Stepper Motor
... six, and sometimes more wires. Also, when we manually rotate the shaft, we get a ‘notched’ feeling. The simplest way to think about a stepper motor is as a bar magnet that pivots about its center with four individual, but exactly identical electromagnets, as shown in Figure 1A. If we manually rotate ...
... six, and sometimes more wires. Also, when we manually rotate the shaft, we get a ‘notched’ feeling. The simplest way to think about a stepper motor is as a bar magnet that pivots about its center with four individual, but exactly identical electromagnets, as shown in Figure 1A. If we manually rotate ...
Topic 6 - Raymond Junior High School
... flows in the coil, one end of the core becomes a magnetic north pole and the other the south pole. When more coils of wire are wrapped around the iron core, the strength of the magnet increases. Increasing the current also results in a stronger magnet. If the direction of the current is reversed, the ...
... flows in the coil, one end of the core becomes a magnetic north pole and the other the south pole. When more coils of wire are wrapped around the iron core, the strength of the magnet increases. Increasing the current also results in a stronger magnet. If the direction of the current is reversed, the ...
Unit 4 Electrical Principles and Technologies - Topic 6
... flows in the coil, one end of the core becomes a magnetic north pole and the other the south pole. When more coils of wire are wrapped around the iron core, the strength of the magnet increases. Increasing the current also results in a stronger magnet. If the direction of the current is reversed, the ...
... flows in the coil, one end of the core becomes a magnetic north pole and the other the south pole. When more coils of wire are wrapped around the iron core, the strength of the magnet increases. Increasing the current also results in a stronger magnet. If the direction of the current is reversed, the ...
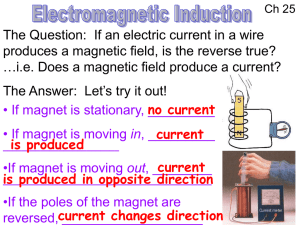
in the primary coil
... nearby secondary coil, which according to voltage in the Faraday’s Law, will induce a _________ secondary coil, (which then produces a current) The effect is enhanced (larger current produced in secondary) if an iron core is added…. DEMO ...
... nearby secondary coil, which according to voltage in the Faraday’s Law, will induce a _________ secondary coil, (which then produces a current) The effect is enhanced (larger current produced in secondary) if an iron core is added…. DEMO ...
Faculty of Electrical Engineering Three phase permanent magnet
... that the rotor of the motor can be rotated at desired angle based on stator axis as the reference. The sequence analysis can be used in order to get the commutation sequence by analyzing hall sensor and phase current signals. The speed of BLDC can be controlled by varying the average voltage or curr ...
... that the rotor of the motor can be rotated at desired angle based on stator axis as the reference. The sequence analysis can be used in order to get the commutation sequence by analyzing hall sensor and phase current signals. The speed of BLDC can be controlled by varying the average voltage or curr ...
Study Guide
... and bound charges is the total charge and the enclosed charges will be the sum of both free and bound charges. Free charges might consist of electrons on a conductor or ions embedded in the dielectric material or whatever. Free Current Free current is the current that is not caused by the magnetic f ...
... and bound charges is the total charge and the enclosed charges will be the sum of both free and bound charges. Free charges might consist of electrons on a conductor or ions embedded in the dielectric material or whatever. Free Current Free current is the current that is not caused by the magnetic f ...
Why do things move? - Utah State University
... • To keep coil turning in an electric motor must reverse current direction every ½ cycle. • AC current is well suited for operating electric motors. • In a DC motor need to use a “split ring” or “commutator” to reverse current. ...
... • To keep coil turning in an electric motor must reverse current direction every ½ cycle. • AC current is well suited for operating electric motors. • In a DC motor need to use a “split ring” or “commutator” to reverse current. ...
Initial Design of 12s-10p and 12s-14p with Outer
... excitation is the best candidate with a decent performance with a low cost of manufactured. Hence, FEFSM motor has a huge advantages in the construction (simple), magnet-less, and variable flux control capabilities which suitable for various performances. Since the permanent magnet is being used wid ...
... excitation is the best candidate with a decent performance with a low cost of manufactured. Hence, FEFSM motor has a huge advantages in the construction (simple), magnet-less, and variable flux control capabilities which suitable for various performances. Since the permanent magnet is being used wid ...
Document
... electrochemical cells supply DC. When the direction of charges reverses periodically back and forth it called Alternating Current (AC). Outlets at home and elsewhere are sources of AC. In the U.S the outlets provide 110 to 120 V, AC at 60 Hz. ...
... electrochemical cells supply DC. When the direction of charges reverses periodically back and forth it called Alternating Current (AC). Outlets at home and elsewhere are sources of AC. In the U.S the outlets provide 110 to 120 V, AC at 60 Hz. ...
April 2007 - CEME Logo Research Projects by Area
... Full-rated converter allows for complete speed and reactive power control. Could also be used with a synchronous generator. ...
... Full-rated converter allows for complete speed and reactive power control. Could also be used with a synchronous generator. ...
experiment 6 - Portal UniMAP
... can be changed from 90°ahead to 90° behind just by switching the connections on the auxiliary winding, the direction of the rotation of the motor can be reversed by switching the connections of the auxiliary winding while leaving the main winding’s connection unchanged. Capacitor-Start Motor In a ca ...
... can be changed from 90°ahead to 90° behind just by switching the connections on the auxiliary winding, the direction of the rotation of the motor can be reversed by switching the connections of the auxiliary winding while leaving the main winding’s connection unchanged. Capacitor-Start Motor In a ca ...
File
... one magnet will attract the south end of the other. On the other hand, the north end of one magnet will repel the north end of the other (and similarly, south will repel south). Inside an electric motor, these attracting and repelling forces create ___________________________________. In the above d ...
... one magnet will attract the south end of the other. On the other hand, the north end of one magnet will repel the north end of the other (and similarly, south will repel south). Inside an electric motor, these attracting and repelling forces create ___________________________________. In the above d ...
Determination of Rotor Slot Number of an Induction Motor Using an
... In this paper a method for the prediction of the number of slots of an induction motor is proposed. The approach is based on FFT analysis of the induced voltage in an external search coil. It is shown that the method works well irrespective of whether the motor is driven by the mains voltage or via ...
... In this paper a method for the prediction of the number of slots of an induction motor is proposed. The approach is based on FFT analysis of the induced voltage in an external search coil. It is shown that the method works well irrespective of whether the motor is driven by the mains voltage or via ...
In this lab we will examine the equipotential lines and electric field
... 1) The electric field inside a conductor is everywhere zero. If it were not, free electrons inside the conductor would feel this field and flow in such a way as to reduce it, soon to zero. 2) The potential is the same everywhere inside a conductor. This follows immediately from 1. 3) A point where t ...
... 1) The electric field inside a conductor is everywhere zero. If it were not, free electrons inside the conductor would feel this field and flow in such a way as to reduce it, soon to zero. 2) The potential is the same everywhere inside a conductor. This follows immediately from 1. 3) A point where t ...
16-8 Field Lines
... 2. Explain the patterns of electric fields in terms of conductors. 3. Explain the key components of Guass’s Law. Homework: 32-38 even, 43-49 odd pp. 466-467 Formula Search –Find all formulas state the units and purpose for making calculations. ...
... 2. Explain the patterns of electric fields in terms of conductors. 3. Explain the key components of Guass’s Law. Homework: 32-38 even, 43-49 odd pp. 466-467 Formula Search –Find all formulas state the units and purpose for making calculations. ...
III. generator systems for wind turbines
... by the reactive power injection into the node, and since the generator must operate within its reactive capability curve it is not possible to control the voltage outside certain limits. The reactive capability of a generator depends on a number of quantities, such as active power, bus voltage and o ...
... by the reactive power injection into the node, and since the generator must operate within its reactive capability curve it is not possible to control the voltage outside certain limits. The reactive capability of a generator depends on a number of quantities, such as active power, bus voltage and o ...