LEO - nina`s Senior project
... of a giant star with the spectral classification K1-IIIbCN0.5 and a dimmer companion star which belongs to the spectral class G7IIICN-I. The brighter giant is 180 times more luminous than the Sun and has an apparent visual magnitude of 2.28. The G7 class star has a visual magnitude of 3.51, is 50 ti ...
... of a giant star with the spectral classification K1-IIIbCN0.5 and a dimmer companion star which belongs to the spectral class G7IIICN-I. The brighter giant is 180 times more luminous than the Sun and has an apparent visual magnitude of 2.28. The G7 class star has a visual magnitude of 3.51, is 50 ti ...
The Celestial Sphere - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... However some stars show small motions, these are due again to the motion of the Earth. An object that moves 1 second of arc in the sky (1/3600 of a degree) as the Earth moves 1 AU in its orbit in 1 ...
... However some stars show small motions, these are due again to the motion of the Earth. An object that moves 1 second of arc in the sky (1/3600 of a degree) as the Earth moves 1 AU in its orbit in 1 ...
SSG Coordinators will be at the Cronan Ranch observing site at 6
... Messier 37 is our third open cluster, and this is my personal favorite. To find it, jump across that imaginary line between Beta and Theta Aurigae to a spot about midway along the line but just outside the pentagon. There you will encounter a much more compressed cluster about 4400 light years away. ...
... Messier 37 is our third open cluster, and this is my personal favorite. To find it, jump across that imaginary line between Beta and Theta Aurigae to a spot about midway along the line but just outside the pentagon. There you will encounter a much more compressed cluster about 4400 light years away. ...
Highlights of the Month - Bridgend Astronomical Society
... observation in a small telescope as Mizar is then shown to be an easily resolved double star. A fainter reddish star forms a triangle with Alcor and Mizar. Ursa Major contains many interesting "deep sky" objects. The brightest, listed in Messier's Catalogue, are shown on the chart, but there are man ...
... observation in a small telescope as Mizar is then shown to be an easily resolved double star. A fainter reddish star forms a triangle with Alcor and Mizar. Ursa Major contains many interesting "deep sky" objects. The brightest, listed in Messier's Catalogue, are shown on the chart, but there are man ...
Northern and Southern Hemisphere Star Chart
... the Sun, actually small and dim M type stars called red dwarfs (stars physically smaller than our Sun are classed as dwarf stars) seem to be the most common stars in space, at least in our part of the Milky Way galaxy. Of the 100 closest stars to the Sun, 80 are M-type red dwarf stars, too dim be se ...
... the Sun, actually small and dim M type stars called red dwarfs (stars physically smaller than our Sun are classed as dwarf stars) seem to be the most common stars in space, at least in our part of the Milky Way galaxy. Of the 100 closest stars to the Sun, 80 are M-type red dwarf stars, too dim be se ...
Morning Announcements
... The reason is that there is a connection between temperature and total energy output, which is described by the Stefan-Boltzmann law. There are two important aspects to remember: • The total amount of light energy that a star emits — called the luminosity (L), and measured by the absolute magnitude ...
... The reason is that there is a connection between temperature and total energy output, which is described by the Stefan-Boltzmann law. There are two important aspects to remember: • The total amount of light energy that a star emits — called the luminosity (L), and measured by the absolute magnitude ...
If you wish to a copy of this months Night Sky News
... Mercury is not well placed low in the east at sunrise, and is best observed in the first days of the month. As it closes in on the Sun over the next month, it will become impossible to observe. Venus is catching up with us on its orbit inside the Earth’s orbit, so its angular size is increasing. How ...
... Mercury is not well placed low in the east at sunrise, and is best observed in the first days of the month. As it closes in on the Sun over the next month, it will become impossible to observe. Venus is catching up with us on its orbit inside the Earth’s orbit, so its angular size is increasing. How ...
Interpreting the HR diagram of stellar clusters
... In fact, it seems that stars are usually born in big groups, as members of a cluster of stars. All the stars in the cluster form at about the same time. So, if we look at a cluster, we see a bunch of stars which are all roughly the same age. However, the stars do not all have the same mass: most ten ...
... In fact, it seems that stars are usually born in big groups, as members of a cluster of stars. All the stars in the cluster form at about the same time. So, if we look at a cluster, we see a bunch of stars which are all roughly the same age. However, the stars do not all have the same mass: most ten ...
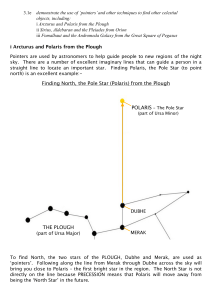
3.1e Finding Polaris and Sirius
... have very dark skies, the Andromeda Galaxy is the furthest object that you can see with your naked eye – 2.4 million light years away! The galaxy appears as a small, white, fuzzy patch. When you have found the Great Square of Pegasus, you need to find the top left hand star of the square (the star d ...
... have very dark skies, the Andromeda Galaxy is the furthest object that you can see with your naked eye – 2.4 million light years away! The galaxy appears as a small, white, fuzzy patch. When you have found the Great Square of Pegasus, you need to find the top left hand star of the square (the star d ...
Daynightseasonsstars-1
... night sky as Earth travels around our Sun throughout the year? 3. Are the constellations themselves moving? 4. What causes this apparent change in positions? ...
... night sky as Earth travels around our Sun throughout the year? 3. Are the constellations themselves moving? 4. What causes this apparent change in positions? ...
Stars and Constellations
... how stars evolve. Lead students to understand the difference between apparent magnitude and absolute magnitude. Showing a flashlight at varying distances is a concrete means of demonstrating the difference. 2) Have students construct simple astrolabes using drinking straws, washers, string and protr ...
... how stars evolve. Lead students to understand the difference between apparent magnitude and absolute magnitude. Showing a flashlight at varying distances is a concrete means of demonstrating the difference. 2) Have students construct simple astrolabes using drinking straws, washers, string and protr ...
PPTX
... During the day, the Sun moves from east to west across the sky. In which direction do the stars move after the Sun has set? (A) The stars are stationary; they don't move (B) West (C) East ...
... During the day, the Sun moves from east to west across the sky. In which direction do the stars move after the Sun has set? (A) The stars are stationary; they don't move (B) West (C) East ...
STUDY GUIDE:
... system explode in the course of a day. Temporarily, this can make their system 300,000 times brighter than the sun. This brightness lasts for a few days or weeks, and then lessens gradually, leaving the stars about the same as they were before. In 1992, Nova Cygni, in the northern constellation Cygn ...
... system explode in the course of a day. Temporarily, this can make their system 300,000 times brighter than the sun. This brightness lasts for a few days or weeks, and then lessens gradually, leaving the stars about the same as they were before. In 1992, Nova Cygni, in the northern constellation Cygn ...
Chapter 10 Measuring the Stars: Giants, Dwarfs, and the Main
... Stellar Motion * Stars have transverse and radial motion • Transverse - perpendicular to line of sight • Radial - along our line of sight * ___________________ - annual movement of a star across the sky as seen from Earth • _____________________ has the largest known proper motion of any star – 10.3 ...
... Stellar Motion * Stars have transverse and radial motion • Transverse - perpendicular to line of sight • Radial - along our line of sight * ___________________ - annual movement of a star across the sky as seen from Earth • _____________________ has the largest known proper motion of any star – 10.3 ...
te acher`s guide te acher`s guide
... • Ask students to explain in 200 wo rds or fewer what a bl a ck hole is and to s h a re their essays with the cl a s s . Demonstrate the effects of a bl a ck hole with a latex balloon, a coffee cup, a one-inch steel ball bearing and some small round beads. Cut the balloon into a flat sheet and tape ...
... • Ask students to explain in 200 wo rds or fewer what a bl a ck hole is and to s h a re their essays with the cl a s s . Demonstrate the effects of a bl a ck hole with a latex balloon, a coffee cup, a one-inch steel ball bearing and some small round beads. Cut the balloon into a flat sheet and tape ...
ref H-R Spectral types
... Sirius A is a type A star, but it has a dwarf companion (Sirius B) which is a type O but is too small to see here. Other examples include Meissa, or Orionis lambda in the constellation Orion (actually, in Orion’s helmet!). ...
... Sirius A is a type A star, but it has a dwarf companion (Sirius B) which is a type O but is too small to see here. Other examples include Meissa, or Orionis lambda in the constellation Orion (actually, in Orion’s helmet!). ...
observingnebulaeclusters-1
... above the critical limit required for stars to form within the nebula. Visible to the naked eye as the middle "star" in the "sword" of the constellation Orion, the nebula is located 1500 light years from Earth. A closer image taken with the Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 aboard the Hubble Space Teles ...
... above the critical limit required for stars to form within the nebula. Visible to the naked eye as the middle "star" in the "sword" of the constellation Orion, the nebula is located 1500 light years from Earth. A closer image taken with the Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 aboard the Hubble Space Teles ...
09astrophysics_2007Nov
... Formula: Distance (pc)=1/parallax Limiting Optical resolution of telescope (due to wave nature of light) limits smallest parallax we can measure ...
... Formula: Distance (pc)=1/parallax Limiting Optical resolution of telescope (due to wave nature of light) limits smallest parallax we can measure ...
An introduction to the HR diagram File
... essentially the central cores of what were main sequence stars like the Sun ...
... essentially the central cores of what were main sequence stars like the Sun ...
Star names and magnitudes
... By grouping stars into constellations, our ancestors developed the first system for unambiguously identifying celestial sources. Now, we use co-ordinate systems based on angular distance scales. Astronomical co-ordinates ...
... By grouping stars into constellations, our ancestors developed the first system for unambiguously identifying celestial sources. Now, we use co-ordinate systems based on angular distance scales. Astronomical co-ordinates ...
Chapter 02
... pole follows a circular pattern on the sky, once every 26,000 years. We are lucky to live at a time when a fairly bright star (Polaris, magnitude 2) is near the north celestial pole. It will be closest to Polaris ~ A.D. 2100. ...
... pole follows a circular pattern on the sky, once every 26,000 years. We are lucky to live at a time when a fairly bright star (Polaris, magnitude 2) is near the north celestial pole. It will be closest to Polaris ~ A.D. 2100. ...
Properties of Stars - Mr. Carter`s Earth
... The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their absolute magnitude, which is how bright they would appear to be if they were all the same distance away. Rather than speak of the brightness of ...
... The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their absolute magnitude, which is how bright they would appear to be if they were all the same distance away. Rather than speak of the brightness of ...
The Night Sky September 2016 - Bridgend Astronomical Society
... In the hours before dawn, November gives us a chance to observe meteors from two showers. The first that it is thought might produce some bright events is the Northern Taurids shower which has a broad peak of around 10 days but normally gives relatively few meteors per hour. The peak is around the 1 ...
... In the hours before dawn, November gives us a chance to observe meteors from two showers. The first that it is thought might produce some bright events is the Northern Taurids shower which has a broad peak of around 10 days but normally gives relatively few meteors per hour. The peak is around the 1 ...
Star Powerpoint notes
... The intensity of light emitted by three hypothetical stars is plotted against wavelength. The range of visible wavelengths is indicated. Where the peak of a star’s intensity curve lies relative to the visible light band determines the apparent color of its visible light. ...
... The intensity of light emitted by three hypothetical stars is plotted against wavelength. The range of visible wavelengths is indicated. Where the peak of a star’s intensity curve lies relative to the visible light band determines the apparent color of its visible light. ...
May 2017 - What`s Out Tonight?
... Globular Clusters look like fuzzy balls because they contain all night and always outshines any star. Everyone enjoys its 4 tens of thousands stars held together by their mutual gravity. All Galilean moons and cloud bands, easily visible at 50x. It is posof the globulars that can be seen in the sky ...
... Globular Clusters look like fuzzy balls because they contain all night and always outshines any star. Everyone enjoys its 4 tens of thousands stars held together by their mutual gravity. All Galilean moons and cloud bands, easily visible at 50x. It is posof the globulars that can be seen in the sky ...
Crux

Crux /ˈkrʌks/, located in the deep southern sky, is the smallest yet one of the most distinctive of the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for cross, and it is dominated by a cross-shaped asterism that is commonly known as the Southern Cross. Although visible to the Ancient Greeks, it was seen as part of the constellation Centaurus, and not defined or accurately mapped till the 16th century.Known as Acrux, blue-white Alpha Crucis is the constellation's brightest star and the bottom star of the cross. Nearly as bright are Beta and Gamma, while Delta and Epsilon make up the asterism. Many of the constellation's brighter stars are members of the Scorpius–Centaurus Association, a loose group of hot blue-white stars that appear to share a common origin and motion across the Milky Way. Two star systems have been found to have planets. The constellation also contains four Cepheid variables visible to the naked eye under optimum conditions. Crux also contains the Jewel Box, a bright open cluster, and the Coalsack Nebula, the most prominent dark nebula in the sky.