DNA Sequence Analysis Using Boolean Algebra
... proteins, phylogeny and evolutionary analysis. Classical methods like Needleman Wunsch ( for global alignment) in 1970 and Smith-Waterman (for local alignment) in 1981 suffer from the drawback that it involves a large number of computational steps and has a statically allocate a large section of mem ...
... proteins, phylogeny and evolutionary analysis. Classical methods like Needleman Wunsch ( for global alignment) in 1970 and Smith-Waterman (for local alignment) in 1981 suffer from the drawback that it involves a large number of computational steps and has a statically allocate a large section of mem ...
Mining Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms from public sequence
... SNPs (single nucleotide polymorphisms) are abundant and useful genetic markers. Software exists to mine them from public data sets, but this doesn’t work in real time. GRID technology could help to deliver up-to-date alignments to users for any query sequence with putative SNPs marked up. Related us ...
... SNPs (single nucleotide polymorphisms) are abundant and useful genetic markers. Software exists to mine them from public data sets, but this doesn’t work in real time. GRID technology could help to deliver up-to-date alignments to users for any query sequence with putative SNPs marked up. Related us ...
Mining SNPs from public sequence Databases
... SNPs (single nucleotide polymorphisms) are abundant and useful genetic markers. Software exists to mine them from public data sets, but this doesn’t work in real time. GRID technology could help to deliver up-to-date alignments to users for any query sequence with putative SNPs marked up. Related us ...
... SNPs (single nucleotide polymorphisms) are abundant and useful genetic markers. Software exists to mine them from public data sets, but this doesn’t work in real time. GRID technology could help to deliver up-to-date alignments to users for any query sequence with putative SNPs marked up. Related us ...
SBARS: fast creation of dotplots for DNA sequences on different
... In addition to the GC-content, we used the GA-content curve with the same parameters W1 and d1, which allow us to unambiguously recover a DNA sequence from this curves (Supplementary Material). Simultaneous recognition by two curves provides more stable results and allows us to define the various ty ...
... In addition to the GC-content, we used the GA-content curve with the same parameters W1 and d1, which allow us to unambiguously recover a DNA sequence from this curves (Supplementary Material). Simultaneous recognition by two curves provides more stable results and allows us to define the various ty ...
Alignment of pairs of sequences
... Why compare sequences? • To find whether two (or more) genes or proteins are evolutionarily related to each other • To find structurally or functionally similar regions within proteins ...
... Why compare sequences? • To find whether two (or more) genes or proteins are evolutionarily related to each other • To find structurally or functionally similar regions within proteins ...
Pair-wise sequence alignment
... Local sequence alignment • Performs an exhaustive search for optimal local ...
... Local sequence alignment • Performs an exhaustive search for optimal local ...
Bioinformatics Individual Projects
... g. Use the wildtype protein sequence and BLAST to obtain 4 more homologous protein sequences for your multiple sequence alignment. Copy those 4 FASTA formatted sequences to your Word sequence file too h. Use ClustalW to align all 6 sequences (wildtype, mutant, plus 4 homologous sequences) i. Save th ...
... g. Use the wildtype protein sequence and BLAST to obtain 4 more homologous protein sequences for your multiple sequence alignment. Copy those 4 FASTA formatted sequences to your Word sequence file too h. Use ClustalW to align all 6 sequences (wildtype, mutant, plus 4 homologous sequences) i. Save th ...
Testing for Natural Selection on Conserved Non-genic Sequences in Mammals
... The observation of high DNA sequence conservation across long periods of evolutionary time is thought to be a good signal of important regions. Otherwise, the similarity between sequences of species would have eroded by neutral mutation processes. This is also why, in general, higher conservation is ...
... The observation of high DNA sequence conservation across long periods of evolutionary time is thought to be a good signal of important regions. Otherwise, the similarity between sequences of species would have eroded by neutral mutation processes. This is also why, in general, higher conservation is ...
Lec-GenomeAllignment2010
... Genome Alignment • Depending on level of similarity, genome alignments may need to contend with rearrangements and large-scale duplications and deletions • Draft or partial genomes can both benefit from and confound alignment • Need to visualize results in summary form ...
... Genome Alignment • Depending on level of similarity, genome alignments may need to contend with rearrangements and large-scale duplications and deletions • Draft or partial genomes can both benefit from and confound alignment • Need to visualize results in summary form ...
BioE/MCB/PMB C146/246, Spring 2005 Problem Set 1
... eventual protein sequence will not be selected against, at least in this overly-simplistic model. The graphs for A and B1 should look very similar. Differences are due only to the random process of choosing which bases mutate. The graph for B2 should show fewer mutations overall, with many positions ...
... eventual protein sequence will not be selected against, at least in this overly-simplistic model. The graphs for A and B1 should look very similar. Differences are due only to the random process of choosing which bases mutate. The graph for B2 should show fewer mutations overall, with many positions ...
Document
... Dotlet dot plots are a good way to provide an overview Dot plots don’t provide residue/residue analysis For this analysis you need an alignment The most convenient tool for making precise local alignments is Lalign ...
... Dotlet dot plots are a good way to provide an overview Dot plots don’t provide residue/residue analysis For this analysis you need an alignment The most convenient tool for making precise local alignments is Lalign ...
Molecular Phylogenetic Analysis: Design and Implementation of
... Condor+DAGMan. The the systems mentioned in the background lack of adaptation to the user needs fixing the tools used as well as their parameterization. Moreover, many of these systems have not been designed to handle large-case scenarios, making them not suitable for input datasets of more than a f ...
... Condor+DAGMan. The the systems mentioned in the background lack of adaptation to the user needs fixing the tools used as well as their parameterization. Moreover, many of these systems have not been designed to handle large-case scenarios, making them not suitable for input datasets of more than a f ...
S x - IBIVU
... B = (S – ln K) / ln 2 •S is the raw alignment score •The bit score (‘bits’) B has a standard set of units •The bit score B is calculated from the number of gaps and substitutions associated with each aligned sequence. The higher the score, the more significant the alignment • and K and are the sta ...
... B = (S – ln K) / ln 2 •S is the raw alignment score •The bit score (‘bits’) B has a standard set of units •The bit score B is calculated from the number of gaps and substitutions associated with each aligned sequence. The higher the score, the more significant the alignment • and K and are the sta ...
Sequencing
... • Perform simple string searches for information retrieval of stored data (GenBank:nucleotides and proteins; and PubMed’s MEDLINE: 3-D structures, genomes and taxonomy databases) • Perform similarity searches (e.g., BLAST) to retrieve , align and compare sequences or structures ...
... • Perform simple string searches for information retrieval of stored data (GenBank:nucleotides and proteins; and PubMed’s MEDLINE: 3-D structures, genomes and taxonomy databases) • Perform similarity searches (e.g., BLAST) to retrieve , align and compare sequences or structures ...
bioinformatics_project
... Cas9 (Cas9) can nick DNA with Cas9 at a target site specified by a small guide RNA(sgRNA) and utilize homology directed repair of DNA with a single stranded donor oligonucleotide (ssODN) as a template. sgRNA sequences typically have the form G(N19)NGG. Cas9 nicks before NGG, which is also known as t ...
... Cas9 (Cas9) can nick DNA with Cas9 at a target site specified by a small guide RNA(sgRNA) and utilize homology directed repair of DNA with a single stranded donor oligonucleotide (ssODN) as a template. sgRNA sequences typically have the form G(N19)NGG. Cas9 nicks before NGG, which is also known as t ...
Bioinformatic Analysis: Designing primers and annotation gene of
... Name the primers with the gene name and append F or R o Example: the forward primer for the rbcL gene should be named rbcL-F o Enter the primer sequences into the Primer Order Form Annotate the Aiptasia or Symbiodinium gene (blast, alignment, Pfam) to evaluate the potential function of this gene ...
... Name the primers with the gene name and append F or R o Example: the forward primer for the rbcL gene should be named rbcL-F o Enter the primer sequences into the Primer Order Form Annotate the Aiptasia or Symbiodinium gene (blast, alignment, Pfam) to evaluate the potential function of this gene ...
presentation source
... Alignments are scored column by column. There is usually a reward for character matches, a small penalty for character mismatches, and a large penalty for gaps. These penalties should be such that the highest scoring alignment is the most likely one to reflect the true evolutionary relationship of t ...
... Alignments are scored column by column. There is usually a reward for character matches, a small penalty for character mismatches, and a large penalty for gaps. These penalties should be such that the highest scoring alignment is the most likely one to reflect the true evolutionary relationship of t ...
Comp. Genomics
... • Can be computed efficiently by Felsenstein’s “pruning algorithm” (recitation 6) • Joint probability of a path in the HMM and and alignment X • Viterbi, forward-backward etc. – as usual ...
... • Can be computed efficiently by Felsenstein’s “pruning algorithm” (recitation 6) • Joint probability of a path in the HMM and and alignment X • Viterbi, forward-backward etc. – as usual ...
Sequence Alignment
... They give a measure of the frequency of changing from one amino acid to another, as compared to the frequency of random change Derived from global alignments of homologus sequences from different, but closely related, species. The sequences had an average of 1 amino acid change per hundred residues. ...
... They give a measure of the frequency of changing from one amino acid to another, as compared to the frequency of random change Derived from global alignments of homologus sequences from different, but closely related, species. The sequences had an average of 1 amino acid change per hundred residues. ...
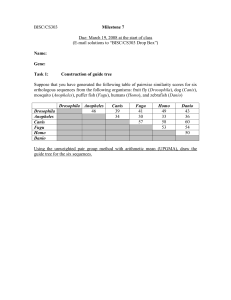
Milestone7
... interactive display of the MSA. One of the advantages of a MSA is that it can provide insight into various properties of a family of proteins. When studying your MSA, if you find portions of your sequences that do not align well, you may want to consider removing these non-homologous regions, partic ...
... interactive display of the MSA. One of the advantages of a MSA is that it can provide insight into various properties of a family of proteins. When studying your MSA, if you find portions of your sequences that do not align well, you may want to consider removing these non-homologous regions, partic ...
Introduction to bioinformatics
... Understanding of genomic variation allows the tailoring of medical treatment to the individual’s genetic make-up Genome analysis allows the targeting of genetic ...
... Understanding of genomic variation allows the tailoring of medical treatment to the individual’s genetic make-up Genome analysis allows the targeting of genetic ...
Molecular phylogeny, part B
... Molecular phylogenetics: A set of techniques that enable the evolutionary relationships between DNA sequences to be inferred by making comparisons between those sequences. Multigene family: A group of genes, clustered or dispersed, with related nucleotide sequences. Multiple alignment: An alignment ...
... Molecular phylogenetics: A set of techniques that enable the evolutionary relationships between DNA sequences to be inferred by making comparisons between those sequences. Multigene family: A group of genes, clustered or dispersed, with related nucleotide sequences. Multiple alignment: An alignment ...
Ch15-Computational_Approaches_in_Comparative_Genomics
... The goal is still to find the best alignments between two sequences No different than Ch. 11 But, the traditional workhorses for pairwise sequence alignments (BLAST & FASTA) would be inefficient MegaBLAST & BLAT are optimized rapidly to longer nucleotide sequences, but not to entire genomes ...
... The goal is still to find the best alignments between two sequences No different than Ch. 11 But, the traditional workhorses for pairwise sequence alignments (BLAST & FASTA) would be inefficient MegaBLAST & BLAT are optimized rapidly to longer nucleotide sequences, but not to entire genomes ...
Multiple sequence alignment

A multiple sequence alignment (MSA) is a sequence alignment of three or more biological sequences, generally protein, DNA, or RNA. In many cases, the input set of query sequences are assumed to have an evolutionary relationship by which they share a lineage and are descended from a common ancestor. From the resulting MSA, sequence homology can be inferred and phylogenetic analysis can be conducted to assess the sequences' shared evolutionary origins. Visual depictions of the alignment as in the image at right illustrate mutation events such as point mutations (single amino acid or nucleotide changes) that appear as differing characters in a single alignment column, and insertion or deletion mutations (indels or gaps) that appear as hyphens in one or more of the sequences in the alignment. Multiple sequence alignment is often used to assess sequence conservation of protein domains, tertiary and secondary structures, and even individual amino acids or nucleotides.Multiple sequence alignment also refers to the process of aligning such a sequence set. Because three or more sequences of biologically relevant length can be difficult and are almost always time-consuming to align by hand, computational algorithms are used to produce and analyze the alignments. MSAs require more sophisticated methodologies than pairwise alignment because they are more computationally complex. Most multiple sequence alignment programs use heuristic methods rather than global optimization because identifying the optimal alignment between more than a few sequences of moderate length is prohibitively computationally expensive.