Binocular Universe: Summer`s Swan Song
... but he did spot a small clump of starlight a little less than 2° south-southeast of Sadr. Noting its position, he added it as the 29th entry in his famous catalog. Though not one of Messier’s best, M29 is visible through small, hand-supported binoculars as a tiny, rectangular patch of light, with pe ...
... but he did spot a small clump of starlight a little less than 2° south-southeast of Sadr. Noting its position, he added it as the 29th entry in his famous catalog. Though not one of Messier’s best, M29 is visible through small, hand-supported binoculars as a tiny, rectangular patch of light, with pe ...
ILÍDIO LOPES ()
... quality of the data provided by the space missions Kepler and CoRoT (NASA/ESA), are now available in unprecedented numbers, predicting very interesting times for stellar physics. In a nearby future, the missions TESS and PLATO (NASA/ESA) will improve, even more, the quantity and quality of the obser ...
... quality of the data provided by the space missions Kepler and CoRoT (NASA/ESA), are now available in unprecedented numbers, predicting very interesting times for stellar physics. In a nearby future, the missions TESS and PLATO (NASA/ESA) will improve, even more, the quantity and quality of the obser ...
Chapter 10 Hertzsprung-Russel Diagrams and Distance to Stars
... Discovering whether this was true presented some obvious challenges. Since the distances to the stars were unknown, one could not determine the intrinsic brightness of a star, but only its apparent brightness. As we’ve already said, a bright star that’s very far away would appear much fainter than ...
... Discovering whether this was true presented some obvious challenges. Since the distances to the stars were unknown, one could not determine the intrinsic brightness of a star, but only its apparent brightness. As we’ve already said, a bright star that’s very far away would appear much fainter than ...
There are 88 constellations in the sky around the Earth. 12 are the
... Principal stars are: Altarf (Beta Cancri), magnitude 3.5; Asellus Australis (Delta Cancri), magnitude 3.9; Iota Cancri, magnitude 4.0; Acubens (Alpha Cancri), magnitude 4.2; Asellus Borealis (Gamma Cancri), magnitude 4.7 Noteable doubles are: Zeta Cancri, magnitudes 5.6 & 6.0 (A binary with separati ...
... Principal stars are: Altarf (Beta Cancri), magnitude 3.5; Asellus Australis (Delta Cancri), magnitude 3.9; Iota Cancri, magnitude 4.0; Acubens (Alpha Cancri), magnitude 4.2; Asellus Borealis (Gamma Cancri), magnitude 4.7 Noteable doubles are: Zeta Cancri, magnitudes 5.6 & 6.0 (A binary with separati ...
Characteristics of Stars
... thus incredibly dense. Just a sugar cube of neutron star matter would weigh about one hundred million tons on Earth. ...
... thus incredibly dense. Just a sugar cube of neutron star matter would weigh about one hundred million tons on Earth. ...
Star Show FACILITATOR NOTES
... closely matches the Sun’s spectrum must have a temperature very close to the temperature at the Sun’s visible surface—well over 5000°C. Except for specialized lights used in photography, most real light filaments operate at a lower temperature (around 2500°C) which gives a more reddish-orange color ...
... closely matches the Sun’s spectrum must have a temperature very close to the temperature at the Sun’s visible surface—well over 5000°C. Except for specialized lights used in photography, most real light filaments operate at a lower temperature (around 2500°C) which gives a more reddish-orange color ...
Lesson 6 - Magnitudes of Stars
... Magnitudes are a way of assigning a number to a star so we know how bright it is Similar to how the Richter scale assigns a number to the strength of an earthquake Betelgeuse and Rigel, stars in Orion with apparent magnitudes 0.3 and 0.9 ...
... Magnitudes are a way of assigning a number to a star so we know how bright it is Similar to how the Richter scale assigns a number to the strength of an earthquake Betelgeuse and Rigel, stars in Orion with apparent magnitudes 0.3 and 0.9 ...
Reach for the Stars B
... 34. What is one common nickname for this DSO? 35. What cluster of stars causes this nebula to shine? 36. Which DSO is depicted in Image [13]? 37. What is the cause of the bright yellow feature down the middle of the image? 38. Sirius A (α Canis Majoris) has a white dwarf companion, creatively named ...
... 34. What is one common nickname for this DSO? 35. What cluster of stars causes this nebula to shine? 36. Which DSO is depicted in Image [13]? 37. What is the cause of the bright yellow feature down the middle of the image? 38. Sirius A (α Canis Majoris) has a white dwarf companion, creatively named ...
VISIT TO NORMAN LOCKYER OBSERVATORY IN SIDMOUTH
... smaller and less massive that had been thought when it was discovered and, to be honest, if Pluto were discovered now it would never be classified as a planet. I was a little sad though when it was demoted and would have liked it to have been allowed to stay as an 'honorary planet'. Charon is 1,200 ...
... smaller and less massive that had been thought when it was discovered and, to be honest, if Pluto were discovered now it would never be classified as a planet. I was a little sad though when it was demoted and would have liked it to have been allowed to stay as an 'honorary planet'. Charon is 1,200 ...
The Stars education kit - Student activities 5-10
... Sirius is the brightest star in the night sky and is part of the constellation Canis Major. It is a blue-white supergiant star about 9 light years away. Alpha Centauri lies in the constellation of Centaurus. It is one of the bright Pointers that point to the Southern Cross. It is the third brightest ...
... Sirius is the brightest star in the night sky and is part of the constellation Canis Major. It is a blue-white supergiant star about 9 light years away. Alpha Centauri lies in the constellation of Centaurus. It is one of the bright Pointers that point to the Southern Cross. It is the third brightest ...
the May 2017 Newsletter!
... at intervals to see if they had opened up enough to appear separated. Our observing evening records over the past few years suggest that we sometimes thought we could split them, and sometimes thought we couldn’t split them. However, on this evening, although very close, the star could quite easily ...
... at intervals to see if they had opened up enough to appear separated. Our observing evening records over the past few years suggest that we sometimes thought we could split them, and sometimes thought we couldn’t split them. However, on this evening, although very close, the star could quite easily ...
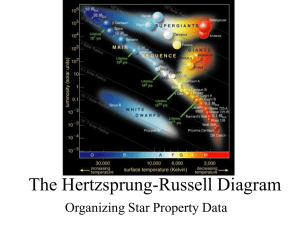
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... Equal Radius Lines In general the hotter the star is the brighter it will be. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
... Equal Radius Lines In general the hotter the star is the brighter it will be. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
Apparent Magnitude
... of mass. For each star, the other is its companion star. A large percentage of stars are part of systems with at least two stars. Binary star systems are very important in astrophysics, because observing their mutual orbits allows their mass to be determined. The masses of many single stars can then ...
... of mass. For each star, the other is its companion star. A large percentage of stars are part of systems with at least two stars. Binary star systems are very important in astrophysics, because observing their mutual orbits allows their mass to be determined. The masses of many single stars can then ...
bright - TutorPlus
... • Stars can be classified into characteristic types depending on their position on the H-R diagram. • Most stars line up along a slightly curved diagonal line called the main sequence. Our Sun is located on the main sequence. • On the main sequence, low mass stars tend to be cooler and less bright w ...
... • Stars can be classified into characteristic types depending on their position on the H-R diagram. • Most stars line up along a slightly curved diagonal line called the main sequence. Our Sun is located on the main sequence. • On the main sequence, low mass stars tend to be cooler and less bright w ...
Stars
... in the sky Stars appear close together in the sky, however, they are actually light years from each other ...
... in the sky Stars appear close together in the sky, however, they are actually light years from each other ...
supplemental educational materials PDF
... • Different constellations are visible at certain times of the year due to Earth’s orbit around the Sun. Each day our sky changes a little bit, which causes some constellations to disappear from sight and others to appear. Since we see different parts of the sky each season, we also see different co ...
... • Different constellations are visible at certain times of the year due to Earth’s orbit around the Sun. Each day our sky changes a little bit, which causes some constellations to disappear from sight and others to appear. Since we see different parts of the sky each season, we also see different co ...
30.2 PowerPoint Stellar Evolution
... the core of the star The energy from fusion balances the force of gravity and makes it a very stable stage ...
... the core of the star The energy from fusion balances the force of gravity and makes it a very stable stage ...
File - YEAR 11 EBSS PHYSICS DETAILED STUDIES
... Watts and is know as Luminosity (L). The apparent brightness (b) of a star can be determined by calculating the amount of received radiation, this is measured in Watts per square meter. Luminosity L=b × 4πR2 Where L is the luminosity in Watts b is the apparent brightness in W m-2 R is the distanc ...
... Watts and is know as Luminosity (L). The apparent brightness (b) of a star can be determined by calculating the amount of received radiation, this is measured in Watts per square meter. Luminosity L=b × 4πR2 Where L is the luminosity in Watts b is the apparent brightness in W m-2 R is the distanc ...
PDF of story and photos
... appear close to each other, they formed geometric patterns that represented features of gods, heroes, animals, and mythological creatures. Often, ancient people created myths or stories about why these creatures appear in the sky. The constellation tales not only provided amusement but also helped t ...
... appear close to each other, they formed geometric patterns that represented features of gods, heroes, animals, and mythological creatures. Often, ancient people created myths or stories about why these creatures appear in the sky. The constellation tales not only provided amusement but also helped t ...
What is a star?
... Apparent magnitude is the measure of a star’s brightness as seen from Earth. • Ancient astronomers, using only their eyes, described star brightness by magnitude. • They called the brightest stars they could see first magnitude and the faintest stars they could see sixth magnitude. ...
... Apparent magnitude is the measure of a star’s brightness as seen from Earth. • Ancient astronomers, using only their eyes, described star brightness by magnitude. • They called the brightest stars they could see first magnitude and the faintest stars they could see sixth magnitude. ...
Earth Science Notes
... in the sky Stars appear close together in the sky, however, they are actually light years from each other ...
... in the sky Stars appear close together in the sky, however, they are actually light years from each other ...
www.aavso.org
... The accumulated charge in each pixel from photons falling on is measured. CCDs are very sensitive, respond to light over a wide range of wavelengths and can measure many stars at once, as compared to photomultiplier tubes which only measure one star at a time. ...
... The accumulated charge in each pixel from photons falling on is measured. CCDs are very sensitive, respond to light over a wide range of wavelengths and can measure many stars at once, as compared to photomultiplier tubes which only measure one star at a time. ...
Introduction to Celestial Spheres (Professor Powerpoint)
... With these two directions, any object can be located on the celestial sphere. ...
... With these two directions, any object can be located on the celestial sphere. ...
Draco: The Dragon - Courtney Stookey
... constellation quite literally looks like a snake slithering through the northern sky. While it’s not a very prominent constellation, it is still the 8th largest. There are quite a few versions of Greek mythology that are linked to Draco. There are 3 main contenders though. The most well-known myth i ...
... constellation quite literally looks like a snake slithering through the northern sky. While it’s not a very prominent constellation, it is still the 8th largest. There are quite a few versions of Greek mythology that are linked to Draco. There are 3 main contenders though. The most well-known myth i ...
Universe 19
... 3. What is meant by a “first-magnitude” or “second-magnitude” star? 4. Why are some stars red and others blue? 5. What are the stars made of? 6. As stars go, is our Sun especially large or small? 7. What are giant, main-sequence, and white dwarf stars? 8. How do we know the distances to remote stars ...
... 3. What is meant by a “first-magnitude” or “second-magnitude” star? 4. Why are some stars red and others blue? 5. What are the stars made of? 6. As stars go, is our Sun especially large or small? 7. What are giant, main-sequence, and white dwarf stars? 8. How do we know the distances to remote stars ...
Crux

Crux /ˈkrʌks/, located in the deep southern sky, is the smallest yet one of the most distinctive of the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for cross, and it is dominated by a cross-shaped asterism that is commonly known as the Southern Cross. Although visible to the Ancient Greeks, it was seen as part of the constellation Centaurus, and not defined or accurately mapped till the 16th century.Known as Acrux, blue-white Alpha Crucis is the constellation's brightest star and the bottom star of the cross. Nearly as bright are Beta and Gamma, while Delta and Epsilon make up the asterism. Many of the constellation's brighter stars are members of the Scorpius–Centaurus Association, a loose group of hot blue-white stars that appear to share a common origin and motion across the Milky Way. Two star systems have been found to have planets. The constellation also contains four Cepheid variables visible to the naked eye under optimum conditions. Crux also contains the Jewel Box, a bright open cluster, and the Coalsack Nebula, the most prominent dark nebula in the sky.