Biochemistry of Cells - Lakewood City Schools
... creates an area known as the active site. The nature and arrangement of amino acids in the active site make it specific for only one type of substrate. ...
... creates an area known as the active site. The nature and arrangement of amino acids in the active site make it specific for only one type of substrate. ...
Amino Acid Structure
... Amino Acid ID Quiz: http://www.bio.cmu.edu/Courses/BiochemMols/aaIDCQz/aaQCMain.htm Amino Acid Structures: http://www.clunet.edu/BioDev/omm/aa/aa.htm Amino Acid Tutorial: http://iws.ohiolink.edu/chemistry/biochemistry/aatut.html Chemistry for Kids: http://www.chem4kids.com/map.html California Scienc ...
... Amino Acid ID Quiz: http://www.bio.cmu.edu/Courses/BiochemMols/aaIDCQz/aaQCMain.htm Amino Acid Structures: http://www.clunet.edu/BioDev/omm/aa/aa.htm Amino Acid Tutorial: http://iws.ohiolink.edu/chemistry/biochemistry/aatut.html Chemistry for Kids: http://www.chem4kids.com/map.html California Scienc ...
Name: :___________Date
... Name:_________________________Period:___________Date:______________ Google: “biology interactive” and choose: “life organization” and view animation. List the steps of organization in order from smallest to largest and an example of each. CELLS ALIVE ...
... Name:_________________________Period:___________Date:______________ Google: “biology interactive” and choose: “life organization” and view animation. List the steps of organization in order from smallest to largest and an example of each. CELLS ALIVE ...
CHEMISTRY LIST OF TOPICS 1. Nature of chemistry (matter, mass
... heterocycles, five and six- membered ring containing heterocycles with one and more heteroatom(s), heterocycle derivatives);. 12. Carbohydrates (monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides); 13. Lipids (simple and complex lipids, fatty acids, waxes, phospholipids, isoprenoids, terpenes and st ...
... heterocycles, five and six- membered ring containing heterocycles with one and more heteroatom(s), heterocycle derivatives);. 12. Carbohydrates (monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides); 13. Lipids (simple and complex lipids, fatty acids, waxes, phospholipids, isoprenoids, terpenes and st ...
Molecular Models Concept Map
... Word Bank: Amino acids, animals, carbohydrates, DNA, disaccharide, fructose, glucose, glycogen, isoleucine, leucine, lipids, monosaccharide, nucleic acids, phospholipids, plants, polypeptides, polysaccharides, proteins, RNA, saturated, serine, starch, steroids, ...
... Word Bank: Amino acids, animals, carbohydrates, DNA, disaccharide, fructose, glucose, glycogen, isoleucine, leucine, lipids, monosaccharide, nucleic acids, phospholipids, plants, polypeptides, polysaccharides, proteins, RNA, saturated, serine, starch, steroids, ...
What is DNA?
... • Some mutations are negative, and have some negative impact on the organism • Some mutations are beneficial and help the organism to be more successful ...
... • Some mutations are negative, and have some negative impact on the organism • Some mutations are beneficial and help the organism to be more successful ...
3. Organic Compounds
... Amino Acids are the subunits of proteins. Each amino acid contains an amino group (which is basic) and an acid group. Proteins consist of long chains of amino acids, with the acid group of one bonded to the amino group of the next. There are 20 different kinds of amino acids in proteins. Each one ha ...
... Amino Acids are the subunits of proteins. Each amino acid contains an amino group (which is basic) and an acid group. Proteins consist of long chains of amino acids, with the acid group of one bonded to the amino group of the next. There are 20 different kinds of amino acids in proteins. Each one ha ...
Chapter 1 • Lesson 3
... long-term energy storage, and they insulate and waterproof the organism. For example, cutin and other waxes coat the leaves of some plants to help prevent water loss. Steroids and phospholipids are two groups of lipids. Steroids are lipids that have molecules arranged in rings, rather than as long c ...
... long-term energy storage, and they insulate and waterproof the organism. For example, cutin and other waxes coat the leaves of some plants to help prevent water loss. Steroids and phospholipids are two groups of lipids. Steroids are lipids that have molecules arranged in rings, rather than as long c ...
Lecture 3
... Amino acid monomers held together by covalent bonds Peptide bonds. Polypeptides: thousands or millions of amino acids Have two distinct ends: one terminating in an a amino group (the amino- or N- terminus) and the other is an a carboxylic group (carboxyl or ...
... Amino acid monomers held together by covalent bonds Peptide bonds. Polypeptides: thousands or millions of amino acids Have two distinct ends: one terminating in an a amino group (the amino- or N- terminus) and the other is an a carboxylic group (carboxyl or ...
sugar
... Proteins = built from amino acids amino amino amino amino amino amino acid – acid – acid – acid – acid – acid Nucleic acids (DNA) = built from nucleotides ...
... Proteins = built from amino acids amino amino amino amino amino amino acid – acid – acid – acid – acid – acid Nucleic acids (DNA) = built from nucleotides ...
File
... There are exactly 20 different amino acids. Think of them like beads on a strand. Which beads you put on and in which order determines the necklace. The _________ is unique to each amino acid. It is what makes it different from other amino acids. Amino acids are monomers and they come together to ma ...
... There are exactly 20 different amino acids. Think of them like beads on a strand. Which beads you put on and in which order determines the necklace. The _________ is unique to each amino acid. It is what makes it different from other amino acids. Amino acids are monomers and they come together to ma ...
Pairwise Alignments Part 1
... Pairwise GLOBAL alignment of retinol-binding protein from human (top) and rainbow trout (O. mykiss) ...
... Pairwise GLOBAL alignment of retinol-binding protein from human (top) and rainbow trout (O. mykiss) ...
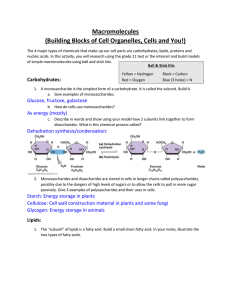
Macromolecules
... Lipids Lipids constitute a very diverse group of molecules that all share the property of being hydrophobic. Fats and oils are lipids generally associated with ...
... Lipids Lipids constitute a very diverse group of molecules that all share the property of being hydrophobic. Fats and oils are lipids generally associated with ...
Molecules of Life---Whoa! - Rimac-Science-Web
... • The R-group can also be a Hydrogen. • In this case it is whatever is attached to the amino and carboxyl groups that make up the amino acid. ...
... • The R-group can also be a Hydrogen. • In this case it is whatever is attached to the amino and carboxyl groups that make up the amino acid. ...
Macromolecules
... 4. Looking at an overall protein, would you say that amino acids more closely resemble monosaccharides in carbohydrates or fatty acids in lipids? Explain. ...
... 4. Looking at an overall protein, would you say that amino acids more closely resemble monosaccharides in carbohydrates or fatty acids in lipids? Explain. ...
snews
... Asteriods carrying alien life ?? The search for life outside the earth has always fascinated humanity. The big question is this: if there is life elsewhere, what form might it have taken ? Naturally, we would look for life forms similar to ours. Some scientists have even suggested that life on earth ...
... Asteriods carrying alien life ?? The search for life outside the earth has always fascinated humanity. The big question is this: if there is life elsewhere, what form might it have taken ? Naturally, we would look for life forms similar to ours. Some scientists have even suggested that life on earth ...
DNA - KK College of Nursing
... DNA is also used as a long term storage device to store the genetic instructions ...
... DNA is also used as a long term storage device to store the genetic instructions ...
Translation - St. Robert CHS
... by the ribosomes • AUG ensures that the correct reading frame is used by the ...
... by the ribosomes • AUG ensures that the correct reading frame is used by the ...
HW and review worksheet
... acids; many amino acids linked together is called a polypeptide. Is a polypeptide the same as a protein? Know the general structure of amino acids and how to recognize a peptide bond 2. Amino acids differ from each other only by a variable part of the molecule called the R group. Based on the R grou ...
... acids; many amino acids linked together is called a polypeptide. Is a polypeptide the same as a protein? Know the general structure of amino acids and how to recognize a peptide bond 2. Amino acids differ from each other only by a variable part of the molecule called the R group. Based on the R grou ...
File
... 1. DNA or RNA? 2. Write the complimentary DNA sequence 3. Write the mRNA sequence 4. Write the protein sequence. ...
... 1. DNA or RNA? 2. Write the complimentary DNA sequence 3. Write the mRNA sequence 4. Write the protein sequence. ...
Amino Acid Instruction Sheet
... Proteins are made of small building blocks called amino acids. Humans can make all but 8 amino acids in our bodies. Humans acquire the 8 amino acids we do not make in our bodies by eating food. When we eat animal or vegetable protein, our body breaks down the protein back into amino acids. Once dig ...
... Proteins are made of small building blocks called amino acids. Humans can make all but 8 amino acids in our bodies. Humans acquire the 8 amino acids we do not make in our bodies by eating food. When we eat animal or vegetable protein, our body breaks down the protein back into amino acids. Once dig ...
Biochemistry: the study of the chemical reactions of life
... Life involves the most complex chemistry known to man. For example, the chemical composition of the human body is known down to the microgram, but we are unable to replicate even the simplest living thing in the lab. Knowing the chemicals involved and understanding how the reaction mechanisms fit to ...
... Life involves the most complex chemistry known to man. For example, the chemical composition of the human body is known down to the microgram, but we are unable to replicate even the simplest living thing in the lab. Knowing the chemicals involved and understanding how the reaction mechanisms fit to ...
Point accepted mutation

A point accepted mutation — also known as a PAM — is the replacement of a single amino acid in the primary structure of a protein with another single amino acid, which is accepted by the processes of natural selection. This definition does not include all point mutations in the DNA of an organism. In particular, silent mutations are not point accepted mutations, nor are mutations which are lethal or which are rejected by natural selection in other ways.A PAM matrix is a matrix where each column and row represents one of the twenty standard amino acids. In bioinformatics, PAM matrices are regularly used as substitution matrices to score sequence alignments for proteins. Each entry in a PAM matrix indicates the likelihood of the amino acid of that row being replaced with the amino acid of that column through a series of one or more point accepted mutations during a specified evolutionary interval, rather than these two amino acids being aligned due to chance. Different PAM matrices correspond to different lengths of time in the evolution of the protein sequence.