PowerPoint slides - Physics 420 UBC Physics Demonstrations
... • Different designs: magnet can be either rotor or stator • Some motors use an electromagnet instead of a permanent magnet • All designs operate on the same principle described here ...
... • Different designs: magnet can be either rotor or stator • Some motors use an electromagnet instead of a permanent magnet • All designs operate on the same principle described here ...
Chapter 8 Section 3
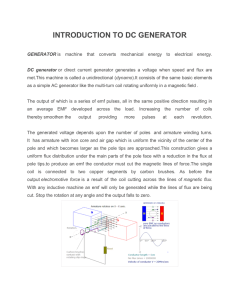
... When the coil is fixed and the magnet rotates, the current is the same as if the coil rotates and the magnet is fixed. Construction of a generator in a power plant Electromagnets contain coils of wire wrapped around ...
... When the coil is fixed and the magnet rotates, the current is the same as if the coil rotates and the magnet is fixed. Construction of a generator in a power plant Electromagnets contain coils of wire wrapped around ...
fourth nine weeks
... 1. Know that electrical energy is the flow of electrons through electrical conductors that connect sources of electrical energy to points of use, including: • electrical current paths through parallel and series circuits • production of electricity by fossil-fueled and nuclear power plants, wind gen ...
... 1. Know that electrical energy is the flow of electrons through electrical conductors that connect sources of electrical energy to points of use, including: • electrical current paths through parallel and series circuits • production of electricity by fossil-fueled and nuclear power plants, wind gen ...
Induction Motors
... Induction Motor by Bullet Points • Stator generates rotating, sinusoidal B-Field: • This field induces current in the rotor cage loops at f f f ur ur i • The stator B-Field at each rotor wire is such that B $ • Torque pushes in direction of field rotation! (That’s it!!) • Rotor currents ge ...
... Induction Motor by Bullet Points • Stator generates rotating, sinusoidal B-Field: • This field induces current in the rotor cage loops at f f f ur ur i • The stator B-Field at each rotor wire is such that B $ • Torque pushes in direction of field rotation! (That’s it!!) • Rotor currents ge ...
Physics 10 chapter 22 HW Solution
... becomes heat energy. In this sense it is used up. 30. Damage generally occurs by excess heating when too much current is driven through an appliance. For an appliance that converts electrical energy directly to thermal energy this happens when excess voltage is applied. So don’t connect a 110-volt i ...
... becomes heat energy. In this sense it is used up. 30. Damage generally occurs by excess heating when too much current is driven through an appliance. For an appliance that converts electrical energy directly to thermal energy this happens when excess voltage is applied. So don’t connect a 110-volt i ...
Used to determine the direction of emf induced in a conductor
... A generator works on the principles of Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction Whenever a conductor is moved in the magnetic field , an emf is induced and the magnitude of the induced emf is directly proportional to the rate of change of flux ...
... A generator works on the principles of Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction Whenever a conductor is moved in the magnetic field , an emf is induced and the magnitude of the induced emf is directly proportional to the rate of change of flux ...
General Science Mr. Tiesler Magnetism Test Study Guide
... Moving electric charges produce magnetic force and moving magnets produce electric force. Galvanometers detect electric current using a solenoid. A commutator is also called a reversing switch. It reverses the direction of the current in an electromagnet. Electromagnets convert electrical en ...
... Moving electric charges produce magnetic force and moving magnets produce electric force. Galvanometers detect electric current using a solenoid. A commutator is also called a reversing switch. It reverses the direction of the current in an electromagnet. Electromagnets convert electrical en ...
Experiment 5: Principle of 3 phase induction motor
... Objective: To understand the structure and principle of 3 – phase induction motor and to control the rotary direction ...
... Objective: To understand the structure and principle of 3 – phase induction motor and to control the rotary direction ...
EE3003-ModelPaper-2013
... (a) Draw the typical Toque/Slip and Torque/Speed characteristics of a three phase induction motor separately. Indicate all the operating modes on the same plot. (b) A three phase 4-pole, 400V, 50Hz squirrel cage induction motor has the following equivalent circuit parameters referred to the stator s ...
... (a) Draw the typical Toque/Slip and Torque/Speed characteristics of a three phase induction motor separately. Indicate all the operating modes on the same plot. (b) A three phase 4-pole, 400V, 50Hz squirrel cage induction motor has the following equivalent circuit parameters referred to the stator s ...
Magnetism and spintransport in the heterostructure of Ferroelectric/ferromagnetic films
... The operation of the current generation magnetic memories is based on the control of magnetization by a magnetic field generated by a current through wires or a local magnetic field generated from current through the spin-torque transfer. These two approaches unfortunately suffer from significant en ...
... The operation of the current generation magnetic memories is based on the control of magnetization by a magnetic field generated by a current through wires or a local magnetic field generated from current through the spin-torque transfer. These two approaches unfortunately suffer from significant en ...
Electromagnetic Induction Notes
... materials, the voltage induced is the same for each case • The most current will be produced in the material where the electrons are bound most loosely – i.e.) The magnet will produce a larger current when moving past copper than rubber ...
... materials, the voltage induced is the same for each case • The most current will be produced in the material where the electrons are bound most loosely – i.e.) The magnet will produce a larger current when moving past copper than rubber ...
Lesson 5 Magnetism and Electricity Notes
... Has the same parts as a motor (power source, magnet, and wire loop attached to a shaft). ...
... Has the same parts as a motor (power source, magnet, and wire loop attached to a shaft). ...
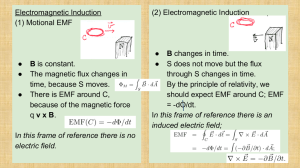
Electromagnetic Induction (2) Electromagnetic Induction (1) Motional EMF ●
... opposes the change of flux. Example -- The magnet is above the conductor, moving downward. -- Calculate the clockwise EMF. -- Define n to be the downward normal vector. ...
... opposes the change of flux. Example -- The magnet is above the conductor, moving downward. -- Calculate the clockwise EMF. -- Define n to be the downward normal vector. ...