Lecture 17/18 - Aerobic and Anaerobic Metabolism
... 2.) Is glycolysis an aerobic or anaerobic pathway? If you oxidize one molecule of glucose, what is the approximate net yield of ATP? 3.) The reactions of glycolysis can all be categorized into one type of chemical reaction, what are these reactions called? How many total reactions occur in glycolysi ...
... 2.) Is glycolysis an aerobic or anaerobic pathway? If you oxidize one molecule of glucose, what is the approximate net yield of ATP? 3.) The reactions of glycolysis can all be categorized into one type of chemical reaction, what are these reactions called? How many total reactions occur in glycolysi ...
Previous studies have nonspecifically attached a single protein to a
... monitored in real-time. Part of the investigation was accomplished by mutagenesis followed by overexpression and purification three different DNase E9 mutants. The latter portion of this project involves attachment to the nanotube through cysteine chemistry and visualization of changes in conductanc ...
... monitored in real-time. Part of the investigation was accomplished by mutagenesis followed by overexpression and purification three different DNase E9 mutants. The latter portion of this project involves attachment to the nanotube through cysteine chemistry and visualization of changes in conductanc ...
fulltext
... result of minimization of hydrophobic exposure in an aqueous environment. The individual protein molecules may exist alone or form complexes with others. A protein which is capable of catalysing a chemical reaction is called an enzyme. Observed at macro scale proteins behave in unexpected ways. E.g. ...
... result of minimization of hydrophobic exposure in an aqueous environment. The individual protein molecules may exist alone or form complexes with others. A protein which is capable of catalysing a chemical reaction is called an enzyme. Observed at macro scale proteins behave in unexpected ways. E.g. ...
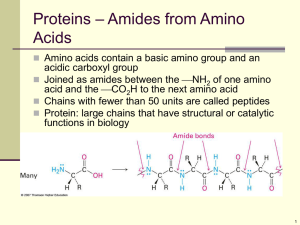
Chapter 26:Biomolecules: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
... In basic solution, the groups are in their base forms, an overall anion In neutral solution cation and anion forms are present This pH where the overall charge is 0 is the isoelectric point, pI ...
... In basic solution, the groups are in their base forms, an overall anion In neutral solution cation and anion forms are present This pH where the overall charge is 0 is the isoelectric point, pI ...
Slide 1
... – Side chains may have different pKas • pKa affected by charges on amino/carboxyl groups • pKa may be affected by interactions with other side chains in the larger molecule ...
... – Side chains may have different pKas • pKa affected by charges on amino/carboxyl groups • pKa may be affected by interactions with other side chains in the larger molecule ...
energy carrier!
... 2 ATP, CO2, NADH, FADH Enzymes not embedded Energy carriers Escort molecule to Krebs cycle ...
... 2 ATP, CO2, NADH, FADH Enzymes not embedded Energy carriers Escort molecule to Krebs cycle ...
The hunt for original microbial enzymes
... eDNA from a studied environment might be used to construct (meta)genomic libraries in a well-known cultivable host cell, and then screening these libraries for clones displaying the sought enzymatic activity. Functional (meta)genomics, which relies solely on gene function rather than sequence simila ...
... eDNA from a studied environment might be used to construct (meta)genomic libraries in a well-known cultivable host cell, and then screening these libraries for clones displaying the sought enzymatic activity. Functional (meta)genomics, which relies solely on gene function rather than sequence simila ...
1 Lecture 27: Metabolic Pathways Part I: Glycolysis
... This completes the “first stage” of glycolysis. Overall Δ G for the first 5 steps under cellular conditions is -53 kJ/mol. So far, 2 ATP molecules have been consumed. ...
... This completes the “first stage” of glycolysis. Overall Δ G for the first 5 steps under cellular conditions is -53 kJ/mol. So far, 2 ATP molecules have been consumed. ...
Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase-A New Target in the Fight against Obesity
... leading disease of the 21st century in the U.S. Obesity is determined by the body mass index(BMI). Diseases that are caused from Obesity is type 2 diabetes, high ...
... leading disease of the 21st century in the U.S. Obesity is determined by the body mass index(BMI). Diseases that are caused from Obesity is type 2 diabetes, high ...
B2 – Keeping healthy - The Bicester School
... How do chemical reactions take place in living things? The basic processes of life carried out by all living things depend on chemical reactions within cells. ...
... How do chemical reactions take place in living things? The basic processes of life carried out by all living things depend on chemical reactions within cells. ...
Final Exam Summer 04
... Taq DNA Pol is used in PCR because A. it is inexpensive D. it works at high temperatures B. it is not processive E. none of the above C. it doesn't require a primer An Okazaki fragment has which structure? A. short DNA strand D. short RNA strand B. DNA at 5' end, RNA at 3' E. none of the above C. RN ...
... Taq DNA Pol is used in PCR because A. it is inexpensive D. it works at high temperatures B. it is not processive E. none of the above C. it doesn't require a primer An Okazaki fragment has which structure? A. short DNA strand D. short RNA strand B. DNA at 5' end, RNA at 3' E. none of the above C. RN ...
Biol 1406 notes Ch 8 8thed
... ○ If a small amount of the enzyme sucrase is added to a solution of sugar, all the sucrose is hydrolyzed within seconds. An enzyme is a macromolecule that acts as a catalyst, a chemical agent that speeds up the rate of a reaction without being consumed by the reaction. Here we will focus on protein ...
... ○ If a small amount of the enzyme sucrase is added to a solution of sugar, all the sucrose is hydrolyzed within seconds. An enzyme is a macromolecule that acts as a catalyst, a chemical agent that speeds up the rate of a reaction without being consumed by the reaction. Here we will focus on protein ...
S1 Text Section A Annotation by structural analysis In case of aldose
... would probably remain conserved even if reactions from other pathways are included within the iAS142 network as they represent a tightly balanced subset which satisfies ATP and redox balance within different compartments and thereby maximizes the biomass. Reactions that form a part of this subnetwor ...
... would probably remain conserved even if reactions from other pathways are included within the iAS142 network as they represent a tightly balanced subset which satisfies ATP and redox balance within different compartments and thereby maximizes the biomass. Reactions that form a part of this subnetwor ...
Assessing in silico the recruitment and functional spectrum of
... means of specific biosynthetic pathways and the corresponding genes are organized in biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) [5]. Compared to products of PM, secondary metabolites have a wider range of structures and biological activities [6]. This remarkable diversity reflects the random manner in which ...
... means of specific biosynthetic pathways and the corresponding genes are organized in biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) [5]. Compared to products of PM, secondary metabolites have a wider range of structures and biological activities [6]. This remarkable diversity reflects the random manner in which ...
Carbohydrate metabolism
... Glycogen is a store of glucose. The human body can store up to 450 g of glycogen in the liver and in the muscles. The glycogen content of the other organs is low. Liver glycogen serves as a glucose reserve for the maintenance of blood glucose level. Muscle glycogen serves as an energy reserve. It is ...
... Glycogen is a store of glucose. The human body can store up to 450 g of glycogen in the liver and in the muscles. The glycogen content of the other organs is low. Liver glycogen serves as a glucose reserve for the maintenance of blood glucose level. Muscle glycogen serves as an energy reserve. It is ...
Chapter 1 Answer Key
... Protein sequencing is useful because once the sequence of a polypeptide is known it can be synthesized artificially. Once the sequence is known, it is also possible to better understand the protein and its function in the body. Insulin was the first protein fully sequenced. Fredrick Sanger was the f ...
... Protein sequencing is useful because once the sequence of a polypeptide is known it can be synthesized artificially. Once the sequence is known, it is also possible to better understand the protein and its function in the body. Insulin was the first protein fully sequenced. Fredrick Sanger was the f ...
Krebs (Citric Acid) Cycle
... acid cycle occurs in the cytoplasm; in eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle takes place in the matrix of the mitochondria. The Krebs Cycle is the source for the precursors of many molecules, so it is an amphibolic pathway (meaning it is both anabolic and catabolic). ...
... acid cycle occurs in the cytoplasm; in eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle takes place in the matrix of the mitochondria. The Krebs Cycle is the source for the precursors of many molecules, so it is an amphibolic pathway (meaning it is both anabolic and catabolic). ...
Lecture 1 Course overview and intro to enzymes
... Web page http;//courses.ucsd.edu/rhampton/bibc102 Ideas in metabolism non-iterated structures but common structural themes metabolic pathway Why study metabolism relevant to all life numerous diseases and conditions catabolism and anabolism we think on many levels from atomic to ecological Proteins ...
... Web page http;//courses.ucsd.edu/rhampton/bibc102 Ideas in metabolism non-iterated structures but common structural themes metabolic pathway Why study metabolism relevant to all life numerous diseases and conditions catabolism and anabolism we think on many levels from atomic to ecological Proteins ...
Lecture 10
... of the smallest prokaryotic cell. Therefore there are something like 10003 or about a billion atoms in a very small cell. This is way too much to have arisen in one jump, especially because there are some intricate arrangements of proteins in, e.g., the secretory system. We can then take a step into ...
... of the smallest prokaryotic cell. Therefore there are something like 10003 or about a billion atoms in a very small cell. This is way too much to have arisen in one jump, especially because there are some intricate arrangements of proteins in, e.g., the secretory system. We can then take a step into ...
University of Groningen Mutants and homologs of
... deficient in processing. It was shown that a bound water molecule plays a pivotal role in activating the hydroxyl group of Serβ1, which is the nucleophile in the first processing step [53-55] (Figure 3). If this water is forced out by mutating Pheβ177 to proline, the hydroxyl group is not positioned ...
... deficient in processing. It was shown that a bound water molecule plays a pivotal role in activating the hydroxyl group of Serβ1, which is the nucleophile in the first processing step [53-55] (Figure 3). If this water is forced out by mutating Pheβ177 to proline, the hydroxyl group is not positioned ...
Midterm Review
... an enzyme, competing with the substrate – Noncompetitive inhibitors bind to another part of an enzyme, causing the enzyme to change shape and making the active site less effective ...
... an enzyme, competing with the substrate – Noncompetitive inhibitors bind to another part of an enzyme, causing the enzyme to change shape and making the active site less effective ...
SBI 4U Cellular Respiration Review Game2
... 1. How many ATP are produced in Cellular Respiration? 2. What is oxidative phosphorylation? 3. What is substrate-level phosphorylation? 4. What 3 modifications occur to pyruvate in pyruvate oxidation? 5. Where does the Kreb’s Cycle occur in the cell? 6. How molecules of ATP are produced from NADH? 7 ...
... 1. How many ATP are produced in Cellular Respiration? 2. What is oxidative phosphorylation? 3. What is substrate-level phosphorylation? 4. What 3 modifications occur to pyruvate in pyruvate oxidation? 5. Where does the Kreb’s Cycle occur in the cell? 6. How molecules of ATP are produced from NADH? 7 ...
Chapter 38 Plant Nutrition - Tri
... Plants and Nitrogen Plants require nitrogen to produce proteins, nucleic acids, and other organic molecules They CANNOT use nitrogen in gaseous form (N2) To be used, must be in form of ammonium (NH4+) or nitrate (NO3-) Plants acquire most of their nitrogen in the form of nitrate (NO3-) ...
... Plants and Nitrogen Plants require nitrogen to produce proteins, nucleic acids, and other organic molecules They CANNOT use nitrogen in gaseous form (N2) To be used, must be in form of ammonium (NH4+) or nitrate (NO3-) Plants acquire most of their nitrogen in the form of nitrate (NO3-) ...
Enzyme

Enzymes /ˈɛnzaɪmz/ are macromolecular biological catalysts. Enzymes accelerate, or catalyze, chemical reactions. The molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates and the enzyme converts these into different molecules, called products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. The set of enzymes made in a cell determines which metabolic pathways occur in that cell. The study of enzymes is called enzymology.Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Most enzymes are proteins, although a few are catalytic RNA molecules. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures.Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by lowering its activation energy. Some enzymes can make their conversion of substrate to product occur many millions of times faster. An extreme example is orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase, which allows a reaction that would otherwise take millions of years to occur in milliseconds. Chemically, enzymes are like any catalyst and are not consumed in chemical reactions, nor do they alter the equilibrium of a reaction. Enzymes differ from most other catalysts by being much more specific. Enzyme activity can be affected by other molecules: inhibitors are molecules that decrease enzyme activity, and activators are molecules that increase activity. Many drugs and poisons are enzyme inhibitors. An enzyme's activity decreases markedly outside its optimal temperature and pH.Some enzymes are used commercially, for example, in the synthesis of antibiotics. Some household products use enzymes to speed up chemical reactions: enzymes in biological washing powders break down protein, starch or fat stains on clothes, and enzymes in meat tenderizer break down proteins into smaller molecules, making the meat easier to chew.