reflective listening, therapist paraphrases the clients words, capturing the emotional tone so they can see and hear themselves Therapist provides unconditioned positive regard ○ Complete acceptance of a person regardless of actions or ...
... ○ Reflection of feelings: reflective listening, therapist paraphrases the clients words, capturing the emotional tone so they can see and hear themselves Therapist provides unconditioned positive regard ○ Complete acceptance of a person regardless of actions or ...
Mental status examination

The mental status examination or mental state examination, abbreviated MSE, is an important part of the clinical assessment process in psychiatric practice. It is a structured way of observing and describing a patient's current state of mind, under the domains of appearance, attitude, behavior, mood and affect, speech, thought process, thought content, perception, cognition, insight and judgment. There are some minor variations in the subdivision of the MSE and the sequence and names of MSE domains.The purpose of the MSE is to obtain a comprehensive cross-sectional description of the patient's mental state, which, when combined with the biographical and historical information of the psychiatric history, allows the clinician to make an accurate diagnosis and formulation, which are required for coherent treatment planning.The data are collected through a combination of direct and indirect means: unstructured observation while obtaining the biographical and social information, focused questions about current symptoms, and formalised psychological tests.The MSE is not to be confused with the mini-mental state examination (MMSE), which is a brief neuro-psychological screening test for dementia.