Beers_First_Stars_NIC_School
... Stars with enhanced abundances of carbon (CEMP stars), and other light elements (including the lowest [Fe/H] star yet discovered), and lack of over-abundances of neutron-capture elements (CEMP-no stars) Associated with production by “faint SNe” – progenitors with mass on the order of 10-100 Mo under ...
... Stars with enhanced abundances of carbon (CEMP stars), and other light elements (including the lowest [Fe/H] star yet discovered), and lack of over-abundances of neutron-capture elements (CEMP-no stars) Associated with production by “faint SNe” – progenitors with mass on the order of 10-100 Mo under ...
Spatial distribution of stars in the Milky Way
... Note that the faintest stars, M dwarfs, are restricted to the inner 20 pc or so, while progressively brighter stars are seen fill progressively larger spheres. There are only a handful of the earliest types in the sphere (O, B and A) stars. These are in black, and there is an indication that they ar ...
... Note that the faintest stars, M dwarfs, are restricted to the inner 20 pc or so, while progressively brighter stars are seen fill progressively larger spheres. There are only a handful of the earliest types in the sphere (O, B and A) stars. These are in black, and there is an indication that they ar ...
Li-cai Deng
... of one galaxy instead of comparing snapshots of many. It is only now that we have large surveys of the whole sky that we are able to comprehend the Milky Way as a whole. Unlike external galaxies, the picture we are building is in three dimensions of position and velocity, with much higher accuracy i ...
... of one galaxy instead of comparing snapshots of many. It is only now that we have large surveys of the whole sky that we are able to comprehend the Milky Way as a whole. Unlike external galaxies, the picture we are building is in three dimensions of position and velocity, with much higher accuracy i ...
June 2015 - Bristol Astronomical Society
... arabic name, is one of the largest stars known, with a diameter of around 500 times that of our Sun. In common with most giant stars it varies its size, changing in brightness as it does so from 3rd to 4th magnitude (see p 25). The Globular Cluster M13 is easily found on the western side of the Herc ...
... arabic name, is one of the largest stars known, with a diameter of around 500 times that of our Sun. In common with most giant stars it varies its size, changing in brightness as it does so from 3rd to 4th magnitude (see p 25). The Globular Cluster M13 is easily found on the western side of the Herc ...
Dipper, Sword, Snake and Turtle
... on the back. Whether the symbols on the reverse side of the coins were added already contemporary with their use as currency or later is as yet an unsettled matter. The representations are all rendered mirror inverted including the angle towards each other and towards the center of the coin. They po ...
... on the back. Whether the symbols on the reverse side of the coins were added already contemporary with their use as currency or later is as yet an unsettled matter. The representations are all rendered mirror inverted including the angle towards each other and towards the center of the coin. They po ...
Stellar Census
... reactions, but do not become hot enough to fuse protons They are intermediate in mass between stars and planets ...
... reactions, but do not become hot enough to fuse protons They are intermediate in mass between stars and planets ...
Magnitudes and Colours of Stars - Lincoln
... In fact, as we will see in the next Module, stars behave very like practical examples of black bodies - theoretical objects with properties that have been determined by classical physicists. (We will leave the tricky question of how someone could describe a star as a black body to the next Module!) ...
... In fact, as we will see in the next Module, stars behave very like practical examples of black bodies - theoretical objects with properties that have been determined by classical physicists. (We will leave the tricky question of how someone could describe a star as a black body to the next Module!) ...
INTERSTELLAR MedLab
... Dark – high densities of dust and gas that redden or extinct the light from the stars located behind the cloud. These are also where molecules are likely to be found. During the course of this laboratory exercise, you will study the interstellar medium – where stars are formed and into which the ste ...
... Dark – high densities of dust and gas that redden or extinct the light from the stars located behind the cloud. These are also where molecules are likely to be found. During the course of this laboratory exercise, you will study the interstellar medium – where stars are formed and into which the ste ...
THE HERTZSPRUNG-RUSSELL DIAGRAM
... expressed as a colour index, sometimes—especially in old plots—as spectral class), with luminosity decreasing from the top of the plot to the bottom and temperature decreasing from left to right. Note that large magnitudes correspond to small luminosities. 2. Stars on the HR diagram are concentrated ...
... expressed as a colour index, sometimes—especially in old plots—as spectral class), with luminosity decreasing from the top of the plot to the bottom and temperature decreasing from left to right. Note that large magnitudes correspond to small luminosities. 2. Stars on the HR diagram are concentrated ...
Sky Maps Teacher`s Guide - Northern Stars Planetarium
... Circumpolar Constellations and Stars are the constellations and stars that never set. The number of circumpolar constellations you see depends on your latitude. The further north or south you travel from the equator, the more stars become circumpolar. At the equator, no stars are circumpolar. At the ...
... Circumpolar Constellations and Stars are the constellations and stars that never set. The number of circumpolar constellations you see depends on your latitude. The further north or south you travel from the equator, the more stars become circumpolar. At the equator, no stars are circumpolar. At the ...
ph507lecnote06
... Distance: Distance is an easy concept to understand: it is just a length in some units such as in feet, km, light years, parsecs etc. It has been excrutiatingly difficult to measure astronomical distances until this century. Unfortunately most stars are so far away that it is impossible to directly ...
... Distance: Distance is an easy concept to understand: it is just a length in some units such as in feet, km, light years, parsecs etc. It has been excrutiatingly difficult to measure astronomical distances until this century. Unfortunately most stars are so far away that it is impossible to directly ...
Goal: To understand how to find the brightness of stars and what
... • So, instead of 1,2,3, we go by X1, X2,X3. • X can be anything. • For stars, X is about 2.5. • So, 5 orders of magnitude is a factor of 2.55 (which turns out to be about a factor of 100) • Some scales also have logarithmic scales for ...
... • So, instead of 1,2,3, we go by X1, X2,X3. • X can be anything. • For stars, X is about 2.5. • So, 5 orders of magnitude is a factor of 2.55 (which turns out to be about a factor of 100) • Some scales also have logarithmic scales for ...
interactive.hr.diagram
... You need a 100 percent on the quiz to receive a stamp. The stamp is worth 12 points! The stamp is worth ...
... You need a 100 percent on the quiz to receive a stamp. The stamp is worth 12 points! The stamp is worth ...
Photoelectric Photometry of the Pleiades
... located on the right hand side of the menu bar. Getting Started gives you a brief overview on how to operate the telescope. When you have finished with the Getting Started help screen, select Help…Taking Data. Taking Data provides information on how to access and operate the photometer, and take the ...
... located on the right hand side of the menu bar. Getting Started gives you a brief overview on how to operate the telescope. When you have finished with the Getting Started help screen, select Help…Taking Data. Taking Data provides information on how to access and operate the photometer, and take the ...
Polaris
... another very close dwarf companion (variously α UMi P, α UMi a or α UMi Ab). In January 2006, NASA released images from the Hubble telescope, directly showing all three members of the Polaris trinary system. The nearer dwarf star is in an orbit of only 18.5 AU (2.8 billion km; about the distance fro ...
... another very close dwarf companion (variously α UMi P, α UMi a or α UMi Ab). In January 2006, NASA released images from the Hubble telescope, directly showing all three members of the Polaris trinary system. The nearer dwarf star is in an orbit of only 18.5 AU (2.8 billion km; about the distance fro ...
Time From the Perspective of a Particle Physicist
... • Stars “move” East to West over the course of one Night (in circle about the North Star) • Stars “move” East to West by 2 hours per month and “return” to the same position after one Year • It’s just caused by Earth’s daily spin and yearly orbit about the Sun • Star wheel depends on latitude: northe ...
... • Stars “move” East to West over the course of one Night (in circle about the North Star) • Stars “move” East to West by 2 hours per month and “return” to the same position after one Year • It’s just caused by Earth’s daily spin and yearly orbit about the Sun • Star wheel depends on latitude: northe ...
August 2014 Saguaro Skies
... 20” f5 Dobsonian, 180X, Ken Reeves: Very large, pretty bright, very slight green color. Filter brings out some detail in the outer part. Brightest part is elongated NE/SW, faint part is elongated NW/SE. WOW! 9 stars involved including central star. Next is the relatively nearby M57, another magnific ...
... 20” f5 Dobsonian, 180X, Ken Reeves: Very large, pretty bright, very slight green color. Filter brings out some detail in the outer part. Brightest part is elongated NE/SW, faint part is elongated NW/SE. WOW! 9 stars involved including central star. Next is the relatively nearby M57, another magnific ...
How to Plot the H-R Diagram and Use its Applications
... varies and it seems that flickers stars. Stars according to their spectral characteristics to be classified. Decaying it would stellar spectrum of radiation of different wavelengths of radiation elements show, is obtained. With this information, temperature, color and chemical composition of stars i ...
... varies and it seems that flickers stars. Stars according to their spectral characteristics to be classified. Decaying it would stellar spectrum of radiation of different wavelengths of radiation elements show, is obtained. With this information, temperature, color and chemical composition of stars i ...
WSN 42 (2016) 132-142
... varies and it seems that flickers stars. Stars according to their spectral characteristics to be classified. Decaying it would stellar spectrum of radiation of different wavelengths of radiation elements show, is obtained. With this information, temperature, color and chemical composition of stars i ...
... varies and it seems that flickers stars. Stars according to their spectral characteristics to be classified. Decaying it would stellar spectrum of radiation of different wavelengths of radiation elements show, is obtained. With this information, temperature, color and chemical composition of stars i ...
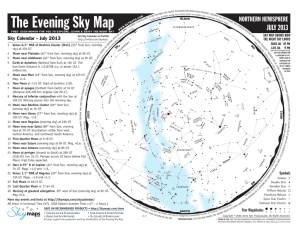
The Evening Sky Map
... Universal Time (UT) – A time system used by astronomers. Also known as Greenwich Mean Time. USA Eastern Standard Time (for example, New York) is 5 hours behind UT. Variable Star – A star that changes brightness over a period of time. ...
... Universal Time (UT) – A time system used by astronomers. Also known as Greenwich Mean Time. USA Eastern Standard Time (for example, New York) is 5 hours behind UT. Variable Star – A star that changes brightness over a period of time. ...
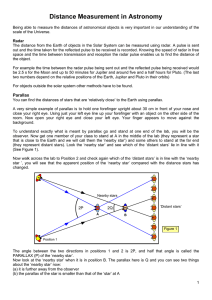
Distance Measurement in Astronomy
... be 2.5 s for the Moon and up to 50 minutes for Jupiter and around five and a half hours for Pluto. (The last two numbers depend on the relative positions of the Earth, Jupiter and Pluto in their orbits) For objects outside the solar system other methods have to be found. ...
... be 2.5 s for the Moon and up to 50 minutes for Jupiter and around five and a half hours for Pluto. (The last two numbers depend on the relative positions of the Earth, Jupiter and Pluto in their orbits) For objects outside the solar system other methods have to be found. ...
The Physical Properties of Normal A Stars
... I give the name, spectral type, Teff, log g, log Fe/H, log Si/log Sr, v sin i, and . My “model” was that stars rotating sufficiently fast have normal abundances all over their surfaces. When the rotation decreases below some critical value, the poles begin to show peculiar abundances. These regions ...
... I give the name, spectral type, Teff, log g, log Fe/H, log Si/log Sr, v sin i, and . My “model” was that stars rotating sufficiently fast have normal abundances all over their surfaces. When the rotation decreases below some critical value, the poles begin to show peculiar abundances. These regions ...
Andromeda: Daughter of Cassiopeia Ἀνδρομέδη Kaitlyn Heaton
... The Andromeda Galaxy. (Shown in figure 2) is the most distant object visible to the naked eye. You can find this famous galaxy on the right side of Andromeda, about half-way up the constellation. [2] It is a spiral galaxy approximately 2.5 million light years distant. In the past, it was also referr ...
... The Andromeda Galaxy. (Shown in figure 2) is the most distant object visible to the naked eye. You can find this famous galaxy on the right side of Andromeda, about half-way up the constellation. [2] It is a spiral galaxy approximately 2.5 million light years distant. In the past, it was also referr ...
PHYS_3380_082615_bw - The University of Texas at Dallas
... Brightness of stars specified with the magnitude system. Devised by Greek astronomer Hipparchus (~150 BC) devised - brightest stars into the first magnitude class, the next brightest stars into second magnitude class, until all of the visible stars grouped into six magnitude classes. The dimmest sta ...
... Brightness of stars specified with the magnitude system. Devised by Greek astronomer Hipparchus (~150 BC) devised - brightest stars into the first magnitude class, the next brightest stars into second magnitude class, until all of the visible stars grouped into six magnitude classes. The dimmest sta ...
Crux

Crux /ˈkrʌks/, located in the deep southern sky, is the smallest yet one of the most distinctive of the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for cross, and it is dominated by a cross-shaped asterism that is commonly known as the Southern Cross. Although visible to the Ancient Greeks, it was seen as part of the constellation Centaurus, and not defined or accurately mapped till the 16th century.Known as Acrux, blue-white Alpha Crucis is the constellation's brightest star and the bottom star of the cross. Nearly as bright are Beta and Gamma, while Delta and Epsilon make up the asterism. Many of the constellation's brighter stars are members of the Scorpius–Centaurus Association, a loose group of hot blue-white stars that appear to share a common origin and motion across the Milky Way. Two star systems have been found to have planets. The constellation also contains four Cepheid variables visible to the naked eye under optimum conditions. Crux also contains the Jewel Box, a bright open cluster, and the Coalsack Nebula, the most prominent dark nebula in the sky.