Introduction to Phylum Chordata
... 1. Chordate evolution is a history of innovations that is built upon major invertebrate traits •bilateral symmetry •cephalization •segmentation •coelom or "gut" tube ...
... 1. Chordate evolution is a history of innovations that is built upon major invertebrate traits •bilateral symmetry •cephalization •segmentation •coelom or "gut" tube ...
Invertebrate Lab (2)
... 12. What do the flukes and tapeworms have in common? They are both parasitic flatworms 13. What do flame cells do? Filter and remove excess water and waste from the body 14. What do eyespots detect? Changes in the amount of light 15. Describe the response system of organisms in this phylum. Ganglia ...
... 12. What do the flukes and tapeworms have in common? They are both parasitic flatworms 13. What do flame cells do? Filter and remove excess water and waste from the body 14. What do eyespots detect? Changes in the amount of light 15. Describe the response system of organisms in this phylum. Ganglia ...
Chapter 23: Invertebrate Diversity
... genes called homeotic genes. Homeotic (hoh-mee-AH-tihk) genes are a class of genes that control early development. In animals, an important group of homeotic genes called Hox genes are defined by a sequence of 180 nucleotides called homeobox (HOH-mee-uhbahks) genes. Hox genes define the head-to-tail ...
... genes called homeotic genes. Homeotic (hoh-mee-AH-tihk) genes are a class of genes that control early development. In animals, an important group of homeotic genes called Hox genes are defined by a sequence of 180 nucleotides called homeobox (HOH-mee-uhbahks) genes. Hox genes define the head-to-tail ...
1 - ISpatula
... E) they shed their exoskeleton as they grow The Answer is : A Q15.Consider the following list of animals: giant squid, earthworm, largemouth bass, snail, tapeworm, coral, and starfish. The two that belong to the same phylum are the __________, and their phylum is __________. ( Concept 33.3) ...
... E) they shed their exoskeleton as they grow The Answer is : A Q15.Consider the following list of animals: giant squid, earthworm, largemouth bass, snail, tapeworm, coral, and starfish. The two that belong to the same phylum are the __________, and their phylum is __________. ( Concept 33.3) ...
ctenophores
... In 1997 it was nearly eliminated itself, by accidental introduction of its major predator-- ctenophore Beröe ovata Beröe ...
... In 1997 it was nearly eliminated itself, by accidental introduction of its major predator-- ctenophore Beröe ovata Beröe ...
29-2 Form and Function in Invertebrates
... 29-2 Form and Function in Feeding and Digestion Invertebrates ...
... 29-2 Form and Function in Feeding and Digestion Invertebrates ...
Chapter 29 Foldable Work Comparing Invertebrates
... OUTSIDE: Circulation; INSIDE: (Key Concept page 754) OUTSIDE: Open Circulatory System INSIDE: (Define according to glossary) OUTSIDE: Closed Circulatory System INSIDE: (Define according to glossary) ...
... OUTSIDE: Circulation; INSIDE: (Key Concept page 754) OUTSIDE: Open Circulatory System INSIDE: (Define according to glossary) OUTSIDE: Closed Circulatory System INSIDE: (Define according to glossary) ...
Animal kingdom
... used as the basis for animal classification.They are 1.Levels of organisation-cellular level,tissue level,organ level & organ system level. 2.Symmetry-asymmetrical,radial symmetry,bilateral symmetry. 3.Diploblastic & triploblastic organisation. ...
... used as the basis for animal classification.They are 1.Levels of organisation-cellular level,tissue level,organ level & organ system level. 2.Symmetry-asymmetrical,radial symmetry,bilateral symmetry. 3.Diploblastic & triploblastic organisation. ...
The Phylum Annelida: A Short Introduction
... Polychaetes can reproduce asexually, by dividing into two or more pieces or by budding off a new individual while the parent remains a complete organism. [3][15] Some oligochaetes, such as Aulophorus furcatus, seem to reproduce entirely asexually, while others reproduce asexually in summer and sexua ...
... Polychaetes can reproduce asexually, by dividing into two or more pieces or by budding off a new individual while the parent remains a complete organism. [3][15] Some oligochaetes, such as Aulophorus furcatus, seem to reproduce entirely asexually, while others reproduce asexually in summer and sexua ...
Sponges and Cnidarians
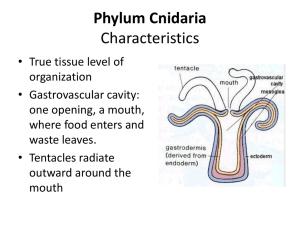
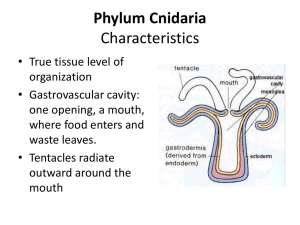
... the inner layer is called the gastrodermis and lines the digestive cavity. Between these two layers is a non-living, jelly-like mesoglea. There are differentiated cell types in each tissue layer, such as nerve cells, enzyme-secreting cells, and nutrient-absorbing cells, as well as intercellular conn ...
... the inner layer is called the gastrodermis and lines the digestive cavity. Between these two layers is a non-living, jelly-like mesoglea. There are differentiated cell types in each tissue layer, such as nerve cells, enzyme-secreting cells, and nutrient-absorbing cells, as well as intercellular conn ...
1. Invertebrates
... -One or more hearts or heart-like organs pump blood through vessels into surrounding ...
... -One or more hearts or heart-like organs pump blood through vessels into surrounding ...
Phylum Cnidaria
... pointing down. Some jelly "fish" are very poisonous to humans, occasionally even fatal. However, most jelly "fish" are not dangerous to people, their poison will only cause a mild rash similar to poison ivy. ...
... pointing down. Some jelly "fish" are very poisonous to humans, occasionally even fatal. However, most jelly "fish" are not dangerous to people, their poison will only cause a mild rash similar to poison ivy. ...
Phylum Cnidaria Characteristics
... pointing down. Some jelly "fish" are very poisonous to humans, occasionally even fatal. However, most jelly "fish" are not dangerous to people, their poison will only cause a mild rash similar to poison ivy. ...
... pointing down. Some jelly "fish" are very poisonous to humans, occasionally even fatal. However, most jelly "fish" are not dangerous to people, their poison will only cause a mild rash similar to poison ivy. ...
PDF
... tebrates, we tend to think of an individual but a negligible effect (commensalism) on invertebrate animal as just that: an individ- the other. Most commonly, the selective ual genome, a representative of a single effect on the host or endosymbiont is either taxon. But many invertebrate organisms are ...
... tebrates, we tend to think of an individual but a negligible effect (commensalism) on invertebrate animal as just that: an individ- the other. Most commonly, the selective ual genome, a representative of a single effect on the host or endosymbiont is either taxon. But many invertebrate organisms are ...
Vertebrate Origins 2
... and they have an excretory system that is remarkable similar to that of some chordates. Problem – the nerve cord is ventral and bifurcates to go around the pharyngeal tube to a dorsal brain. If you turn the organism upside down, the brain is ventral and the mouth dorsal … a situation which does not ...
... and they have an excretory system that is remarkable similar to that of some chordates. Problem – the nerve cord is ventral and bifurcates to go around the pharyngeal tube to a dorsal brain. If you turn the organism upside down, the brain is ventral and the mouth dorsal … a situation which does not ...
13-Lower Chordates
... • Blood moves by microcirculation through tissues and returns to the ventral aorta. • Blood has no erythrocytes or hemoglobin and mainly transports nutrients. ...
... • Blood moves by microcirculation through tissues and returns to the ventral aorta. • Blood has no erythrocytes or hemoglobin and mainly transports nutrients. ...
Ch. 18 Presentation
... – sponges and eumetazoans (animals with true tissues), – animals with radial or bilateral symmetry (bilaterians), and – which have two branches, lophotrochozoans named for a feeding part called a lophophore in some and trochophore larvae as well as Ecydysozoans, which shed their exoskeletons – Deute ...
... – sponges and eumetazoans (animals with true tissues), – animals with radial or bilateral symmetry (bilaterians), and – which have two branches, lophotrochozoans named for a feeding part called a lophophore in some and trochophore larvae as well as Ecydysozoans, which shed their exoskeletons – Deute ...
Lecture 13a - BlakeMathys.com
... • 95% of all known animals • Mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fishes are a small part of animal diversity ...
... • 95% of all known animals • Mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fishes are a small part of animal diversity ...
Invertebrates
... the upper reaches of the atmosphere, in the driest of the deserts and in the canopies of the wettest rainforests. They can even be found in the frozen Antarctic or on the deepest parts of the ocean floor. ...
... the upper reaches of the atmosphere, in the driest of the deserts and in the canopies of the wettest rainforests. They can even be found in the frozen Antarctic or on the deepest parts of the ocean floor. ...
Chordates File - ISMScience.org
... Ex. sharks rays, and skates Cartilage skeletons; very small rough scales These were the first animals with jaws. Jaws helped vertebrates become successful predators ...
... Ex. sharks rays, and skates Cartilage skeletons; very small rough scales These were the first animals with jaws. Jaws helped vertebrates become successful predators ...
AP Biology
... digestive tract and body wall cushions the internal organs enables growth and movement ...
... digestive tract and body wall cushions the internal organs enables growth and movement ...
BIO 102: GENERAL BIOLOGY II UNIT: 4
... • They are diploblastic animals • They have tissue grade organisation • They possess single cavity in the body known as enteron or gastro vascular cavity, which serves for ingestion and egestion • They lack anus • Their mouth is surrounded by tentacles • They produce nematocysts which serve for defe ...
... • They are diploblastic animals • They have tissue grade organisation • They possess single cavity in the body known as enteron or gastro vascular cavity, which serves for ingestion and egestion • They lack anus • Their mouth is surrounded by tentacles • They produce nematocysts which serve for defe ...
Invertebrate
.jpg?width=300)
Invertebrates are animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebrae (vertebral column) , derived from the notochord. This includes all animals apart from the subphylum Vertebrata. Familiar examples of invertebrates include insects, crabs, lobsters and their kin, snails, clams, octopuses and their kin, starfish, sea-urchins and their kin, and worms.The majority of animal species are invertebrates. One estimate puts the figure at 97%. Many invertebrate taxa have a greater number and variety of species than the entire subphylum of Vertebrata.Some of the so-called invertebrates, such as the Chaetognatha, Hemichordata, Tunicata and Cephalochordata are more closely related to the vertebrates than to other invertebrates. This makes the term ""invertebrate"" almost meaningless for taxonomic purposes.