File
... After Djoser, the stepped pyramid became the norm for royal burials, although none of those planned by his dynastic successors were completed (probably due to their relatively short reigns). The earliest tomb constructed as a "true" (smooth-sided, not stepped) pyramid was the Red Pyramid at Dahshur, ...
... After Djoser, the stepped pyramid became the norm for royal burials, although none of those planned by his dynastic successors were completed (probably due to their relatively short reigns). The earliest tomb constructed as a "true" (smooth-sided, not stepped) pyramid was the Red Pyramid at Dahshur, ...
Ancient Egypt
... 3. 3100 B.C. – King Menes unites Upper and Lower Egypt and established a capital at Memphis a. Hereditary Rule - Menes’ reign marks the beginning of the first Egyptian dynasty – a line of rulers from one family. ...
... 3. 3100 B.C. – King Menes unites Upper and Lower Egypt and established a capital at Memphis a. Hereditary Rule - Menes’ reign marks the beginning of the first Egyptian dynasty – a line of rulers from one family. ...
Egypt unit 1 - Cobb Learning
... scribes developed hieroglyphics (which comes from the Greek for sacred carving) • Originally written on stone, but developed papyrus, a paper-like substance made from reeds. ...
... scribes developed hieroglyphics (which comes from the Greek for sacred carving) • Originally written on stone, but developed papyrus, a paper-like substance made from reeds. ...
Three Kingdoms of Egypt
... The Egyptians took control of all possible invasion routes into the kingdom by conquering certain people and becoming the leading military power in that area. 3. Why was trade important to the Egyptians? Trade brought valuable resources into Egypt. Also, money made from trade helped to fund the arts ...
... The Egyptians took control of all possible invasion routes into the kingdom by conquering certain people and becoming the leading military power in that area. 3. Why was trade important to the Egyptians? Trade brought valuable resources into Egypt. Also, money made from trade helped to fund the arts ...
Government
... • Led his armies down the mountains into the delta • Conquered Lower Egypt and married one of Lower Egyptian princesses • This unified the kingdoms – for the first time, all of Egypt was ruled by one king • He established a new capital at Memphis which is a border city between Upper and Lower Egypt ...
... • Led his armies down the mountains into the delta • Conquered Lower Egypt and married one of Lower Egyptian princesses • This unified the kingdoms – for the first time, all of Egypt was ruled by one king • He established a new capital at Memphis which is a border city between Upper and Lower Egypt ...
CH-3-LECTURE
... – Food and drink was provided – nothing that was enjoyed on earth was lacking. – These practices existed for thousands of years, even when ruled by the Greeks & Romans. ...
... – Food and drink was provided – nothing that was enjoyed on earth was lacking. – These practices existed for thousands of years, even when ruled by the Greeks & Romans. ...
Lesson - Haiku
... Khufu was one child who followed his father’s example. His father, Snefru (SNEHF•ROO), was a warrior king who brought prosperity to Egypt. Snefru celebrated his deeds by building the first true pyramid as his burial monument. Khufu liked the pyramid’s design, but he decided that bigger was even bett ...
... Khufu was one child who followed his father’s example. His father, Snefru (SNEHF•ROO), was a warrior king who brought prosperity to Egypt. Snefru celebrated his deeds by building the first true pyramid as his burial monument. Khufu liked the pyramid’s design, but he decided that bigger was even bett ...
The Later Middle Ages
... triangle-shaped area of soil deposited by a river. (delta/cataract) 2. Egyptians believed that a person’s ________________________ left the body and became a spirit after death. (sarcophagus/ka) 3. A powerful pharaoh reunited the ________________________ around 2050 BC. (Middle Kingdom/New Kingdom) ...
... triangle-shaped area of soil deposited by a river. (delta/cataract) 2. Egyptians believed that a person’s ________________________ left the body and became a spirit after death. (sarcophagus/ka) 3. A powerful pharaoh reunited the ________________________ around 2050 BC. (Middle Kingdom/New Kingdom) ...
Egypt`s Religious, Intellectual, Technological, and Economic History
... constructing them as well as a monument to his greatness. The one female pharaoh did not build a pyramid, but she did build a temple. Hatshepsut called her temple the Sublime of the Sublimes which is considered to be the most beautiful temple in Egypt and is being completely restored by the governme ...
... constructing them as well as a monument to his greatness. The one female pharaoh did not build a pyramid, but she did build a temple. Hatshepsut called her temple the Sublime of the Sublimes which is considered to be the most beautiful temple in Egypt and is being completely restored by the governme ...
Egypt Common Assessment
... 1. “Egypt is the gift of the Nile.” - Herodotus What did Herodotus mean when he made this statement? ...
... 1. “Egypt is the gift of the Nile.” - Herodotus What did Herodotus mean when he made this statement? ...
Study Guide: Ancient Egypt
... 2. The Greeks called Egypt “The Gift of the Nile” because the Nile was so important 3. I think that Upper Egypt was more important to a ruler because it had more cities. ...
... 2. The Greeks called Egypt “The Gift of the Nile” because the Nile was so important 3. I think that Upper Egypt was more important to a ruler because it had more cities. ...
Ancient Egypt: Crucible of Civilization
... The shape of the pyramid represented the sun’s rays which the dead king would use as a ramp to the heavens. It also represented the primordial mound from which, according to Egyptian mythology, the god Re created the world. On a practical level, the pyramids represented the Pharaoh’s power and wealt ...
... The shape of the pyramid represented the sun’s rays which the dead king would use as a ramp to the heavens. It also represented the primordial mound from which, according to Egyptian mythology, the god Re created the world. On a practical level, the pyramids represented the Pharaoh’s power and wealt ...
Ancient Egypt - Broughton Primary School
... Who were they? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Page 1 Pyramids . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Page 2 Gods . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
... Who were they? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Page 1 Pyramids . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Page 2 Gods . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Ch. 3 Reading Questions
... Because the weather became hot and dry the people were driven into the Nile regions (because of the river). Since they were close to the Nile River, its annual flooding made the soil rich and good for prosperous agriculture and allowed the early cultivators to be lenient in their early farming techn ...
... Because the weather became hot and dry the people were driven into the Nile regions (because of the river). Since they were close to the Nile River, its annual flooding made the soil rich and good for prosperous agriculture and allowed the early cultivators to be lenient in their early farming techn ...
Nile River Valley Civilization
... They were the kings or Queens of Egypt. They were the head of the government and high priest of every temple. The pharaoh owned all of Egypt. He or she decided what was right or wrong and their word was law. The people of Egypt considered the pharaoh to be a half-human and halfgod. ...
... They were the kings or Queens of Egypt. They were the head of the government and high priest of every temple. The pharaoh owned all of Egypt. He or she decided what was right or wrong and their word was law. The people of Egypt considered the pharaoh to be a half-human and halfgod. ...
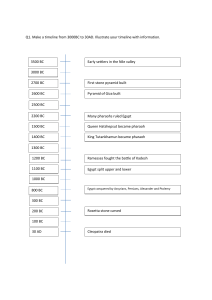
Q1. Make a timeline from 3000BC to 30AD. Illustrate your timeline
... boy who delivered water to the thirsty labourers accidentally tripped on a stone. They cleared the sand around the stone and they saw steps leading to a tomb which they realised belonged to a royal pharaoh because they saw a royal stamp on the door of the tomb. They made a hole on the door of the to ...
... boy who delivered water to the thirsty labourers accidentally tripped on a stone. They cleared the sand around the stone and they saw steps leading to a tomb which they realised belonged to a royal pharaoh because they saw a royal stamp on the door of the tomb. They made a hole on the door of the to ...
3.4 Ancient Egypt Outline
... 1. Early tombs of pharaohs were mastabas a. Mastaba = a rectangular tomb with a burial shaft below 2. Then pharaohs began to have pyramids constructed for their tombs a. Built by farmers who were unemployed in the summer months while their fields were flooded b. Built on the west side of the Nile (s ...
... 1. Early tombs of pharaohs were mastabas a. Mastaba = a rectangular tomb with a burial shaft below 2. Then pharaohs began to have pyramids constructed for their tombs a. Built by farmers who were unemployed in the summer months while their fields were flooded b. Built on the west side of the Nile (s ...
Ancient Egypt - sheehansocialstudies
... belonged to him. The Pharaoh was the ruler of the economy, which means he managed how money and resources were used. Egypt was able to thrive and be successful because farmers produced a lot of extra food that could be used for trade. The Pharaoh collected taxes from everyone, usually in the form of ...
... belonged to him. The Pharaoh was the ruler of the economy, which means he managed how money and resources were used. Egypt was able to thrive and be successful because farmers produced a lot of extra food that could be used for trade. The Pharaoh collected taxes from everyone, usually in the form of ...
Egypt Review Slideshow
... • Black, stone tablet which had writing in three different forms • Tablet used to “decode” the hieroglyphics ...
... • Black, stone tablet which had writing in three different forms • Tablet used to “decode” the hieroglyphics ...
the pyramids - Mr. Dowling
... pharaoh. Imhotep was a brilliant architect who built an elaborate monument for his pharaoh, Zoser, more than 26 centuries before the Common Era. Imhotep placed six mastabas over Zoser’s grave. Each mastaba was smaller than the one below it. Imhotep then covered the mastabas with polished white limes ...
... pharaoh. Imhotep was a brilliant architect who built an elaborate monument for his pharaoh, Zoser, more than 26 centuries before the Common Era. Imhotep placed six mastabas over Zoser’s grave. Each mastaba was smaller than the one below it. Imhotep then covered the mastabas with polished white limes ...
Major Time Periods of Egypt
... Hieroglyphics, Demotic (everyday Egyptian language), and Greek. • In 1821, Jean Francis Champollion began translating the Egyptian writings from his knowledge of Greek. It had taken him 10 years to figure out the “pictures” were pieces of language! ...
... Hieroglyphics, Demotic (everyday Egyptian language), and Greek. • In 1821, Jean Francis Champollion began translating the Egyptian writings from his knowledge of Greek. It had taken him 10 years to figure out the “pictures” were pieces of language! ...
The Later Middle Ages
... C paintings B sphinxes D sanctuary 18 Why were tombs filled with art, jewelry, and other treasures? A The tombs served as museums. B The tombs were the private storage rooms of the pharaoh. C Egyptians believed tombs to be the safest places in the kingdom. D Egyptians believed the dead enjoyed such ...
... C paintings B sphinxes D sanctuary 18 Why were tombs filled with art, jewelry, and other treasures? A The tombs served as museums. B The tombs were the private storage rooms of the pharaoh. C Egyptians believed tombs to be the safest places in the kingdom. D Egyptians believed the dead enjoyed such ...
Ancient Egypt
... afterlife, his body had to be protected. They practiced embalming, or mummifying the Pharaoh’s body. • A mummy is then placed in a decorated sarcophagus, which is like a coffin. ...
... afterlife, his body had to be protected. They practiced embalming, or mummifying the Pharaoh’s body. • A mummy is then placed in a decorated sarcophagus, which is like a coffin. ...