Review Questions and Answers What is the best definition of
... What are the name of the respective payments for the resources of land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship? The name of the payments are rent, wages, interest, and profit respectively. ...
... What are the name of the respective payments for the resources of land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship? The name of the payments are rent, wages, interest, and profit respectively. ...
The Economic Problem
... What is the Price Mechanism? Prices: • Convey information • Give incentives • Enables producers the financial capital to satisfy consumers wants and needs. ...
... What is the Price Mechanism? Prices: • Convey information • Give incentives • Enables producers the financial capital to satisfy consumers wants and needs. ...
RachKcomparing economic systems project copy
... legally binding contracts to buy, sell, lease, or rent their property. That means free market has to do with household and firm because they both go with owning property and selling items. The household owns the factors of production and they privately own the property. Firm is the organization that ...
... legally binding contracts to buy, sell, lease, or rent their property. That means free market has to do with household and firm because they both go with owning property and selling items. The household owns the factors of production and they privately own the property. Firm is the organization that ...
Roles in Mixed and Market Economies
... market (buyers and sellers meet) regulates most economic decision-making production is as efficient as possible to create the maximum amount of profit goods are produced only if there is a market Free Enterprise: (Adam Smith) mercantilism wrong allow colonies to be equal trading partners ...
... market (buyers and sellers meet) regulates most economic decision-making production is as efficient as possible to create the maximum amount of profit goods are produced only if there is a market Free Enterprise: (Adam Smith) mercantilism wrong allow colonies to be equal trading partners ...
Mr. Greenspan examines the process by which former centrally
... arrears, or even defaults, are largely irrelevant in the sense that they are essentially transactions among enterprises owned by the same entity, that is, the state. Under central planning there are no credit standards, no interest rate risks, no market value changes, that is, none of the key financ ...
... arrears, or even defaults, are largely irrelevant in the sense that they are essentially transactions among enterprises owned by the same entity, that is, the state. Under central planning there are no credit standards, no interest rate risks, no market value changes, that is, none of the key financ ...
Textbook: Microeconomics
... Efficiency is one criterion. Efficiency means that an economy’s resources are used in such a way that all opportunities to make people better off are exhausted. So you can only make some people better off by making someone else worse off. Another criterion many economists take into account is equity ...
... Efficiency is one criterion. Efficiency means that an economy’s resources are used in such a way that all opportunities to make people better off are exhausted. So you can only make some people better off by making someone else worse off. Another criterion many economists take into account is equity ...
Black Market Reading
... penalty for so-called “economic crimes.” The Nazi regime was destroyed by World War II before it was old enough to undergo any very extensive modifications, but it was surely no accident that even the first very tentative and partial gestures by the various Communist regimes to abolish or restrain m ...
... penalty for so-called “economic crimes.” The Nazi regime was destroyed by World War II before it was old enough to undergo any very extensive modifications, but it was surely no accident that even the first very tentative and partial gestures by the various Communist regimes to abolish or restrain m ...
title slide - De Anza College
... • Contrary to Malthus, some economists believe a large population can be a resource. - An educated population is a highly valuable. - Business owners provide jobs and economic growth for their employees and communities as well as for themselves. ...
... • Contrary to Malthus, some economists believe a large population can be a resource. - An educated population is a highly valuable. - Business owners provide jobs and economic growth for their employees and communities as well as for themselves. ...
Free market system
... until 1936, when John Maynard Keynes published his revolutionary General Theory of Employment, interest and money. A that time, England and the United States were still stuck in the Great Depression of the 1930’s with over one- quarter of the American labor force unemployed. In his new theory Keynes ...
... until 1936, when John Maynard Keynes published his revolutionary General Theory of Employment, interest and money. A that time, England and the United States were still stuck in the Great Depression of the 1930’s with over one- quarter of the American labor force unemployed. In his new theory Keynes ...
Economics_files/econ unit 1and2 Online
... 24) The feature that distinguishes the U.S. economy from the pure market model is a. private ownership of the factors of production. b. contractual relationships between businesses and individuals. c. limited government involvement. d. self-interest and incentives. 25) Which of the following economi ...
... 24) The feature that distinguishes the U.S. economy from the pure market model is a. private ownership of the factors of production. b. contractual relationships between businesses and individuals. c. limited government involvement. d. self-interest and incentives. 25) Which of the following economi ...
January 2016
... Although we rarely find instances where all the conditions for pure competition are met, the foreign exchange market displays many of these characteristics. For example, in this market there are a large number of banks (or dealers) active in the market, each bank holding a very small share of the to ...
... Although we rarely find instances where all the conditions for pure competition are met, the foreign exchange market displays many of these characteristics. For example, in this market there are a large number of banks (or dealers) active in the market, each bank holding a very small share of the to ...
market notice - The Australian Financial Markets Association
... [Issuer name] [Rating] [Guarantee if applicable] has launched a minimum A$ [XXX] increase to its [Coupon] [Maturity date] line. The trade is being marketed at asw+[XX]sq / ACGB MMYY+[XX] and will price on or before DD-MM-YY. [Dealer name/s] are the lead managers. Queries in relation to this should b ...
... [Issuer name] [Rating] [Guarantee if applicable] has launched a minimum A$ [XXX] increase to its [Coupon] [Maturity date] line. The trade is being marketed at asw+[XX]sq / ACGB MMYY+[XX] and will price on or before DD-MM-YY. [Dealer name/s] are the lead managers. Queries in relation to this should b ...
Economics - Teddington School
... Friedrich Hayek was a key supporter of the free market and deeply critical of socialism (state planning). He believed that the resource allocation brought about by individuals, spontaneously, by the operation of market forces, would be far superior to any state planning system. He believed that gove ...
... Friedrich Hayek was a key supporter of the free market and deeply critical of socialism (state planning). He believed that the resource allocation brought about by individuals, spontaneously, by the operation of market forces, would be far superior to any state planning system. He believed that gove ...
The Market System and the Circular Flow
... • Set of institutional arrangements • Coordinating mechanism • Differences in systems exist by: • Who owns the factors of production • What method is used to motivate, coordinate, and direct economic activity LO1 ...
... • Set of institutional arrangements • Coordinating mechanism • Differences in systems exist by: • Who owns the factors of production • What method is used to motivate, coordinate, and direct economic activity LO1 ...
The Political Economy of Asian Transition from Communism Edited
... developmental stagnation caused a crisis of the central planning system. The crisis was intensified by the disastrous economic results of leftist policies in China and in other countries. Economic stagnation and comparisons with the western world adversely influenced ideology and shattered the faith o ...
... developmental stagnation caused a crisis of the central planning system. The crisis was intensified by the disastrous economic results of leftist policies in China and in other countries. Economic stagnation and comparisons with the western world adversely influenced ideology and shattered the faith o ...
Markets and Economic Theory
... allows individuals to benefit from natural differences in tastes and talents and (in the case of international trade) differences in climate and institutional arrangements. The second aspect allows individuals to take advantage of the productivity increases that specialization creates – increases th ...
... allows individuals to benefit from natural differences in tastes and talents and (in the case of international trade) differences in climate and institutional arrangements. The second aspect allows individuals to take advantage of the productivity increases that specialization creates – increases th ...
ideologies and perspectives
... the norm that governments should not . Positives of the neoclassical perspective are that it highlights the importance of markets. It seeks to avoid the command economy with controlled markets such as occurred in the old Soviet Union. This perspective promotes incentives to produce; it can contribut ...
... the norm that governments should not . Positives of the neoclassical perspective are that it highlights the importance of markets. It seeks to avoid the command economy with controlled markets such as occurred in the old Soviet Union. This perspective promotes incentives to produce; it can contribut ...
Chapter 2 Economic Theories and Measurements
... IMPERFECT COMPETITION is an economic situation in which many sellers and buyers have some degree of control over prices ...
... IMPERFECT COMPETITION is an economic situation in which many sellers and buyers have some degree of control over prices ...
When the Market Was Not Free Economics Name: E. Napp Date
... 7- Laissez faire is A- The doctrine that states that government generally should not intervene in the marketplace. B- A period of change in which an economy moves away from a centrally planned economy toward a market-based system. C- A social and political philosophy characterized by its fair distri ...
... 7- Laissez faire is A- The doctrine that states that government generally should not intervene in the marketplace. B- A period of change in which an economy moves away from a centrally planned economy toward a market-based system. C- A social and political philosophy characterized by its fair distri ...
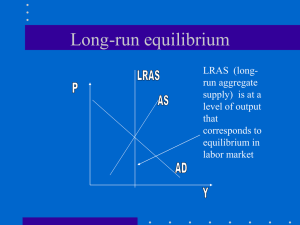
Long-run equilibrium
... taken place in the goods market) the economy returns to its potential level of RGDP. ...
... taken place in the goods market) the economy returns to its potential level of RGDP. ...
Gregory Mankiw Ten Principles of Economics
... Definition of market economy: an economy that allocates resources through the decentralized decisions of many firms and households as they interact in markets for goods and services. Market prices reflect both the value of a product to consumers and the cost of the resources used to produce it. Cent ...
... Definition of market economy: an economy that allocates resources through the decentralized decisions of many firms and households as they interact in markets for goods and services. Market prices reflect both the value of a product to consumers and the cost of the resources used to produce it. Cent ...
market
... own self-interests without any central direction or regulation. • The central institution of a laissezfaire economy is the free-market system. • A market is the institution through which buyers and sellers interact and engage in exchange. ...
... own self-interests without any central direction or regulation. • The central institution of a laissezfaire economy is the free-market system. • A market is the institution through which buyers and sellers interact and engage in exchange. ...
What Economic Structure for Socialism?
... would like to purchase, with the power to set rewards and penalties to back up their demands. If the top political leaders are dependent on popular support for staying in office, they would be under pressure to make the system work to meet the needs of ordinary people. Democratic institutions, which ...
... would like to purchase, with the power to set rewards and penalties to back up their demands. If the top political leaders are dependent on popular support for staying in office, they would be under pressure to make the system work to meet the needs of ordinary people. Democratic institutions, which ...
Economics
... Although there are mainly two systems, many economic principles and theories derive from either Socialism or Capitalism. Most countries have a mixed economy, such as Welfare Capitalism in the United States. ...
... Although there are mainly two systems, many economic principles and theories derive from either Socialism or Capitalism. Most countries have a mixed economy, such as Welfare Capitalism in the United States. ...
Moral_underpinnigs_of_capitalism
... MARKET FAILURES THIS SYSTEMS, THOUGH STILL IMPLEMENTED, IGNITES SERIOUS LACK OF MORALITY AND IGNITES URGENT NEED FOR SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY. WHY? BECAUSE, THE SYSTEM THAT PROMOTES SALE AND PRICING FOR EVERYTHING THAT CAN COME TO YOUR MIND, MONETIZING IDEALS AND COMMERCIALIZING FAITH CREATES SLOW BUT ...
... MARKET FAILURES THIS SYSTEMS, THOUGH STILL IMPLEMENTED, IGNITES SERIOUS LACK OF MORALITY AND IGNITES URGENT NEED FOR SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY. WHY? BECAUSE, THE SYSTEM THAT PROMOTES SALE AND PRICING FOR EVERYTHING THAT CAN COME TO YOUR MIND, MONETIZING IDEALS AND COMMERCIALIZING FAITH CREATES SLOW BUT ...