Memory - Hensley
... Fact or Falsehood? 1. Memory storage is never automatic; it always takes effort. 2. The day after you are introduced to a number of new students, you will more easily recall the names of those you met first. 3. Memory aids are no more useful than simple rehearsal of information. 4. Only a few peopl ...
... Fact or Falsehood? 1. Memory storage is never automatic; it always takes effort. 2. The day after you are introduced to a number of new students, you will more easily recall the names of those you met first. 3. Memory aids are no more useful than simple rehearsal of information. 4. Only a few peopl ...
Module 3 - socialscienceteacher
... between situational cues and learned information. If you study while listening to your favorite CD, you will remember better if you played that CD. 2. State-Dependent: You will remember info better if you are in the same emotional state of mind when you learned it. Ex: You read a book angry> you wil ...
... between situational cues and learned information. If you study while listening to your favorite CD, you will remember better if you played that CD. 2. State-Dependent: You will remember info better if you are in the same emotional state of mind when you learned it. Ex: You read a book angry> you wil ...
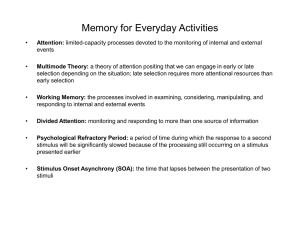
Memory for Everyday Activities
... Attention: limited-capacity processes devoted to the monitoring of internal and external events ...
... Attention: limited-capacity processes devoted to the monitoring of internal and external events ...
Cognitive Neuroscience of Language: 18: Memory and language
... (1)The experienced soldiers warned about the dangers before the midnight raid. (2)The experienced soldiers warned about the dangers conducted the midnight raid. The claim is that individual differences in verbal working memory predict performance on language comprehension tasks. Alternatively, there ...
... (1)The experienced soldiers warned about the dangers before the midnight raid. (2)The experienced soldiers warned about the dangers conducted the midnight raid. The claim is that individual differences in verbal working memory predict performance on language comprehension tasks. Alternatively, there ...
3.10 notes
... • Retrograde amnesia – Loss of memory for the past – Memory loss coincides with injury or illness ...
... • Retrograde amnesia – Loss of memory for the past – Memory loss coincides with injury or illness ...
“Describe the neuroanatomy of and neural processes related to
... “Describe the neuroanatomy of and neural processes related to learning based on current literature.” The difference between learning and memory is rather subtle; learning is the process by which new information and abilities are incorporated into one’s mind, whereas memory is the way in which that i ...
... “Describe the neuroanatomy of and neural processes related to learning based on current literature.” The difference between learning and memory is rather subtle; learning is the process by which new information and abilities are incorporated into one’s mind, whereas memory is the way in which that i ...
Social Memory Presentation - School of Communication and
... • Inability to focus theoretical discussion • Lacked coherence • Too much unassociated information to sift through • Beneficial to examine only a few key points ...
... • Inability to focus theoretical discussion • Lacked coherence • Too much unassociated information to sift through • Beneficial to examine only a few key points ...
Midterm Review Project
... Memory- learning that has persisted over time; it has been acquired, stored, and can be retrieved In order to remember something it must be: ● Encoded- perceived by the brain ● Stored- retained in the brain for a long period of time ● Retrieved- come back out of storage and into conscious thought Pa ...
... Memory- learning that has persisted over time; it has been acquired, stored, and can be retrieved In order to remember something it must be: ● Encoded- perceived by the brain ● Stored- retained in the brain for a long period of time ● Retrieved- come back out of storage and into conscious thought Pa ...
Lecture 16
... a specific state is recalled most accurately if the person is in that state again State-dependent learning is associated with drug use, time of day, and traumatic experiences ...
... a specific state is recalled most accurately if the person is in that state again State-dependent learning is associated with drug use, time of day, and traumatic experiences ...
social-and-cultural-factors-which-affect-cognitive
... You will present your research orally to the group for discussion and finally for display. In the Western world, a ‘good’ memory is highly prized, particularly by those revising for end of year exams. Better memory, means better grades, means better opportunities for further study and enhanced emplo ...
... You will present your research orally to the group for discussion and finally for display. In the Western world, a ‘good’ memory is highly prized, particularly by those revising for end of year exams. Better memory, means better grades, means better opportunities for further study and enhanced emplo ...
Spatial Working Memory
... prefrontal cortex (DLPFC), as opposed to ventral PFC, has been associated more with spatial memory, in particular in the right hemisphere. However, some current investigators associated DLPFC more with executive control. DLPFC forms part of a VWM network that includes a number of areas closely relat ...
... prefrontal cortex (DLPFC), as opposed to ventral PFC, has been associated more with spatial memory, in particular in the right hemisphere. However, some current investigators associated DLPFC more with executive control. DLPFC forms part of a VWM network that includes a number of areas closely relat ...
Biological Basis of Memory
... o Implicit memories like memories do still occur showing that these may not involve the hippocampus but knowing they are there ( memory) does not work showing the hippocampus is involved in these. 3. Infantile Amnesia – Inability to recall events from the first few of life. Possible Reasons for this ...
... o Implicit memories like memories do still occur showing that these may not involve the hippocampus but knowing they are there ( memory) does not work showing the hippocampus is involved in these. 3. Infantile Amnesia – Inability to recall events from the first few of life. Possible Reasons for this ...
The Neural Basis Of Memory
... neurons can be seen by the naked eye, so can be observed, stimulated or removed . ...
... neurons can be seen by the naked eye, so can be observed, stimulated or removed . ...
Immediate Memory….
... we build schema, take apart or rework ideas for eventual storage somewhere else. Generally captures our focus and demands our attention. Can handle only a few items at once. Adolescents can process items intently up to 10-20 minutes before becoming fatigued. Adults, up to 45. ...
... we build schema, take apart or rework ideas for eventual storage somewhere else. Generally captures our focus and demands our attention. Can handle only a few items at once. Adolescents can process items intently up to 10-20 minutes before becoming fatigued. Adults, up to 45. ...
Brain Jeopardy Game
... This component of shortterm memory is where we build, take apart, or rework ideas for eventual storage. ...
... This component of shortterm memory is where we build, take apart, or rework ideas for eventual storage. ...