AIM: Analyze “Victory and Defeat in the Greek World.” Do Now
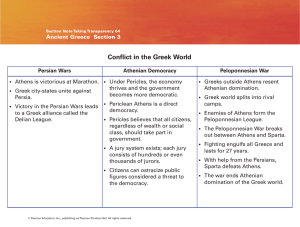
... 1. Victory over the Persians increased the Greeks’ sense of their own uniqueness. 2. Athens emerged as the most powerful city-state. 3. Athens organized the Delian League, an alliance with other Greek city-states. 4. Athens used the Delian League to create an Athenian empire B. Golden Age of Pericle ...
... 1. Victory over the Persians increased the Greeks’ sense of their own uniqueness. 2. Athens emerged as the most powerful city-state. 3. Athens organized the Delian League, an alliance with other Greek city-states. 4. Athens used the Delian League to create an Athenian empire B. Golden Age of Pericle ...
CL1550 Greek History and the City State
... CL1550 Greek History and the City-State Lecture plan 1. Introduction to the Greek world 499-362 B.C. 2. Political organisation, civic duties, and public finance 3. Sources for Greek history. What do we know? How do we know? 4. Citizens, civic identity, and non citizens 5. Democracy in practice: the ...
... CL1550 Greek History and the City-State Lecture plan 1. Introduction to the Greek world 499-362 B.C. 2. Political organisation, civic duties, and public finance 3. Sources for Greek history. What do we know? How do we know? 4. Citizens, civic identity, and non citizens 5. Democracy in practice: the ...
Greece Notes 6 Key
... Pericles was a popular Athenian general. He made Athens a strong city-state. Sparta and Athens went to war to control Greece. ...
... Pericles was a popular Athenian general. He made Athens a strong city-state. Sparta and Athens went to war to control Greece. ...
Athens
... 19. The ________________________________ was formed to guard Greece against future attacks. 20. The __________________________ War between Sparta (Peloponnesians) and Athens (Delians) ended Athenian greatness. 21. The Age of Pericles, was considered a ___________________________, when Athens became ...
... 19. The ________________________________ was formed to guard Greece against future attacks. 20. The __________________________ War between Sparta (Peloponnesians) and Athens (Delians) ended Athenian greatness. 21. The Age of Pericles, was considered a ___________________________, when Athens became ...
The Persian War
... “The magnificent grove of Marathon can confirm his bravery – as well as the long-haired Persian – who remembers it well.” Epitaph of Aeschylus Where were the Spartans? ...
... “The magnificent grove of Marathon can confirm his bravery – as well as the long-haired Persian – who remembers it well.” Epitaph of Aeschylus Where were the Spartans? ...
The Peloponnesian War
... The Parthenon Most famous of all Athenian buildings Built under leadership of Pericles A temple dedicated to Athena Over 2500 years old (still partially standing!) ...
... The Parthenon Most famous of all Athenian buildings Built under leadership of Pericles A temple dedicated to Athena Over 2500 years old (still partially standing!) ...
The Peloponnesian War
... barricade inside walls of Athens and let Navy supply food from colonies. Also attack Peloponnesian Coast and shipping Idea is to wear Sparta down without fighting, then go to war with them ...
... barricade inside walls of Athens and let Navy supply food from colonies. Also attack Peloponnesian Coast and shipping Idea is to wear Sparta down without fighting, then go to war with them ...
The Peloponnesian War Name
... 4.) Name the three major battles from the Persian Wars. ______________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Part B. Use the reading to answer the following questions. 5.) How long did the Peloponnesian War between Sparta and Athens last? ______ 6.) The Gre ...
... 4.) Name the three major battles from the Persian Wars. ______________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Part B. Use the reading to answer the following questions. 5.) How long did the Peloponnesian War between Sparta and Athens last? ______ 6.) The Gre ...
First Peloponnesian War
The First Peloponnesian War (460–445 BC) was fought between Sparta as the leaders of the Peloponnesian League and Sparta's other allies, most notably Thebes, and the Delian League led by Athens with support from Argos. This war consisted of a series of conflicts and minor wars, such as the Second Sacred War. There were several causes for the war including the building of the Athenian long walls, Megara's defection and the envy and concern felt by Sparta at the growth of the Athenian Empire.The war began in 460 BC (Battle of Oenoe). At first the Athenians had the better of the fighting, winning the naval engagements using their superior fleet. They also had the better of the fighting on land, until 457 BC when the Spartans and their allies defeated the Athenian army at Tanagra. The Athenians, however, counterattacked and scored a crushing victory over the Boeotians at the Battle of Oenophyta and followed this victory up by conquering all of Boeotia except for Thebes.Athens further consolidated their position by making Aegina a member of the Delian League and by ravaging the Peloponnese. The Athenians were defeated in 454 BC by the Macedonians which caused them to enter into a five years' truce with Sparta. However, the war flared up again in 448 BC with the start of the Second Sacred War. In 446 BC, Boeotia revolted and defeated the Athenians at Coronea and regained their independence.The First Peloponnesian War ended in an arrangement between Sparta and Athens, which was ratified by the Thirty Years' Peace (winter of 446–445 BC). According to the provisions of this peace treaty, both sides maintained the main parts of their empires. Athens continued its domination of the sea while Sparta dominated the land. Megara returned to the Peloponnesian League and Aegina becoming a tribute paying but autonomous member of the Delian League. The war between the two leagues restarted in 431 BC and in 404 BC, Athens was occupied by Sparta.