Constellation Catalog
... 1.) Cassiopeia has three stars with known planets and contains two Messier objects (objects similar yet not classified as comets) 2.) Cassiopeia is the 25th largest constellation in the night sky occupying 598 square degrees. 3.) The Perseids meteor shower is associated with Cassiopeia ...
... 1.) Cassiopeia has three stars with known planets and contains two Messier objects (objects similar yet not classified as comets) 2.) Cassiopeia is the 25th largest constellation in the night sky occupying 598 square degrees. 3.) The Perseids meteor shower is associated with Cassiopeia ...
AST4930 Star and Planet Formation
... enough that these objects are already on the main sequence as soon as the stellar system is non embedded. ...
... enough that these objects are already on the main sequence as soon as the stellar system is non embedded. ...
the printable Observing Olympics Object Info Sheet in pdf
... magnitude of 10.0v making it visible in almost any telescope. Its distance is about 80 million light years from the Earth. Large telescopes reveal the presence of nine separate knots threading the inner rim, which are gas clouds compressed by recent passages of shock waves. A companion galaxy, NGC58 ...
... magnitude of 10.0v making it visible in almost any telescope. Its distance is about 80 million light years from the Earth. Large telescopes reveal the presence of nine separate knots threading the inner rim, which are gas clouds compressed by recent passages of shock waves. A companion galaxy, NGC58 ...
constellation.
... (Your project should include: how many kilometers there are in 1 AU and 1 light year along with some interesting distances in space using these measurements, such as, distance from the Sun to Earth, from Earth to the next nearest star and at least 5 other interesting distances in the Universe) d. St ...
... (Your project should include: how many kilometers there are in 1 AU and 1 light year along with some interesting distances in space using these measurements, such as, distance from the Sun to Earth, from Earth to the next nearest star and at least 5 other interesting distances in the Universe) d. St ...
Lecture 10 Spectra of Stars and Binaries
... – A pair of stars bound by gravity. – Orbit each other about their center of mass. – Between 20% and 80% of all stars are binaries. ...
... – A pair of stars bound by gravity. – Orbit each other about their center of mass. – Between 20% and 80% of all stars are binaries. ...
Arcturus - bYTEBoss
... Story #2 Another version portrays Boötes as a grape grower called Icarius, who one day invited the Roman god Bacchus, also called Dionysus, to inspect his vineyards. Bacchus revealed the secret of wine making to Icarius, who was so impressed by this alcoholic beverage that he invited his friends rou ...
... Story #2 Another version portrays Boötes as a grape grower called Icarius, who one day invited the Roman god Bacchus, also called Dionysus, to inspect his vineyards. Bacchus revealed the secret of wine making to Icarius, who was so impressed by this alcoholic beverage that he invited his friends rou ...
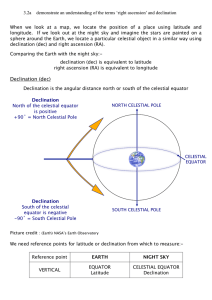
3.2a Right Ascension and Declination
... celestial equator moving North (the Vernal/Spring equinox). Two hours later, the stars will have drifted 30˚ across the night sky. The term Right Ascension (RA) in effect represents the hours (angular distance eastwards) from the reference point that a particular celestial object will be. As an exam ...
... celestial equator moving North (the Vernal/Spring equinox). Two hours later, the stars will have drifted 30˚ across the night sky. The term Right Ascension (RA) in effect represents the hours (angular distance eastwards) from the reference point that a particular celestial object will be. As an exam ...
26.4 Groups of Stars
... Riccioli used a telescope like this one to observe a star in the handle of the Big Dipper, he discovered two stars that orbit each other. ...
... Riccioli used a telescope like this one to observe a star in the handle of the Big Dipper, he discovered two stars that orbit each other. ...
Name:
... Start by resetting the H-R Explorer and then carefully examining the images. The H-R diagram is shown to the upper right. Note that is a graph showing luminosity versus temperature. Note, too, that the luminosity is in terms of solar luminosities (Lo). That is, if a star has a luminosity of 10Lo, it ...
... Start by resetting the H-R Explorer and then carefully examining the images. The H-R diagram is shown to the upper right. Note that is a graph showing luminosity versus temperature. Note, too, that the luminosity is in terms of solar luminosities (Lo). That is, if a star has a luminosity of 10Lo, it ...
ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS Letter to the Editor Low
... The resulting net CMD for cluster stars within r ≤ 3300 of NGC 3603 is shown at the right in Fig. 2. We overlayed the theoretical isochrones of pre-main sequence stars from Palla & Stahler (1999) down to 0.1M . We assumed a distance modulus of (m − M )o = 13.9 based on the distance of 6 kpc (De Pre ...
... The resulting net CMD for cluster stars within r ≤ 3300 of NGC 3603 is shown at the right in Fig. 2. We overlayed the theoretical isochrones of pre-main sequence stars from Palla & Stahler (1999) down to 0.1M . We assumed a distance modulus of (m − M )o = 13.9 based on the distance of 6 kpc (De Pre ...
3 - Celestial Sphere
... 1) There are imaginary points such as the North and South Celestial Poles (NCP. and SCP) and imaginary lines such as the Celestial Equator (CE) positioned on this sphere. Earth is located at the sphere’s center. Currently, the North Celestial Pole is very close to a star called Polaris. 2) The eclip ...
... 1) There are imaginary points such as the North and South Celestial Poles (NCP. and SCP) and imaginary lines such as the Celestial Equator (CE) positioned on this sphere. Earth is located at the sphere’s center. Currently, the North Celestial Pole is very close to a star called Polaris. 2) The eclip ...
Stars - gilbertmath.com
... A Star is Born The material falling inward to the _________ has excess ________________ that causes the central ball of material to begin to ________________. Extremely high _________________ build up inside the ball, which in turn causes tightly packed ___________ to heat up. As the __________ ...
... A Star is Born The material falling inward to the _________ has excess ________________ that causes the central ball of material to begin to ________________. Extremely high _________________ build up inside the ball, which in turn causes tightly packed ___________ to heat up. As the __________ ...
Color-Magnitude Diagram Lab Manual
... on a particular cluster, its CMD will be loaded onto the same graph used in the lab. For each of the following clusters, use the Zero-Age Main Sequence and Isochrones to determine the distance modulus and age of each cluster. (Note, if the clusters data does not load when selected, try opening the Z ...
... on a particular cluster, its CMD will be loaded onto the same graph used in the lab. For each of the following clusters, use the Zero-Age Main Sequence and Isochrones to determine the distance modulus and age of each cluster. (Note, if the clusters data does not load when selected, try opening the Z ...
LAB #3 - GEOCITIES.ws
... LAB. You will begin lab with a short quiz on these questions. What are Magnitudes? Because what we know about stars is due solely to our analysis of their light, it is very important to develop further the idea of stellar magnitude, or how bright a star is. When the Greeks scientist Hipparcos determ ...
... LAB. You will begin lab with a short quiz on these questions. What are Magnitudes? Because what we know about stars is due solely to our analysis of their light, it is very important to develop further the idea of stellar magnitude, or how bright a star is. When the Greeks scientist Hipparcos determ ...
celestial sphere
... star chart mounted in such a fashion that it can be oriented to represent the true aspect of the sky as seen by an observer at any point on the earth at any time. Since the surface is spherical, the distortion inherent in flat star maps is avoided. On the other hand, it forces you to view the conste ...
... star chart mounted in such a fashion that it can be oriented to represent the true aspect of the sky as seen by an observer at any point on the earth at any time. Since the surface is spherical, the distortion inherent in flat star maps is avoided. On the other hand, it forces you to view the conste ...
THE ORION CONSTELLATION the Great Hunter
... 2. Betelgeuse (Alpha Orionis) is the second brightest star in Orion and the eighth brightest star in the sky. It is a red supergiant, belonging to the spectral class M2lab. The star has an apparent visual magnitude of 0.42 and is approximately 643 light years distant. Betelgeuse is one of the most l ...
... 2. Betelgeuse (Alpha Orionis) is the second brightest star in Orion and the eighth brightest star in the sky. It is a red supergiant, belonging to the spectral class M2lab. The star has an apparent visual magnitude of 0.42 and is approximately 643 light years distant. Betelgeuse is one of the most l ...
Adult education at Scienceworks
... never sets meaning it is daytime continuously. During winter the Sun never rises and it is constantly night. ...
... never sets meaning it is daytime continuously. During winter the Sun never rises and it is constantly night. ...
Plotting Variable Stars on the H
... cycle of change that is periodic - as regular as the AAVSO Cepheid Light Curve (Delta Cephei) beating of a heart, with a period of 1 to 70 days with an amplitude variation of 0.1 to 2.0 magnitudes. These massive stars (~8 solar masses) have a high luminosity and are spectral class F at maximum, and ...
... cycle of change that is periodic - as regular as the AAVSO Cepheid Light Curve (Delta Cephei) beating of a heart, with a period of 1 to 70 days with an amplitude variation of 0.1 to 2.0 magnitudes. These massive stars (~8 solar masses) have a high luminosity and are spectral class F at maximum, and ...
doc - Pocket Stars
... are performed for proper motions and parallax. Planet ephemeris data from Jet Propulsion Laboratory using the DE405 database. DE405 is JPL’s latest planetary ephemeris with correction for both nutations and librations. DE405 uses the J2000 International Celestial Reference Frame (ICRF). The portion ...
... are performed for proper motions and parallax. Planet ephemeris data from Jet Propulsion Laboratory using the DE405 database. DE405 is JPL’s latest planetary ephemeris with correction for both nutations and librations. DE405 uses the J2000 International Celestial Reference Frame (ICRF). The portion ...
Stellarium Astronomy Software
... Raise or lower the planetarium until the stars are in sharp focus. 2. Rotate your planetarium so that N (North) on the compass lines up with the raised dot. This allows your planetarium to project the stars in the same directional orientation as they are in the real night sky outside. Your planetari ...
... Raise or lower the planetarium until the stars are in sharp focus. 2. Rotate your planetarium so that N (North) on the compass lines up with the raised dot. This allows your planetarium to project the stars in the same directional orientation as they are in the real night sky outside. Your planetari ...
ASTR3007/4007/6007, Class 1: Observing the Stars 23 February
... Although this is not the case for the Sun, in some stars there are strong emission lines as well as absorption lines. Emission lines are like absorption lines in reverse: they are upward spikes in the spectrum, where there is much more light at a given frequency than you would get from a blackbody. ...
... Although this is not the case for the Sun, in some stars there are strong emission lines as well as absorption lines. Emission lines are like absorption lines in reverse: they are upward spikes in the spectrum, where there is much more light at a given frequency than you would get from a blackbody. ...
Autumn Asterisms for binoculars 2013
... over half way down you’ll sweep through M38 – slow down now and look for the ...
... over half way down you’ll sweep through M38 – slow down now and look for the ...
star signs - Museum of the Rockies
... North Celestial Pole, -90° to the South Celestial Pole, and 0° to the Celestial Equator. RA is measured in hours, with each hour divided into 60 minutes, and there are 24 hours of RA corresponding to the 24 hours of the day. If you go outside at 10:00pm, choose a bright star near the horizon, and ma ...
... North Celestial Pole, -90° to the South Celestial Pole, and 0° to the Celestial Equator. RA is measured in hours, with each hour divided into 60 minutes, and there are 24 hours of RA corresponding to the 24 hours of the day. If you go outside at 10:00pm, choose a bright star near the horizon, and ma ...
The Earth and Man In the Universe
... It has often been suggested that the stars are infinite in number and that the universe is therefore infinite in extent. But the latest investigations, telescopic as well as photographic, show that the proportion of increase in the number of the stars diminishes when the. lowest magnitudes are reach ...
... It has often been suggested that the stars are infinite in number and that the universe is therefore infinite in extent. But the latest investigations, telescopic as well as photographic, show that the proportion of increase in the number of the stars diminishes when the. lowest magnitudes are reach ...
fred`s 2017 astronomy challenge
... astronomers. It is found just below the first star (Alkaid) in the handle of the saucepan shaped Plough. It is bright enough that the smallest binoculars will pick it up as a blurry fuzz ...
... astronomers. It is found just below the first star (Alkaid) in the handle of the saucepan shaped Plough. It is bright enough that the smallest binoculars will pick it up as a blurry fuzz ...
Crux

Crux /ˈkrʌks/, located in the deep southern sky, is the smallest yet one of the most distinctive of the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for cross, and it is dominated by a cross-shaped asterism that is commonly known as the Southern Cross. Although visible to the Ancient Greeks, it was seen as part of the constellation Centaurus, and not defined or accurately mapped till the 16th century.Known as Acrux, blue-white Alpha Crucis is the constellation's brightest star and the bottom star of the cross. Nearly as bright are Beta and Gamma, while Delta and Epsilon make up the asterism. Many of the constellation's brighter stars are members of the Scorpius–Centaurus Association, a loose group of hot blue-white stars that appear to share a common origin and motion across the Milky Way. Two star systems have been found to have planets. The constellation also contains four Cepheid variables visible to the naked eye under optimum conditions. Crux also contains the Jewel Box, a bright open cluster, and the Coalsack Nebula, the most prominent dark nebula in the sky.