Notes - Bill Wolf
... and luminosity to denote how much light the star is actually giving off. These two words have analogous magnitude scales. The magnitude scale that measures brightness is the one that Hipparchus thought up. We call it Apparent Magnitude, often denoted m. The scale corresponding to luminosity is calle ...
... and luminosity to denote how much light the star is actually giving off. These two words have analogous magnitude scales. The magnitude scale that measures brightness is the one that Hipparchus thought up. We call it Apparent Magnitude, often denoted m. The scale corresponding to luminosity is calle ...
Grade Nine Planetarium script
... As the earth revolves around the sun the stars positions, at a given time of night, also will shift. They move about 3 fists per month, from the east to the west, or about as far as they move in two hours on a given night. So, Orion at midnight on February 1st is in the same position that it was at ...
... As the earth revolves around the sun the stars positions, at a given time of night, also will shift. They move about 3 fists per month, from the east to the west, or about as far as they move in two hours on a given night. So, Orion at midnight on February 1st is in the same position that it was at ...
Apparent Motion of the Stars Worksheet
... [Rule: The Celestial Equator (0° dec) intersects the horizon due East and West for all observers. All stars follow their respective lines of declination and, near the celestial equator, the slant angle relative to the vertical of lines of declination are equal to the observer’s latitude.] Draw the ...
... [Rule: The Celestial Equator (0° dec) intersects the horizon due East and West for all observers. All stars follow their respective lines of declination and, near the celestial equator, the slant angle relative to the vertical of lines of declination are equal to the observer’s latitude.] Draw the ...
FREE Sample Here
... This chapter focuses on the appearance of the night sky. Many of the concepts presented were common knowledge before time became quantified on clocks and city lights blocked our nightly view of the sky. Most people today no longer have an understanding of the basic appearance or motions of the sky. ...
... This chapter focuses on the appearance of the night sky. Many of the concepts presented were common knowledge before time became quantified on clocks and city lights blocked our nightly view of the sky. Most people today no longer have an understanding of the basic appearance or motions of the sky. ...
Document
... • A is correct because absolute magnitude is a measure of a star’s luminosity, which is how bright a star actually is. • B is incorrect because apparent magnitude can be used to calculate absolute magnitude, but the term does not relate directly to the actual brightness of a star. • C is incorrect b ...
... • A is correct because absolute magnitude is a measure of a star’s luminosity, which is how bright a star actually is. • B is incorrect because apparent magnitude can be used to calculate absolute magnitude, but the term does not relate directly to the actual brightness of a star. • C is incorrect b ...
Rotation in the ZAMS: Be and Bn stars
... than spectral type B7. This could be due to genuine Be stars whose discs are minute and/or too cool for the Hα emission be detectable and/or, to fast rotating B stars that still had not attained the required properties to become fully-fledged Be stars. According to findings in Sect. 1., which are su ...
... than spectral type B7. This could be due to genuine Be stars whose discs are minute and/or too cool for the Hα emission be detectable and/or, to fast rotating B stars that still had not attained the required properties to become fully-fledged Be stars. According to findings in Sect. 1., which are su ...
Chapter 12: Measuring the Properties of Stars
... 1. An astrometric binary is an orbiting pair of stars in which the motion of one of the stars reveals the presence of the other. 2. A composite spectrum binary is a binary star system with stars having spectra different enough to distinguish them from one another. 12-6 Stellar Masses and Sizes from ...
... 1. An astrometric binary is an orbiting pair of stars in which the motion of one of the stars reveals the presence of the other. 2. A composite spectrum binary is a binary star system with stars having spectra different enough to distinguish them from one another. 12-6 Stellar Masses and Sizes from ...
SM_Taurus - Cloudy Nights
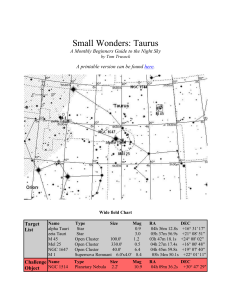
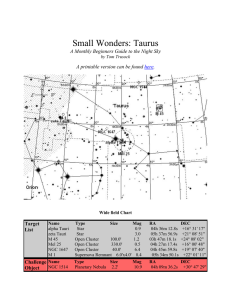
... beginning of spring planting. Our constellation for the month is located on the edge of the winter Milky Way, and our targets include; three open clusters, one of the brightest supernova remnants in the night sky and a lesser known planetary nebula. By no means is this an exhaustive list of targets ...
... beginning of spring planting. Our constellation for the month is located on the edge of the winter Milky Way, and our targets include; three open clusters, one of the brightest supernova remnants in the night sky and a lesser known planetary nebula. By no means is this an exhaustive list of targets ...
Small Wonders: Taurus
... beginning of spring planting. Our constellation for the month is located on the edge of the winter Milky Way, and our targets include; three open clusters, one of the brightest supernova remnants in the night sky and a lesser known planetary nebula. By no means is this an exhaustive list of targets ...
... beginning of spring planting. Our constellation for the month is located on the edge of the winter Milky Way, and our targets include; three open clusters, one of the brightest supernova remnants in the night sky and a lesser known planetary nebula. By no means is this an exhaustive list of targets ...
chapter 2 - Test Bank 1
... This chapter focuses on the appearance of the night sky. Many of the concepts presented were common knowledge before time became quantified on clocks and city lights blocked our nightly view of the sky. Most people today no longer have an understanding of the basic appearance or motions of the sky. ...
... This chapter focuses on the appearance of the night sky. Many of the concepts presented were common knowledge before time became quantified on clocks and city lights blocked our nightly view of the sky. Most people today no longer have an understanding of the basic appearance or motions of the sky. ...
MS Word
... 4.2 Estimate the average apparent magnitude of these stars from the table.__________________ 4.3 When you look at a bright, 1st magnitude star in the sky, you are probably looking at what kind of star? (hot/cool/blue/red)_______________________________ ...
... 4.2 Estimate the average apparent magnitude of these stars from the table.__________________ 4.3 When you look at a bright, 1st magnitude star in the sky, you are probably looking at what kind of star? (hot/cool/blue/red)_______________________________ ...
chapter 7
... Astronomers have now detected hundreds of planetary bodies, called exoplanets, moving in orbit around other stars. Most of these are more massive than any of the Sun's planets. These planetary-like bodies are detected because of their strong gravitationally interactions with their stars. However, te ...
... Astronomers have now detected hundreds of planetary bodies, called exoplanets, moving in orbit around other stars. Most of these are more massive than any of the Sun's planets. These planetary-like bodies are detected because of their strong gravitationally interactions with their stars. However, te ...
Introduction to Astronomy (high school)
... orange star in the constellation Orion, and Dubhe, the second-magnitude star at the edge of the Big Dipper's cup (Ursa Major). A few proper star names are not Arabic. One is Polaris, the second-magnitude star at the end of the handle of the Little Dipper (Ursa Minor). Polaris also carries the popula ...
... orange star in the constellation Orion, and Dubhe, the second-magnitude star at the edge of the Big Dipper's cup (Ursa Major). A few proper star names are not Arabic. One is Polaris, the second-magnitude star at the end of the handle of the Little Dipper (Ursa Minor). Polaris also carries the popula ...
about Stars
... • Astronomers quantify the “color” of a star by using the difference in brightness between the brightness in the B and V spectral regions • The B-V color is related to the slope of the ...
... • Astronomers quantify the “color” of a star by using the difference in brightness between the brightness in the B and V spectral regions • The B-V color is related to the slope of the ...
Luminosities and magnitudes of stars
... Intensity I = energy emitted at some frequency , per unit time dt, per unit area of the source dA, per unit frequency d, per unit solid angle d in a given direction (,) (see p. 151-152) Units: w m-2 Hz-1 ster-1 ...
... Intensity I = energy emitted at some frequency , per unit time dt, per unit area of the source dA, per unit frequency d, per unit solid angle d in a given direction (,) (see p. 151-152) Units: w m-2 Hz-1 ster-1 ...
Sun - UNT Physics
... over period of ~ 100,000 years) • Precession (Period of ~ 26,000 years) • Inclination of Earth’s axis versus orbital plane Milankovitch Hypothesis: Changes in all three of these ...
... over period of ~ 100,000 years) • Precession (Period of ~ 26,000 years) • Inclination of Earth’s axis versus orbital plane Milankovitch Hypothesis: Changes in all three of these ...
The Sky Viewed from Earth - Beck-Shop
... from the southern. But at any one time, in either hemisphere, only about 2000 stars can be seen because the other 2000 are then in the daytime sky. To see even the night-sky 2000 requires a very dark site, however, well away from any city, and the eye must be fully dark adapted, which means a wait o ...
... from the southern. But at any one time, in either hemisphere, only about 2000 stars can be seen because the other 2000 are then in the daytime sky. To see even the night-sky 2000 requires a very dark site, however, well away from any city, and the eye must be fully dark adapted, which means a wait o ...
Bright versus Nearby Stars
... A Comparison of the Nearest and Brightest Stars • The nearest stars to the Sun are thought to represent the true distribution of stars in the disk of the Milky Way Galaxy. • To truly understand the Galaxy, these stars must be studied. ...
... A Comparison of the Nearest and Brightest Stars • The nearest stars to the Sun are thought to represent the true distribution of stars in the disk of the Milky Way Galaxy. • To truly understand the Galaxy, these stars must be studied. ...
Define the following terms in the space provided
... 1) Imagine that you are visiting Antarctica on a cruise to see penguins. You step outside at night and look at the stars. Where would you look to see the South Celestial Pole? A) North, near the horizon (0 altitude) B) Near the zenith (90altitude) C) North, near 43 altitude D) Northwest, in the d ...
... 1) Imagine that you are visiting Antarctica on a cruise to see penguins. You step outside at night and look at the stars. Where would you look to see the South Celestial Pole? A) North, near the horizon (0 altitude) B) Near the zenith (90altitude) C) North, near 43 altitude D) Northwest, in the d ...
Sun - Cobb Learning
... once every 26,000 years. It will be closest to Polaris ~ A.D. 2100. There is nothing peculiar about Polaris at all (neither particularly bright nor nearby etc.) ...
... once every 26,000 years. It will be closest to Polaris ~ A.D. 2100. There is nothing peculiar about Polaris at all (neither particularly bright nor nearby etc.) ...
Life Histories Stars
... the universe is about 15 billion years, what does this say about the kind of stars most likely to have remained from the beginnings of the universe? What’s Going On? In this activity, you can see that the very massive stars live much shorted “lives” compared to the smaller, less massive stars. Why i ...
... the universe is about 15 billion years, what does this say about the kind of stars most likely to have remained from the beginnings of the universe? What’s Going On? In this activity, you can see that the very massive stars live much shorted “lives” compared to the smaller, less massive stars. Why i ...
Merak
... To the Greeks, this star was named Helike, one of their names to the whole constellation, Ursa Major. According to Burnham, Merak is part of a star cluster including at least 16 other stars from the Ursa Major area of the sky. (http://domeofthesky.com/clicks/merak.html) ...
... To the Greeks, this star was named Helike, one of their names to the whole constellation, Ursa Major. According to Burnham, Merak is part of a star cluster including at least 16 other stars from the Ursa Major area of the sky. (http://domeofthesky.com/clicks/merak.html) ...
Life Histories Of Some Stars
... the universe is about 15 billion years, what does this say about the kind of stars most likely to have remained from the beginnings of the universe? What’s Going On? In this activity, you can see that the very massive stars live much shorted “lives” compared to the smaller, less massive stars. Why i ...
... the universe is about 15 billion years, what does this say about the kind of stars most likely to have remained from the beginnings of the universe? What’s Going On? In this activity, you can see that the very massive stars live much shorted “lives” compared to the smaller, less massive stars. Why i ...
Life Histories Of Some Stars
... The Exploratorium grants reprint permission of this material for noncommercial, educational use only. Copyright notice must be included on all reprints. Requests for electronic or other uses should be directed to
...
... The Exploratorium grants reprint permission of this material for noncommercial, educational use only. Copyright notice must be included on all reprints. Requests for electronic or other uses should be directed to
Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Section 1 Distances to Stars
... from Earth, is caused by the movement of Earth. • The stars seem as though they are moving counterclockwise around a central star called Polaris, the North Star. Polaris is almost directly above the North Pole, and thus the star does not appear to move much. • Earth’s revolution around the sun cause ...
... from Earth, is caused by the movement of Earth. • The stars seem as though they are moving counterclockwise around a central star called Polaris, the North Star. Polaris is almost directly above the North Pole, and thus the star does not appear to move much. • Earth’s revolution around the sun cause ...
Crux

Crux /ˈkrʌks/, located in the deep southern sky, is the smallest yet one of the most distinctive of the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for cross, and it is dominated by a cross-shaped asterism that is commonly known as the Southern Cross. Although visible to the Ancient Greeks, it was seen as part of the constellation Centaurus, and not defined or accurately mapped till the 16th century.Known as Acrux, blue-white Alpha Crucis is the constellation's brightest star and the bottom star of the cross. Nearly as bright are Beta and Gamma, while Delta and Epsilon make up the asterism. Many of the constellation's brighter stars are members of the Scorpius–Centaurus Association, a loose group of hot blue-white stars that appear to share a common origin and motion across the Milky Way. Two star systems have been found to have planets. The constellation also contains four Cepheid variables visible to the naked eye under optimum conditions. Crux also contains the Jewel Box, a bright open cluster, and the Coalsack Nebula, the most prominent dark nebula in the sky.