Study Guide-Econ Unit 1
... Why do our national economic goals sometimes require trade-offs? Explain the three questions all economic systems must address in order to allocate resources effectively. Describe production possibilities curves. Include the assumptions on which they are based and the factors that cause them to chan ...
... Why do our national economic goals sometimes require trade-offs? Explain the three questions all economic systems must address in order to allocate resources effectively. Describe production possibilities curves. Include the assumptions on which they are based and the factors that cause them to chan ...
economics and politics.ppt
... Business cycle fluctuations result from imbalances between aggregate demand and productive capacity • Aggregate demand is the total amount of money available in the economy to be spent on goods and services • Productive capacity is the total value of goods and services that can be produced by the ec ...
... Business cycle fluctuations result from imbalances between aggregate demand and productive capacity • Aggregate demand is the total amount of money available in the economy to be spent on goods and services • Productive capacity is the total value of goods and services that can be produced by the ec ...
Econ 247 - Trinity College
... Resource owners offer them to the best uses Workers decide how many hours to work. Similarly landowners and capital owners decide where to put their resources All decisions are coordinated in markets The market outcome determines the quantity of resources allocated for each use and the price ...
... Resource owners offer them to the best uses Workers decide how many hours to work. Similarly landowners and capital owners decide where to put their resources All decisions are coordinated in markets The market outcome determines the quantity of resources allocated for each use and the price ...
NSE boss pledges to sustain capital market reforms
... Oscar Onyema, yesterday pledged to sustain the on going reforms in the market as part of strategies to accelerate Nigeria and Africa’s economic development. In his presentation to the House of Representative Committee on Capital Market and Institutions, Onyema said that it was unfortunate that the m ...
... Oscar Onyema, yesterday pledged to sustain the on going reforms in the market as part of strategies to accelerate Nigeria and Africa’s economic development. In his presentation to the House of Representative Committee on Capital Market and Institutions, Onyema said that it was unfortunate that the m ...
What Is an Economy?
... form of government; this means that the government runs everything and makes all decisions. Theoretically, there is no unemployment in ...
... form of government; this means that the government runs everything and makes all decisions. Theoretically, there is no unemployment in ...
ch01 Modern Economics
... In some markets information is so crucial it shapes the whole market: ◦ Market for used cars ◦ Stock market and other security markets ◦ Insurance ...
... In some markets information is so crucial it shapes the whole market: ◦ Market for used cars ◦ Stock market and other security markets ◦ Insurance ...
1.1.6 Free Market Economies, Mixed Economy and Command
... o Also known as laissez-faire economies, where governments leave markets to their own devices, so the market forces of supply and demand allocate scarce resources. o Economic decisions are taken by private individuals and firms, and private individuals own everything. There is no government interven ...
... o Also known as laissez-faire economies, where governments leave markets to their own devices, so the market forces of supply and demand allocate scarce resources. o Economic decisions are taken by private individuals and firms, and private individuals own everything. There is no government interven ...
Made in America
... paragraph response in your spiral notebook. There should be no talking during the Bellwork. ...
... paragraph response in your spiral notebook. There should be no talking during the Bellwork. ...
Price $ Quantity
... Resource owners offer them to the best uses Workers decide how many hours to work. Similarly landowners and capital owners decide where to put their resources All decisions are coordinated in markets The market outcome determines the quantity of resources allocated for each use and the price ...
... Resource owners offer them to the best uses Workers decide how many hours to work. Similarly landowners and capital owners decide where to put their resources All decisions are coordinated in markets The market outcome determines the quantity of resources allocated for each use and the price ...
ECON1000: Principles of Economics
... ideas underlying the economic way of thinking and apply it a range of phenomena both within and outside of the areas of traditional economic analysis. The objective is that, by the end of the course, you will be able to approach a problem in the way that an economist would. Along the way, we introdu ...
... ideas underlying the economic way of thinking and apply it a range of phenomena both within and outside of the areas of traditional economic analysis. The objective is that, by the end of the course, you will be able to approach a problem in the way that an economist would. Along the way, we introdu ...
Econ 372 - Marietta College
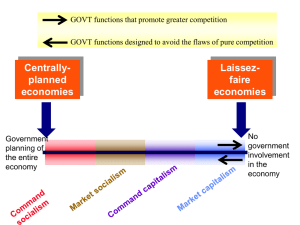
... Probably the single most important characteristic by which different economic systems have been classified is property rights. Why are property rights considered so important in the classification of economic systems? ...
... Probably the single most important characteristic by which different economic systems have been classified is property rights. Why are property rights considered so important in the classification of economic systems? ...
EconPol.ppt
... Private property - people can obtain, control, use, and dispose of the property resources they own [subject to only minimal governmentimposed limitations] Freedom of enterprise and freedom of choice exist - individuals can become entrepreneurs; consumers can buy what they want [a.k.a., consumer sove ...
... Private property - people can obtain, control, use, and dispose of the property resources they own [subject to only minimal governmentimposed limitations] Freedom of enterprise and freedom of choice exist - individuals can become entrepreneurs; consumers can buy what they want [a.k.a., consumer sove ...
It`s All About Efficiency…
... – More we have, the more utility we have – Declining marginal utility ...
... – More we have, the more utility we have – Declining marginal utility ...
Economic Systems - Swan Hills School
... ◦ Examples of and values underlying the three main economic systems ◦ The features of the Canadian and American economies ◦ Mechanisms of control in mixed and market economies ◦ The impact of economic systems on individuals and groups within society ...
... ◦ Examples of and values underlying the three main economic systems ◦ The features of the Canadian and American economies ◦ Mechanisms of control in mixed and market economies ◦ The impact of economic systems on individuals and groups within society ...
How resources are allocated in a free market economy
... Economic decisions are taken by private individuals and firms, and private individuals own everything. There is no government intervention. In reality, governments usually intervene by implementing laws and public services, such as property rights and national defence. Adam Smith and Friedrich Hayek ...
... Economic decisions are taken by private individuals and firms, and private individuals own everything. There is no government intervention. In reality, governments usually intervene by implementing laws and public services, such as property rights and national defence. Adam Smith and Friedrich Hayek ...
Effects on the macro economy of more or less effective Land
... A registered property often serves as a collateral for credits financing the conveyance, without this collateral you may have to pay higher interest rates due to bigger risk. (0,01% of 22 billion is 2,2 million) ...
... A registered property often serves as a collateral for credits financing the conveyance, without this collateral you may have to pay higher interest rates due to bigger risk. (0,01% of 22 billion is 2,2 million) ...
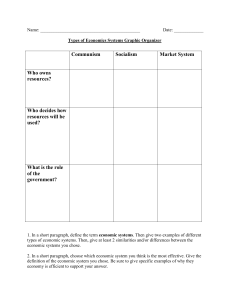
Communism Socialism Market System Who owns resources?
... system that has elements of traditional, command, and/or market economies. I think it is the most efficient economy because they can take the best parts of each individual economic system and combine them. For example, in the United States, we use a lot of market economy characteristics but governme ...
... system that has elements of traditional, command, and/or market economies. I think it is the most efficient economy because they can take the best parts of each individual economic system and combine them. For example, in the United States, we use a lot of market economy characteristics but governme ...
Parameters Evaluating the Impact of Agricultural Policy on the
... (IRC) are the main indicators for evaluating the market oriented to agricultural policy. A substantial reform concerning the agriculture, not only in transition country should include a reduction of the protectionism and a growth of the orientation towards the market. The protection of the market me ...
... (IRC) are the main indicators for evaluating the market oriented to agricultural policy. A substantial reform concerning the agriculture, not only in transition country should include a reduction of the protectionism and a growth of the orientation towards the market. The protection of the market me ...
BUS101 A.Lynch Quiz - Ch. 2
... 25. Michael has inherited $500,000 from the sale of a family business. His banker is advising he find multiple banks to deposit his money. Why? a) The Open Market Operations of the Federal Reserve would invest his money in other securities and might lose it without needing to justify the expenditure ...
... 25. Michael has inherited $500,000 from the sale of a family business. His banker is advising he find multiple banks to deposit his money. Why? a) The Open Market Operations of the Federal Reserve would invest his money in other securities and might lose it without needing to justify the expenditure ...
ECONOMIES IN TRANSITION PART I
... & services usually consumed or distributed by a governmental agency, in quantities, at prices & in locations determined by the ...
... & services usually consumed or distributed by a governmental agency, in quantities, at prices & in locations determined by the ...
How has the Constitution shaped the economic system in the United
... Market brings buyers & sellers of a particular good or service into contact with one another Sellers & buyers are registered on the supply & demand sides of various markets The prices participants in markets pay revise their free choices in furthering their self-interests. ...
... Market brings buyers & sellers of a particular good or service into contact with one another Sellers & buyers are registered on the supply & demand sides of various markets The prices participants in markets pay revise their free choices in furthering their self-interests. ...
Notes for Chapter Two - Old
... enough to dictate the price of a product. Monopolistic competition: The market situation in which a large number of sellers produce products that are very similar but that are perceived by buyers as different. Oligopoly: A form of competition in which just a few sellers dominate the market. Monopoly ...
... enough to dictate the price of a product. Monopolistic competition: The market situation in which a large number of sellers produce products that are very similar but that are perceived by buyers as different. Oligopoly: A form of competition in which just a few sellers dominate the market. Monopoly ...
Economic Systems of Europe
... ◦ C. Compare the basic types of economic systems found in the United Kingdom, Germany, and Russia. ...
... ◦ C. Compare the basic types of economic systems found in the United Kingdom, Germany, and Russia. ...