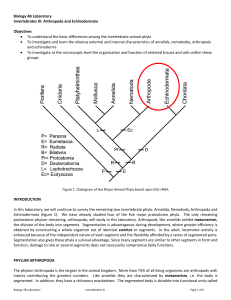
Phylum: Chordata
... are organisms that eat other organisms (heterotrophs). The animal kingdom is the largest kingdom with over one million known species and is divided into two phylums: chordata (vertebrate or backbone) and invertebrate. 98% of the animal species are invertebrates. Examples: from ant to zebra Phylum Pr ...
... are organisms that eat other organisms (heterotrophs). The animal kingdom is the largest kingdom with over one million known species and is divided into two phylums: chordata (vertebrate or backbone) and invertebrate. 98% of the animal species are invertebrates. Examples: from ant to zebra Phylum Pr ...
From Sponges to Invertebrate Chordates
... Flatworms belong to the phylum Platyhelminthes. Examples of flatworms are shown in Figure 1.10. There are more than 25,000 species in the flatworm phylum. ...
... Flatworms belong to the phylum Platyhelminthes. Examples of flatworms are shown in Figure 1.10. There are more than 25,000 species in the flatworm phylum. ...
1.1 - cloudfront.net
... 1. Flatworms have no true body cavity and an incomplete digestive system, meaning that the digestive tract has only one opening. 2. Flatworms do not have a respiratory system, so they have pores that allow oxygen to enter through their body. 3. There are no blood vessels in the flatworms. Their gast ...
... 1. Flatworms have no true body cavity and an incomplete digestive system, meaning that the digestive tract has only one opening. 2. Flatworms do not have a respiratory system, so they have pores that allow oxygen to enter through their body. 3. There are no blood vessels in the flatworms. Their gast ...
VIII. INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT REGULATION, cont
... Notochord – Flexible rod located between digestive tract & nerve cord Dorsal Hollow Nerve Cord – Eventually develops into brain and spinal cord Pharyngeal Slits – Present in developmental stages; may not be found in adult stage Post-anal Tail ...
... Notochord – Flexible rod located between digestive tract & nerve cord Dorsal Hollow Nerve Cord – Eventually develops into brain and spinal cord Pharyngeal Slits – Present in developmental stages; may not be found in adult stage Post-anal Tail ...
Insects
... A series of tubes called the tracheal system and holes called spiracles for air intake ...
... A series of tubes called the tracheal system and holes called spiracles for air intake ...
Name: Period: Pre-Test for Invertebrates: Porifera to Annelids /61
... 13. What prevents the endo-parasites from being digested or disabled by our immune system? (1 mark) ...
... 13. What prevents the endo-parasites from being digested or disabled by our immune system? (1 mark) ...
Invertebrates III
... Examine a preserved grasshopper and observe its external features (Figure 8). The exoskeleton is divided by sutures into plates called sclerites. o HEAD: The head consists of fused sclerites forming a cranium and mouth parts. A pair of antennae arise in front of the compound eyes. Three ocelli (simp ...
... Examine a preserved grasshopper and observe its external features (Figure 8). The exoskeleton is divided by sutures into plates called sclerites. o HEAD: The head consists of fused sclerites forming a cranium and mouth parts. A pair of antennae arise in front of the compound eyes. Three ocelli (simp ...
lect10-9cut
... • 3 marine phyla with special feature: ________________ • Lophophore: Circular or U-shaped ridge around mouth, bearing 1 or 2 rows of hollow ciliated tentacles • Cilia trap detritus/plankton (filter feeders) and tentacles aid in gas exchange • Have mix of protostome and deuterostome features ...
... • 3 marine phyla with special feature: ________________ • Lophophore: Circular or U-shaped ridge around mouth, bearing 1 or 2 rows of hollow ciliated tentacles • Cilia trap detritus/plankton (filter feeders) and tentacles aid in gas exchange • Have mix of protostome and deuterostome features ...
Arthropods
... numerous animals on earth • More than 1 million different species have been identified • They thrive in almost every habitat • There worldwide population is estimated at a billion billion, or 1018 individuals ...
... numerous animals on earth • More than 1 million different species have been identified • They thrive in almost every habitat • There worldwide population is estimated at a billion billion, or 1018 individuals ...
Cnidarians and worms have different body plans.
... an animal’s body. Most cnidarians have a body plan with radial symmetry. This means the body is organized around a central point, a mouthlike opening that leads into a gut. You can see from the diagram of the jellyfish life cycle on page 130 that both the polyp and medusa have radial symmetry. A rad ...
... an animal’s body. Most cnidarians have a body plan with radial symmetry. This means the body is organized around a central point, a mouthlike opening that leads into a gut. You can see from the diagram of the jellyfish life cycle on page 130 that both the polyp and medusa have radial symmetry. A rad ...
04 Chapter
... • The soft bodies of many sponges are supported by sharp, glass-like structures called spicules. • Other sponges have a material called spongin. Spongin is similar to foam rubber because it makes sponges soft and elastic. ...
... • The soft bodies of many sponges are supported by sharp, glass-like structures called spicules. • Other sponges have a material called spongin. Spongin is similar to foam rubber because it makes sponges soft and elastic. ...
Sponges - science151
... The correct answer is B. Squids can use their mantle to squeeze water and squirt it out of a structure called a siphon. When they do this, the force from the expulsion of water, causes the squid to move in the opposite direction of the stream of water. ...
... The correct answer is B. Squids can use their mantle to squeeze water and squirt it out of a structure called a siphon. When they do this, the force from the expulsion of water, causes the squid to move in the opposite direction of the stream of water. ...
deuterostomes
... • no scales; no paired appendages • pore-like gill openings • two chambered heart • no stomach Æ only intestine ...
... • no scales; no paired appendages • pore-like gill openings • two chambered heart • no stomach Æ only intestine ...
vertebrates
... • Vertebrates first appeared in the early Paleozic, about 540 MYA….earth at the time was mostly water covered, extensive continental movements, and an O2 rich atmosphere formed as a result of ________________________ of autotrophs • Movement of land masses and climatic differences/changes resulted i ...
... • Vertebrates first appeared in the early Paleozic, about 540 MYA….earth at the time was mostly water covered, extensive continental movements, and an O2 rich atmosphere formed as a result of ________________________ of autotrophs • Movement of land masses and climatic differences/changes resulted i ...
Introduction to Phylum Chordata
... and tunicates • One hypothesis on the evolution of the vertebrates is Garstang's Hypothesis • It suggests that sessile tunicates were an ancestral stock that evolved a motile larval stage • Garstang speculated that at some point larvae failed to metamorphose into an adult, but developed gonads and r ...
... and tunicates • One hypothesis on the evolution of the vertebrates is Garstang's Hypothesis • It suggests that sessile tunicates were an ancestral stock that evolved a motile larval stage • Garstang speculated that at some point larvae failed to metamorphose into an adult, but developed gonads and r ...
Animals - Killeen ISD
... (good job, nematodes!) • Incomplete digestive system – Only one opening; inefficient! – Ex: jellyfish & flatworms ...
... (good job, nematodes!) • Incomplete digestive system – Only one opening; inefficient! – Ex: jellyfish & flatworms ...
Invertebrate Unit (Ch. 26, 27, 28, 29)
... They move to obtain food and escape predators. They can be both carnivorous or parasitic (this tapeworm lives inside the human intestines). ...
... They move to obtain food and escape predators. They can be both carnivorous or parasitic (this tapeworm lives inside the human intestines). ...
eucoelomate protostomes
... Standard protostomate characters (triploblastic, spiral determinate cleavage; coelom forms by schizocoely) but unique fundamental body plan. About 100,000 described species, extremely diverse body forms. ...
... Standard protostomate characters (triploblastic, spiral determinate cleavage; coelom forms by schizocoely) but unique fundamental body plan. About 100,000 described species, extremely diverse body forms. ...
Animals
... • Amoebocytes- digest & distribute nutrients; produce reproductive cells • Secrete spicules • Porocytes- cells curl end to end to form the ostia pores ...
... • Amoebocytes- digest & distribute nutrients; produce reproductive cells • Secrete spicules • Porocytes- cells curl end to end to form the ostia pores ...
lecture2
... They are unsegmented coelemate animals which are radially symmetrical in the adult (usually five rayed), but bilaterally symmetrical in the larval stage. They possess a DERMAL SKELETON which consists of calcareous ossicles (bones) that may develop short or long spines. The nervous system is diffuse ...
... They are unsegmented coelemate animals which are radially symmetrical in the adult (usually five rayed), but bilaterally symmetrical in the larval stage. They possess a DERMAL SKELETON which consists of calcareous ossicles (bones) that may develop short or long spines. The nervous system is diffuse ...
Class Onycophora e.g. peripatus Characteristics 1. Thin cuticle, soft
... They are unsegmented coelemate animals which are radially symmetrical in the adult (usually five rayed), but bilaterally symmetrical in the larval stage. They possess a DERMAL SKELETON which consists of calcareous ossicles (bones) that may develop short or long spines. The nervous system is diffuse ...
... They are unsegmented coelemate animals which are radially symmetrical in the adult (usually five rayed), but bilaterally symmetrical in the larval stage. They possess a DERMAL SKELETON which consists of calcareous ossicles (bones) that may develop short or long spines. The nervous system is diffuse ...
iIINTRODUCTION TO ARTHROPODS
... __exoskeleton___is a solid coating, not a _living ____ tissue, it cannot __grow__ as the animal _grows____.And __movement_ can occur only at the _joints_ of the _armour_. 6. All arthropods have __jointed_ appendages. (arthro- means __joint_; -pod, means _foot___)that enable them to _move_. In primit ...
... __exoskeleton___is a solid coating, not a _living ____ tissue, it cannot __grow__ as the animal _grows____.And __movement_ can occur only at the _joints_ of the _armour_. 6. All arthropods have __jointed_ appendages. (arthro- means __joint_; -pod, means _foot___)that enable them to _move_. In primit ...
Invertebrate
.jpg?width=300)
Invertebrates are animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebrae (vertebral column) , derived from the notochord. This includes all animals apart from the subphylum Vertebrata. Familiar examples of invertebrates include insects, crabs, lobsters and their kin, snails, clams, octopuses and their kin, starfish, sea-urchins and their kin, and worms.The majority of animal species are invertebrates. One estimate puts the figure at 97%. Many invertebrate taxa have a greater number and variety of species than the entire subphylum of Vertebrata.Some of the so-called invertebrates, such as the Chaetognatha, Hemichordata, Tunicata and Cephalochordata are more closely related to the vertebrates than to other invertebrates. This makes the term ""invertebrate"" almost meaningless for taxonomic purposes.