Study Guide
... Period: ___________________ Date: ___________________ What is a Black Hole and how do Black Holes form? ...
... Period: ___________________ Date: ___________________ What is a Black Hole and how do Black Holes form? ...
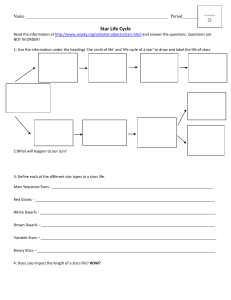
Star Life Cycle Web Quest
... 10: Our solar system formed from a ____________________________________________________generation nebula. 11. What two pieces of information classify stars? ...
... 10: Our solar system formed from a ____________________________________________________generation nebula. 11. What two pieces of information classify stars? ...
Constellation Information
... with the naked eye as a dim, fuzzy patch if you have a clear, moonless evening at an observing site far from light pollution. M44 is also known as the Beehive Cluster, because in binoculars or a low-power, wide-field telescope, it looks like an old-fashion done-shaped beehive with many extra bees ...
... with the naked eye as a dim, fuzzy patch if you have a clear, moonless evening at an observing site far from light pollution. M44 is also known as the Beehive Cluster, because in binoculars or a low-power, wide-field telescope, it looks like an old-fashion done-shaped beehive with many extra bees ...
What is the Zodiac? The Zodiac is defined by 12 constellations
... The 1st decan in the constellation of Virgo is Crux, the Southern Cross. ...
... The 1st decan in the constellation of Virgo is Crux, the Southern Cross. ...
The Evening Sky in February 2016
... tight bunch of fainter stars making the Pleiades/Matariki star cluster. In the late evening, at the beginning of the month, Jupiter rises due east. It is brighter than any of the stars and shines with a steady golden light. Later on Jupiter is already up at dusk, appearing in the eastern sky soon af ...
... tight bunch of fainter stars making the Pleiades/Matariki star cluster. In the late evening, at the beginning of the month, Jupiter rises due east. It is brighter than any of the stars and shines with a steady golden light. Later on Jupiter is already up at dusk, appearing in the eastern sky soon af ...
Slide 1 - Fort Bend ISD
... standard distance from the Earth • Scientists study globular clusters to compare brightness of stars • All about same distance from Earth ...
... standard distance from the Earth • Scientists study globular clusters to compare brightness of stars • All about same distance from Earth ...
3.5-star-id
... stars, Deneb, Vega, and Altair in the constellations Cygnus, Lyra, and Aquila. • Slicing through this triangle is the asterism, the Northern Cross, actually part of Cygnus the Swan. • Tonight you will find the summer triangle above the eastern sky and you’ll see it all through the summer as it rises ...
... stars, Deneb, Vega, and Altair in the constellations Cygnus, Lyra, and Aquila. • Slicing through this triangle is the asterism, the Northern Cross, actually part of Cygnus the Swan. • Tonight you will find the summer triangle above the eastern sky and you’ll see it all through the summer as it rises ...
Characteristics of Stars
... amount of light given off by a star • Apparent magnitude – a measure of the amount of light received on Earth (a dim star can appear bright if its close to Earth; a bright star can appear dim if its far away) ...
... amount of light given off by a star • Apparent magnitude – a measure of the amount of light received on Earth (a dim star can appear bright if its close to Earth; a bright star can appear dim if its far away) ...
October 2013
... and is typical of areas where new stars can form. Between the Scorpion and the Centaur are the Altar, the Level and the Wolf, while to the east of the Milky Way stretches a great expanse of sky with relatively few bright stars, dominated by birds and 'water constellations'. In the south these includ ...
... and is typical of areas where new stars can form. Between the Scorpion and the Centaur are the Altar, the Level and the Wolf, while to the east of the Milky Way stretches a great expanse of sky with relatively few bright stars, dominated by birds and 'water constellations'. In the south these includ ...
Chapter 27 Review Guide// ESS
... 3. How do astronomers determine a star’s composition and temperature? 4. What are the two types of stellar motion? a. What causes the stars to “move” westward across the night sky? b. Why do we see different stars at different times of the year? ...
... 3. How do astronomers determine a star’s composition and temperature? 4. What are the two types of stellar motion? a. What causes the stars to “move” westward across the night sky? b. Why do we see different stars at different times of the year? ...
Spring Constellations
... Libra, the balance of justice, associated with Themis. Very faint, no bright stars. Zuben Elgenubi (southern claw) and Zuben Eschamali (northern claw). σ-Libris (lower right star) is the only greenish naked-eye star visible. ...
... Libra, the balance of justice, associated with Themis. Very faint, no bright stars. Zuben Elgenubi (southern claw) and Zuben Eschamali (northern claw). σ-Libris (lower right star) is the only greenish naked-eye star visible. ...
“Do you have a good caption for the pop-eyed, thin
... Centauri, famous for being the closest visible star, 4.3 light years away. The light left that star 4.3 years ago. At 186 thousand miles per second, the light traveled over 25 trillion miles from Alpha Centauri to reach Earth. Alpha Centauri means this star is the brightest star in the constellation ...
... Centauri, famous for being the closest visible star, 4.3 light years away. The light left that star 4.3 years ago. At 186 thousand miles per second, the light traveled over 25 trillion miles from Alpha Centauri to reach Earth. Alpha Centauri means this star is the brightest star in the constellation ...
The Milky Way
... • What causes the seasons? • How can astronomical cycles affect Earth’s climate? As you study the sky and its motions, you will be learning to think of Earth as a planet rotating on its axis. The next chapter will introduce you to some of the most dramatic cycles in the sky. ...
... • What causes the seasons? • How can astronomical cycles affect Earth’s climate? As you study the sky and its motions, you will be learning to think of Earth as a planet rotating on its axis. The next chapter will introduce you to some of the most dramatic cycles in the sky. ...
Characteristics of Stars
... • 6000 stars are observable to unaided eye • 3 billion stars can be seen with ground based telescopes ...
... • 6000 stars are observable to unaided eye • 3 billion stars can be seen with ground based telescopes ...
The distance that light travels in a year is 9.5 trillion km. The
... Space Quiz Review – Go to 2-103 Tomorrow SC.8.E.5.1 SC.8.E.5.2 SC.8.E.5.3 SC.8.E.5.4 SC.8.E.5.5 ...
... Space Quiz Review – Go to 2-103 Tomorrow SC.8.E.5.1 SC.8.E.5.2 SC.8.E.5.3 SC.8.E.5.4 SC.8.E.5.5 ...
Scale of Apparent Magnitudes of Celestial Objects
... The creator of the system for measuring the apparent brightness of stars is believed to be Hipparchus, who lived in Nicaea (Turkey) during the second century BCE. Hipparchus is believed by many to be the greatest of the ancient astronomers. The original scale of apparent magnitude gave the brightest ...
... The creator of the system for measuring the apparent brightness of stars is believed to be Hipparchus, who lived in Nicaea (Turkey) during the second century BCE. Hipparchus is believed by many to be the greatest of the ancient astronomers. The original scale of apparent magnitude gave the brightest ...
Diapositiva 1
... Ursa Minor is a constellation of the northern sky. It is especially known because within it lies the north celestial pole, although its position is subject to a continuous, slow movement due to the precession of the Earth's rotation. The Little Dipper is easily identifiable because, once detected th ...
... Ursa Minor is a constellation of the northern sky. It is especially known because within it lies the north celestial pole, although its position is subject to a continuous, slow movement due to the precession of the Earth's rotation. The Little Dipper is easily identifiable because, once detected th ...
Sagittarius - columbusastronomy
... Constellation: Carina 2nd brightest star in the night sky Magnitude: -0.72 Type: supergiant, spectral type F Color: white to the naked eye Temperature: 7,350 K Distance: 310 light years RA: 6h 24m ...
... Constellation: Carina 2nd brightest star in the night sky Magnitude: -0.72 Type: supergiant, spectral type F Color: white to the naked eye Temperature: 7,350 K Distance: 310 light years RA: 6h 24m ...
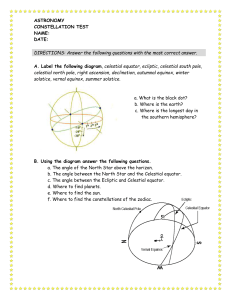
ASTRONOMY
... 2. Which stars in Ursa Major point to Polaris? 3. How can one find the constellation Cassiopeia? 4. To what constellation do Castor and Pollux belong? 5. Where was the first planet outside our solar system found? 6. In what constellation did the spring equinox occur 2000 years ago? 7. How is the Ein ...
... 2. Which stars in Ursa Major point to Polaris? 3. How can one find the constellation Cassiopeia? 4. To what constellation do Castor and Pollux belong? 5. Where was the first planet outside our solar system found? 6. In what constellation did the spring equinox occur 2000 years ago? 7. How is the Ein ...
Crux

Crux /ˈkrʌks/, located in the deep southern sky, is the smallest yet one of the most distinctive of the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for cross, and it is dominated by a cross-shaped asterism that is commonly known as the Southern Cross. Although visible to the Ancient Greeks, it was seen as part of the constellation Centaurus, and not defined or accurately mapped till the 16th century.Known as Acrux, blue-white Alpha Crucis is the constellation's brightest star and the bottom star of the cross. Nearly as bright are Beta and Gamma, while Delta and Epsilon make up the asterism. Many of the constellation's brighter stars are members of the Scorpius–Centaurus Association, a loose group of hot blue-white stars that appear to share a common origin and motion across the Milky Way. Two star systems have been found to have planets. The constellation also contains four Cepheid variables visible to the naked eye under optimum conditions. Crux also contains the Jewel Box, a bright open cluster, and the Coalsack Nebula, the most prominent dark nebula in the sky.