Introduction - Willmann-Bell
... “Great Eruption” in the 1840s. Of course, there are numerous other objects to explore in Carina, not the least of which is the Carina Nebula (NGC 3372), which lies just east of the dark, hourglass-shaped Keyhole Nebula; NGC 2516, also known as the Southern Beehive; the planetary NGC 2867 with its ho ...
... “Great Eruption” in the 1840s. Of course, there are numerous other objects to explore in Carina, not the least of which is the Carina Nebula (NGC 3372), which lies just east of the dark, hourglass-shaped Keyhole Nebula; NGC 2516, also known as the Southern Beehive; the planetary NGC 2867 with its ho ...
Document
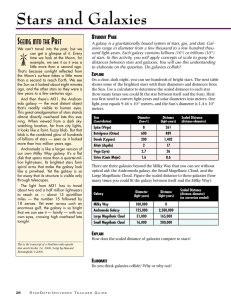
... than the Sun. b. The star is at the lower end of the main sequence. c. The star is at the upper end of the main sequence. d. The star must have a much larger surface area than the Sun. ...
... than the Sun. b. The star is at the lower end of the main sequence. c. The star is at the upper end of the main sequence. d. The star must have a much larger surface area than the Sun. ...
It is evident from our observations of impact craters on planets and
... surface temperature and conditions in the stellar atmosphere. Astronomers have based a classification system for stars based on the spectrum. Spectroscopic parallax using the distance modulus can be used to determine distances to stars too distant for heliocentric parallax measurements. At the teles ...
... surface temperature and conditions in the stellar atmosphere. Astronomers have based a classification system for stars based on the spectrum. Spectroscopic parallax using the distance modulus can be used to determine distances to stars too distant for heliocentric parallax measurements. At the teles ...
Stars
... the Big Dipper. It was the first binary star system to be imaged with a telescope. Spectroscopic observations show periodic Doppler shifts in the spectra of Mizar A and B, indicating that they are each binary stars. But they were too close to be directly imaged - until 2 May 1996, when the NPOI prod ...
... the Big Dipper. It was the first binary star system to be imaged with a telescope. Spectroscopic observations show periodic Doppler shifts in the spectra of Mizar A and B, indicating that they are each binary stars. But they were too close to be directly imaged - until 2 May 1996, when the NPOI prod ...
C H A P T E R 2
... that appear within the circumpolar zone also changes. If on the ancient charts, Thuban is listed as "nearest the pole", then at the latitude of approximately 30° N, Polaris would have been circumpolar, but would have been very near the horizon at its lowest point. Additionally, all of the Big Dipper ...
... that appear within the circumpolar zone also changes. If on the ancient charts, Thuban is listed as "nearest the pole", then at the latitude of approximately 30° N, Polaris would have been circumpolar, but would have been very near the horizon at its lowest point. Additionally, all of the Big Dipper ...
FREE Sample Here
... that appear within the circumpolar zone also changes. If on the ancient charts, Thuban is listed as "nearest the pole", then at the latitude of approximately 30° N, Polaris would have been circumpolar, but would have been very near the horizon at its lowest point. Additionally, all of the Big Dipper ...
... that appear within the circumpolar zone also changes. If on the ancient charts, Thuban is listed as "nearest the pole", then at the latitude of approximately 30° N, Polaris would have been circumpolar, but would have been very near the horizon at its lowest point. Additionally, all of the Big Dipper ...
Slide 1
... M13 Globular Cluster We calculated the age to be between 12 to 14 billion years old It is 25,000 light years away from Earth ...
... M13 Globular Cluster We calculated the age to be between 12 to 14 billion years old It is 25,000 light years away from Earth ...
The Stars
... the main sequence. • Generally, the hotter the star, the more luminous it will be. • The main sequence is not a straight line but a band. ...
... the main sequence. • Generally, the hotter the star, the more luminous it will be. • The main sequence is not a straight line but a band. ...
Constellation Chart Activity
... 10. On October 6th, what constellation will cross your meridian at approximately -20o Dec. at 8 pm? __________________________________ ...
... 10. On October 6th, what constellation will cross your meridian at approximately -20o Dec. at 8 pm? __________________________________ ...
Introduction to Basic Stargazing Part I - Naples Free-Net
... For many years the summer star Vega was the reference star and was assigned a magnitude of 0.0 as a starting point. Now that everything has been reduced to mathematical ratios one can now say Pollux has a magnitude of +1.15 while the dimmer Castor has been assigned a magnitude of +1.9 There is no ma ...
... For many years the summer star Vega was the reference star and was assigned a magnitude of 0.0 as a starting point. Now that everything has been reduced to mathematical ratios one can now say Pollux has a magnitude of +1.15 while the dimmer Castor has been assigned a magnitude of +1.9 There is no ma ...
Stars Study Guide KEY
... Why? They have less self-gravity which means they burn through their fuel slower. 8. What will happen to our star, the Sun, at the end of its life? The sun will expand in the Red Giant phase, then will release its outer layers to form a planetary nebula. It will become a white dwarf and then over ti ...
... Why? They have less self-gravity which means they burn through their fuel slower. 8. What will happen to our star, the Sun, at the end of its life? The sun will expand in the Red Giant phase, then will release its outer layers to form a planetary nebula. It will become a white dwarf and then over ti ...
Star Constellations
... http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (placed in a visible location) in addition to the following terms. Except as otherwise noted, all CK-12 Content (including CK-12 Curriculum Material) is made available to Users in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial 3.0 ...
... http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (placed in a visible location) in addition to the following terms. Except as otherwise noted, all CK-12 Content (including CK-12 Curriculum Material) is made available to Users in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial 3.0 ...
Stars and Galaxies
... And then there’s M31, the Andromeda galaxy — the most distant object that’s readily visible to human eyes. This great amalgamation of stars stands almost directly overhead late this evening. When viewed from a dark skywatching location, far from city lights, it looks like a faint, fuzzy blob. But th ...
... And then there’s M31, the Andromeda galaxy — the most distant object that’s readily visible to human eyes. This great amalgamation of stars stands almost directly overhead late this evening. When viewed from a dark skywatching location, far from city lights, it looks like a faint, fuzzy blob. But th ...
Astronomy Assignment #1
... 6. How does the Sun move with respect to the stars during the day? ...during the year? 7. Why does everyone have 12 hours of daylight on the equinoxes? 8. Why is the length of daylight in the northern hemisphere so short on December 21? 9. When will the Sun be at its highest altitude in the year in ...
... 6. How does the Sun move with respect to the stars during the day? ...during the year? 7. Why does everyone have 12 hours of daylight on the equinoxes? 8. Why is the length of daylight in the northern hemisphere so short on December 21? 9. When will the Sun be at its highest altitude in the year in ...
The Milky Way - Computer Science Technology
... The Sun’s apparent path on the sky is called the Ecliptic. Equivalent: The Ecliptic is the projection of Earth’s orbit onto the celestial sphere. ...
... The Sun’s apparent path on the sky is called the Ecliptic. Equivalent: The Ecliptic is the projection of Earth’s orbit onto the celestial sphere. ...
Chapter 2 User`s Guide to the Sky
... The Sun’s apparent path on the sky is called the Ecliptic. Equivalent: The Ecliptic is the projection of Earth’s orbit onto the celestial sphere. ...
... The Sun’s apparent path on the sky is called the Ecliptic. Equivalent: The Ecliptic is the projection of Earth’s orbit onto the celestial sphere. ...
Monday, October 27
... star, cf. 100 W lightbulb • Apparent brightness B is how bright it appears from Earth – Determined by the amount of light per unit area reaching Earth – B L / d2 ...
... star, cf. 100 W lightbulb • Apparent brightness B is how bright it appears from Earth – Determined by the amount of light per unit area reaching Earth – B L / d2 ...
File - greenscapes4you
... Width of fist ~ 10 degrees Finger width ~ 1 degree 60 arcminutes per degree; 60 arc-seconds per arc-minute ...
... Width of fist ~ 10 degrees Finger width ~ 1 degree 60 arcminutes per degree; 60 arc-seconds per arc-minute ...
Planisphere Exercise
... progresses? Do these directions ever change? Turn the star wheel to find out. ...
... progresses? Do these directions ever change? Turn the star wheel to find out. ...
printer-friendly sample test questions
... to other stars. Depth of Knowledge Level 1 1. When observed from Earth on a clear night, the Milky Way Galaxy appears as a A. circular pattern of stars. B. elliptical pattern of stars. C. glowing band of light. D. random spotting of light. 2. How many times greater is Sun’s diameter than Earth’s dia ...
... to other stars. Depth of Knowledge Level 1 1. When observed from Earth on a clear night, the Milky Way Galaxy appears as a A. circular pattern of stars. B. elliptical pattern of stars. C. glowing band of light. D. random spotting of light. 2. How many times greater is Sun’s diameter than Earth’s dia ...
Tour the sky`s reddest stars
... The standard spectral classes assign letters to stars based on their temperatures. From hottest to coolest, the letters run O, B, A, F, G, K, and M. Since that system debuted, however, astronomers have classified even cooler stars. And the coolest of all are carbon stars, designated C. Carbon stars ...
... The standard spectral classes assign letters to stars based on their temperatures. From hottest to coolest, the letters run O, B, A, F, G, K, and M. Since that system debuted, however, astronomers have classified even cooler stars. And the coolest of all are carbon stars, designated C. Carbon stars ...
$doc.title
... Use Star Walk or your team’s own naked-‐eye observations to check the accuracy of your finding chart. If your chart does not correctly show the position of the planet, explain what went wrong: ...
... Use Star Walk or your team’s own naked-‐eye observations to check the accuracy of your finding chart. If your chart does not correctly show the position of the planet, explain what went wrong: ...
Crux

Crux /ˈkrʌks/, located in the deep southern sky, is the smallest yet one of the most distinctive of the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for cross, and it is dominated by a cross-shaped asterism that is commonly known as the Southern Cross. Although visible to the Ancient Greeks, it was seen as part of the constellation Centaurus, and not defined or accurately mapped till the 16th century.Known as Acrux, blue-white Alpha Crucis is the constellation's brightest star and the bottom star of the cross. Nearly as bright are Beta and Gamma, while Delta and Epsilon make up the asterism. Many of the constellation's brighter stars are members of the Scorpius–Centaurus Association, a loose group of hot blue-white stars that appear to share a common origin and motion across the Milky Way. Two star systems have been found to have planets. The constellation also contains four Cepheid variables visible to the naked eye under optimum conditions. Crux also contains the Jewel Box, a bright open cluster, and the Coalsack Nebula, the most prominent dark nebula in the sky.