Issue 118 - Apr 2014
... Shapley developing the method of using Cepheids to determine the distance to globular clusters and nearby galaxies. Mira Stars - These long period variables are very large red pulsating stars having brightness magnitude ranges of up to 11 magnitudes and a time period from 24 days to 5.7 years. These ...
... Shapley developing the method of using Cepheids to determine the distance to globular clusters and nearby galaxies. Mira Stars - These long period variables are very large red pulsating stars having brightness magnitude ranges of up to 11 magnitudes and a time period from 24 days to 5.7 years. These ...
Version A - Otterbein University
... 8) Use the backside of the computer form to record the answers to the last three questions, which are not multiple-choice but short answer questions. 9) You should be able to answer all questions without using a calculator, but if you wish, you can use a scientific calculator. ...
... 8) Use the backside of the computer form to record the answers to the last three questions, which are not multiple-choice but short answer questions. 9) You should be able to answer all questions without using a calculator, but if you wish, you can use a scientific calculator. ...
Version B - Otterbein University
... b) shifts westward with respect to the stars. c) will be visible only on the southern hemisphere. d) rises in the west and sets in the east. e) will be at the north celestial pole. 24) Hawaii is located at 20 degrees northern latitude. For an observer in Hawaii, what is the maximal altitude above th ...
... b) shifts westward with respect to the stars. c) will be visible only on the southern hemisphere. d) rises in the west and sets in the east. e) will be at the north celestial pole. 24) Hawaii is located at 20 degrees northern latitude. For an observer in Hawaii, what is the maximal altitude above th ...
The HR Diagram - Faculty Web Pages
... brightnesses. Now let's see if we can find some relationships between these stellar properties. We know that hotter stars are brighter, as described by the Stefan-Boltzmann Law, and we know that the hotter stars are also bluer, as described by Wien's Law. The H-R diagram is a way of displaying an im ...
... brightnesses. Now let's see if we can find some relationships between these stellar properties. We know that hotter stars are brighter, as described by the Stefan-Boltzmann Law, and we know that the hotter stars are also bluer, as described by Wien's Law. The H-R diagram is a way of displaying an im ...
COM 2014 January
... NGC 1275 (also known as Perseus A or Caldwell 24) is a type 1.5 Seyfert galaxy located around 237 million light-years away. NGC 1275 corresponds to the radio galaxy Perseus A and is situated near the center of the large Perseus Cluster of galaxies. “Through the 4-inch, NGC 1275 is less a firefly and ...
... NGC 1275 (also known as Perseus A or Caldwell 24) is a type 1.5 Seyfert galaxy located around 237 million light-years away. NGC 1275 corresponds to the radio galaxy Perseus A and is situated near the center of the large Perseus Cluster of galaxies. “Through the 4-inch, NGC 1275 is less a firefly and ...
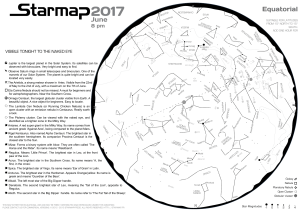
20 pm - Starmap
... The map shows what you see looking at the zenith. The apparent inversion of East and West compared to road maps is normal. Hold the map face down above your head, and the cardinal points will be oriented as usual. As a starting point, face North, holding the map in your eyesight direction, with its ...
... The map shows what you see looking at the zenith. The apparent inversion of East and West compared to road maps is normal. Hold the map face down above your head, and the cardinal points will be oriented as usual. As a starting point, face North, holding the map in your eyesight direction, with its ...
Luminosity Classes
... Some Stars change luminosity significantly and cyclically . They get noticeably dimmer, then brighter, then dimmer again. These are called Variable Stars. The change in luminosity is due to a change in size. (Though temperature changes too.) ...
... Some Stars change luminosity significantly and cyclically . They get noticeably dimmer, then brighter, then dimmer again. These are called Variable Stars. The change in luminosity is due to a change in size. (Though temperature changes too.) ...
The HR Diagram - Faculty Web Pages
... brightnesses. Now let's see if we can find some relationships between these stellar properties. We know that hotter stars are brighter, as described by the Stefan-Boltzmann Law, and we know that the hotter stars are also bluer, as described by Wien's Law. The H-R diagram is a way of displaying an im ...
... brightnesses. Now let's see if we can find some relationships between these stellar properties. We know that hotter stars are brighter, as described by the Stefan-Boltzmann Law, and we know that the hotter stars are also bluer, as described by Wien's Law. The H-R diagram is a way of displaying an im ...
description
... Note: Which wall the constellation goes on, depends on what time of the year you are viewing the night sky. The time represented in this activity is MarchApril. Ask the students to face the front of the room at the Big Dipper poster. Ask the class what direction are they facing? How can they tell? W ...
... Note: Which wall the constellation goes on, depends on what time of the year you are viewing the night sky. The time represented in this activity is MarchApril. Ask the students to face the front of the room at the Big Dipper poster. Ask the class what direction are they facing? How can they tell? W ...
From the reviews - Astrofoto Portugal
... "Navigating the Night Sky is an easy to read book that is essential for all those taking their first steps in finding their w ay around the night sky. Whilst the book is aimed at beginners it also provides information for the more advanced stargazer. The book is arranged into chapters on the Constel ...
... "Navigating the Night Sky is an easy to read book that is essential for all those taking their first steps in finding their w ay around the night sky. Whilst the book is aimed at beginners it also provides information for the more advanced stargazer. The book is arranged into chapters on the Constel ...
22 pm - Starmap
... Many deep sky objects like galaxies and clusters will be within reach. Jupiter satellites and Saturn’s rings will also be visible. A spectacular experience for beginners in astronomy... Avoid the nights when the Moon is too bright as its light would make the observation of faint objects difficult. ...
... Many deep sky objects like galaxies and clusters will be within reach. Jupiter satellites and Saturn’s rings will also be visible. A spectacular experience for beginners in astronomy... Avoid the nights when the Moon is too bright as its light would make the observation of faint objects difficult. ...
THE LIFE CYCLES OF STARS (3)
... The ancient Babylonians 1800 BC put together the first star catalogues. The Greek Hipparchus (180-125 BC) and later Claudius Ptolemy in Alexandria about 150 AD classified stars according to their apparent brightness to the eye, dividing them six into classes of brightness. The brightest stars were c ...
... The ancient Babylonians 1800 BC put together the first star catalogues. The Greek Hipparchus (180-125 BC) and later Claudius Ptolemy in Alexandria about 150 AD classified stars according to their apparent brightness to the eye, dividing them six into classes of brightness. The brightest stars were c ...
Document
... decided to name the object a volcano. • What the gods didn’t know was that the blast had gone so far up to the heavens that it rearranged the stars into the shape of a volcano. Now you can see the stars that form a volcano best in late summer and early, early fall. Hades and Hephaestus were proud of ...
... decided to name the object a volcano. • What the gods didn’t know was that the blast had gone so far up to the heavens that it rearranged the stars into the shape of a volcano. Now you can see the stars that form a volcano best in late summer and early, early fall. Hades and Hephaestus were proud of ...
Define the following terms in the space provided
... A) At what altitude would Polaris appear above the northern horizon? Polaris would appear 26 above the northern horizon. B) Would a star with a declination of +63 be circumpolar? Explain. The circumpolar boundary is 90 - 26 = 64 dec. A star with declination equal to 63 dec would be just outsid ...
... A) At what altitude would Polaris appear above the northern horizon? Polaris would appear 26 above the northern horizon. B) Would a star with a declination of +63 be circumpolar? Explain. The circumpolar boundary is 90 - 26 = 64 dec. A star with declination equal to 63 dec would be just outsid ...
Luminosity Classes
... dimmer again. These are called Variable Stars. The change in luminosity is due to a change in size. (Though temperature changes too.) ...
... dimmer again. These are called Variable Stars. The change in luminosity is due to a change in size. (Though temperature changes too.) ...
Define the following terms in the space provided
... York to Miami. Each night on your journey of a few weeks, you spend some time observing the stars. Which of the statements below would represent one of your observations? A) The region of the sky that was circumpolar diminished each night. B) Polaris was seen higher in the sky on each succeeding nig ...
... York to Miami. Each night on your journey of a few weeks, you spend some time observing the stars. Which of the statements below would represent one of your observations? A) The region of the sky that was circumpolar diminished each night. B) Polaris was seen higher in the sky on each succeeding nig ...
The 22 First Magnitude Stars
... • English names generally based on Greek, Latin, Arabic • Only the brightest stars have proper names in common use • Multiple stars have suffix A, B, C, etc. applied to components in order of apparent brightness ...
... • English names generally based on Greek, Latin, Arabic • Only the brightest stars have proper names in common use • Multiple stars have suffix A, B, C, etc. applied to components in order of apparent brightness ...
every star in the cluster.
... giants, continually forming from evolving stars near the turnoff. But there were originally many stars that were even more massive, that became red giants for a time, and that have moved on to a different final form. The cluster contains a huge number of ‘stellar remnants.’ [Details to follow!] ...
... giants, continually forming from evolving stars near the turnoff. But there were originally many stars that were even more massive, that became red giants for a time, and that have moved on to a different final form. The cluster contains a huge number of ‘stellar remnants.’ [Details to follow!] ...
Sermon Notes
... bringing destruction to anything that is in his way. It is a picture of Christ bringing destruction to the wicked in His judgment. We only see the front half of the bull and he seems to be coming out of Aries – The Lamb/or Ram. We see the Lamb giving rise to the Bull that comes forth in judgment. Th ...
... bringing destruction to anything that is in his way. It is a picture of Christ bringing destruction to the wicked in His judgment. We only see the front half of the bull and he seems to be coming out of Aries – The Lamb/or Ram. We see the Lamb giving rise to the Bull that comes forth in judgment. Th ...
Stars and Constellations
... have higher apparent magnitudes than more distant ones. The sun, for example, has the largest apparent magnitude (-26.73) of any other star in the universe. The actual brightness of a star is called its absolute magnitude. Unlike apparent magnitude, absolute magnitude does not consider distance. It ...
... have higher apparent magnitudes than more distant ones. The sun, for example, has the largest apparent magnitude (-26.73) of any other star in the universe. The actual brightness of a star is called its absolute magnitude. Unlike apparent magnitude, absolute magnitude does not consider distance. It ...
Candles in the Dark
... Since the mid-ninteenth century astronomers have used the principle of parallax to measure the distance to other stars. However this technique gets harder to use for more distant stars and is in fact iuseless for measuring distances of more than about 1600 light years. How then can we tell, for exam ...
... Since the mid-ninteenth century astronomers have used the principle of parallax to measure the distance to other stars. However this technique gets harder to use for more distant stars and is in fact iuseless for measuring distances of more than about 1600 light years. How then can we tell, for exam ...
Part A
... Groups of Stars • Most stars exist in star systems bound by gravity. • Many stars exist in large groupings called clusters. • Stars in a cluster all formed at about the same time and are the same distance from Earth. ...
... Groups of Stars • Most stars exist in star systems bound by gravity. • Many stars exist in large groupings called clusters. • Stars in a cluster all formed at about the same time and are the same distance from Earth. ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... ________________________________ stars that are the remains of low-mass and medium-mass stars. ____________________________________is the theory that states that at one time, the entire universe was confined to a dense, hot, supermassive ball. Then, about 13.7 billion years ago, a violent explosion ...
... ________________________________ stars that are the remains of low-mass and medium-mass stars. ____________________________________is the theory that states that at one time, the entire universe was confined to a dense, hot, supermassive ball. Then, about 13.7 billion years ago, a violent explosion ...
a new isotopic abundance anomaly in chemically peculiar stars
... CP stars. It is significant that we find the 48Ca anomaly over a wide range of effective temperatures and atmospheric conditions. While details of the isotopic fraction processes discussed here are uncertain, one fact is clear. These CP stars have by far the most unusual natural fractionation mechan ...
... CP stars. It is significant that we find the 48Ca anomaly over a wide range of effective temperatures and atmospheric conditions. While details of the isotopic fraction processes discussed here are uncertain, one fact is clear. These CP stars have by far the most unusual natural fractionation mechan ...
Crux

Crux /ˈkrʌks/, located in the deep southern sky, is the smallest yet one of the most distinctive of the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for cross, and it is dominated by a cross-shaped asterism that is commonly known as the Southern Cross. Although visible to the Ancient Greeks, it was seen as part of the constellation Centaurus, and not defined or accurately mapped till the 16th century.Known as Acrux, blue-white Alpha Crucis is the constellation's brightest star and the bottom star of the cross. Nearly as bright are Beta and Gamma, while Delta and Epsilon make up the asterism. Many of the constellation's brighter stars are members of the Scorpius–Centaurus Association, a loose group of hot blue-white stars that appear to share a common origin and motion across the Milky Way. Two star systems have been found to have planets. The constellation also contains four Cepheid variables visible to the naked eye under optimum conditions. Crux also contains the Jewel Box, a bright open cluster, and the Coalsack Nebula, the most prominent dark nebula in the sky.