Chapter 1: Prelude
... Vitamins are a heterogenic group of organic molecules that are needed in small amounts in the diets of some higher animals, which have lost the capacity to synthesize them. They reveal a huge diversity of functions: vitamin K is required for normal blood clotting, vitamin A is a precursor of retinal ...
... Vitamins are a heterogenic group of organic molecules that are needed in small amounts in the diets of some higher animals, which have lost the capacity to synthesize them. They reveal a huge diversity of functions: vitamin K is required for normal blood clotting, vitamin A is a precursor of retinal ...
ELEM_CouvC_V1n3 copy
... two between Ca in calcite (green spheres) and O in the amino acid (orange spheres), and one between O in the calcite (red spheres) and H in the amino acid (white spheres). Grey and blue spheres represent carbon and nitrogen atoms, respectively. (A) Side view; (B) top view. The essential amino acid a ...
... two between Ca in calcite (green spheres) and O in the amino acid (orange spheres), and one between O in the calcite (red spheres) and H in the amino acid (white spheres). Grey and blue spheres represent carbon and nitrogen atoms, respectively. (A) Side view; (B) top view. The essential amino acid a ...
Enzymes at work
... Although enzymes are usually identified using short trivial names, they also have longer systematic names. Furthermore, each type ...
... Although enzymes are usually identified using short trivial names, they also have longer systematic names. Furthermore, each type ...
Learning Objectives
... Proteins are giant molecules that carry out many of the important functions inside living cells. For example: Proteins (enzymes) catalyze cellular reactions (a different protein catalyzes each reaction). Proteins provide structural stability to a cells and tissues (cytoskeleton, cartilage, muscle, h ...
... Proteins are giant molecules that carry out many of the important functions inside living cells. For example: Proteins (enzymes) catalyze cellular reactions (a different protein catalyzes each reaction). Proteins provide structural stability to a cells and tissues (cytoskeleton, cartilage, muscle, h ...
Teaching Notes
... A1: There are 3 polymer chains as seen in the Chimera graphics window – chain A and B are the protease chains, while chain C is that of an inhibitor, designed based on a substrate (of the protease enzyme). Q2. Describe how the polymer chains are organized in the structure? Based on this description ...
... A1: There are 3 polymer chains as seen in the Chimera graphics window – chain A and B are the protease chains, while chain C is that of an inhibitor, designed based on a substrate (of the protease enzyme). Q2. Describe how the polymer chains are organized in the structure? Based on this description ...
Biology 1406: Cell and Molecular Biology
... 2. Interpret chemical and structural formulas. 3. Describe ionic and covalent bonds. 4. Discuss hydrogen bonds and non-polar interactions, and their importance for living organisms. 5. Identify some characteristics of carbon that allow it to play such an important role in the chemistry of life. 6. E ...
... 2. Interpret chemical and structural formulas. 3. Describe ionic and covalent bonds. 4. Discuss hydrogen bonds and non-polar interactions, and their importance for living organisms. 5. Identify some characteristics of carbon that allow it to play such an important role in the chemistry of life. 6. E ...
Curriculum for Excellence Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Nature`s Che
... Ten of the amino acids must be obtained from dietary proteins, and these are referred to as essential amino acids. Amino acids join by a condensation reaction to form proteins. The link joining amino acid residues in polypeptide chains is a peptide (amide) link. Most enzymes are proteins and ...
... Ten of the amino acids must be obtained from dietary proteins, and these are referred to as essential amino acids. Amino acids join by a condensation reaction to form proteins. The link joining amino acid residues in polypeptide chains is a peptide (amide) link. Most enzymes are proteins and ...
Department of Chemistry IIT Kharagpur Biochemical Techniques
... 1. Tabulate absorbance of column eluent at 260 nm vs fraction number. 2. Graph your data, plotting absorbance vs fraction number. 3. Draw the structural formulae of the predominant chemical species for the compounds separated in this experiment. Ionic charges in the species must be clearly labeled. ...
... 1. Tabulate absorbance of column eluent at 260 nm vs fraction number. 2. Graph your data, plotting absorbance vs fraction number. 3. Draw the structural formulae of the predominant chemical species for the compounds separated in this experiment. Ionic charges in the species must be clearly labeled. ...
Please click for sample abstract format
... Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, Bülent Ecevit University, Zonguldak [email protected] ...
... Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, Bülent Ecevit University, Zonguldak [email protected] ...
Document
... Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, Bülent Ecevit University, Zonguldak [email protected] ...
... Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, Bülent Ecevit University, Zonguldak [email protected] ...
Molecules of Life Powerpoint
... Four Levels of Structure In Proteins (a) Primary structure The primary structure of any protein is simply its sequence of amino acids. This sequence determines everything else about the protein’s final shape. ...
... Four Levels of Structure In Proteins (a) Primary structure The primary structure of any protein is simply its sequence of amino acids. This sequence determines everything else about the protein’s final shape. ...
Effect of non-ionic detergents on apparent enzyme mechanism
... sigmoidal in this case and essentially the same with that of wild type. This suggests that the cooperative phenomenon of V121A is dependent on non-ionic detergents. V121 is in a hydrophobic loop which is located near the active site. The loop covers the active site as shown in Figure 1. As the side ...
... sigmoidal in this case and essentially the same with that of wild type. This suggests that the cooperative phenomenon of V121A is dependent on non-ionic detergents. V121 is in a hydrophobic loop which is located near the active site. The loop covers the active site as shown in Figure 1. As the side ...
Principles in heterogeneous catalysis
... b. Formulation spécifique pour cette activité des AA du programme (maximum 10) At the end of this activity, the student is able to : Explain the impact of a catalyst on the different indicators (enthalpy, free energy, equilibrium constant, reaction path, etc) of a chemical reaction Describe the work ...
... b. Formulation spécifique pour cette activité des AA du programme (maximum 10) At the end of this activity, the student is able to : Explain the impact of a catalyst on the different indicators (enthalpy, free energy, equilibrium constant, reaction path, etc) of a chemical reaction Describe the work ...
KEY
... In the acetone-butanol fermentation, acetyl CoA may be converted to either acetate (acetic acid) or to ethanol. i. What is the benefit derived from producing ethanol? ...
... In the acetone-butanol fermentation, acetyl CoA may be converted to either acetate (acetic acid) or to ethanol. i. What is the benefit derived from producing ethanol? ...
Critical role of amino acid 23 in mediating activity - Craik Lab
... substrate specificities of the S1–S4 subsites of vinckepain-2 and vinckepain-2A G as described previously [19]. To determine P1#$ specificity, a P1-diverse library consisting of 20 sublibraries was used. In each sublibrary, the P1 position contained one native amino acid, and the P2, P3 and P4 posit ...
... substrate specificities of the S1–S4 subsites of vinckepain-2 and vinckepain-2A G as described previously [19]. To determine P1#$ specificity, a P1-diverse library consisting of 20 sublibraries was used. In each sublibrary, the P1 position contained one native amino acid, and the P2, P3 and P4 posit ...
In Word
... secondary structure. 3. Tertiary structure results when proteins of secondary structure are folded, due to various interactions between the R groups of their constituent amino acids 4. Quaternary structure results when two or more polypeptides combine. 1) Hemoglobin is globular protein with a quater ...
... secondary structure. 3. Tertiary structure results when proteins of secondary structure are folded, due to various interactions between the R groups of their constituent amino acids 4. Quaternary structure results when two or more polypeptides combine. 1) Hemoglobin is globular protein with a quater ...
Biology I Honors Chapter 3 Biochemistry I. Cells Contain Organic
... secondary structure. 3. Tertiary structure results when proteins of secondary structure are folded, due to various interactions between the R groups of their constituent amino acids 4. Quaternary structure results when two or more polypeptides combine. 1) Hemoglobin is globular protein with a quater ...
... secondary structure. 3. Tertiary structure results when proteins of secondary structure are folded, due to various interactions between the R groups of their constituent amino acids 4. Quaternary structure results when two or more polypeptides combine. 1) Hemoglobin is globular protein with a quater ...
اضغط هنا لتحميل المحاضرة
... that function to pass electrons by reversibly changing the oxidation state of the Fe in heme between the 2+ and 3+ state and serves as an electron acceptor–donor P450 is not a singular hemoprotein but rather a family of related hemoproteins. Over 1000 have been identified in nature with ~50 functi ...
... that function to pass electrons by reversibly changing the oxidation state of the Fe in heme between the 2+ and 3+ state and serves as an electron acceptor–donor P450 is not a singular hemoprotein but rather a family of related hemoproteins. Over 1000 have been identified in nature with ~50 functi ...
Dog and human acid ,-D-galactosidases are structurally similar
... 1982). However, they were present in only trace proportions in our preparations, and we do not believe them to be significant here. The final specific activities of the most purified preparations of the dog enzyme with the 4-methylumbelliferyl substrate averaged 25 umol cleaved/min per mg of protein ...
... 1982). However, they were present in only trace proportions in our preparations, and we do not believe them to be significant here. The final specific activities of the most purified preparations of the dog enzyme with the 4-methylumbelliferyl substrate averaged 25 umol cleaved/min per mg of protein ...
ES 120 TOXICS IN THE ENVIRONMENT
... Pollutants are toxic because they interfere with normal biochemical and physiological processes. Molecular toxicity may translate into ...
... Pollutants are toxic because they interfere with normal biochemical and physiological processes. Molecular toxicity may translate into ...
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex (PDC)
... Purple spheres are the 12 dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase (E3) subunits also form dimers ...
... Purple spheres are the 12 dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase (E3) subunits also form dimers ...
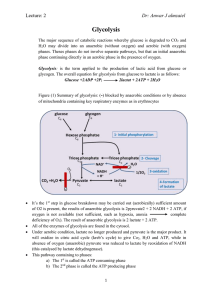
Dr: Anwar J almzaiel Glycolysis
... H2O may divide into an anaerobic (without oxygen) and aerobic (with oxygen) phases. Theses phases do not involve separate pathways, but that an initial anaerobic phase continuing directly in an aerobic phase in the presence of oxygen. Glycolysis: is the term applied to the production of lactic acid ...
... H2O may divide into an anaerobic (without oxygen) and aerobic (with oxygen) phases. Theses phases do not involve separate pathways, but that an initial anaerobic phase continuing directly in an aerobic phase in the presence of oxygen. Glycolysis: is the term applied to the production of lactic acid ...
Enzyme

Enzymes /ˈɛnzaɪmz/ are macromolecular biological catalysts. Enzymes accelerate, or catalyze, chemical reactions. The molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates and the enzyme converts these into different molecules, called products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. The set of enzymes made in a cell determines which metabolic pathways occur in that cell. The study of enzymes is called enzymology.Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Most enzymes are proteins, although a few are catalytic RNA molecules. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures.Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by lowering its activation energy. Some enzymes can make their conversion of substrate to product occur many millions of times faster. An extreme example is orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase, which allows a reaction that would otherwise take millions of years to occur in milliseconds. Chemically, enzymes are like any catalyst and are not consumed in chemical reactions, nor do they alter the equilibrium of a reaction. Enzymes differ from most other catalysts by being much more specific. Enzyme activity can be affected by other molecules: inhibitors are molecules that decrease enzyme activity, and activators are molecules that increase activity. Many drugs and poisons are enzyme inhibitors. An enzyme's activity decreases markedly outside its optimal temperature and pH.Some enzymes are used commercially, for example, in the synthesis of antibiotics. Some household products use enzymes to speed up chemical reactions: enzymes in biological washing powders break down protein, starch or fat stains on clothes, and enzymes in meat tenderizer break down proteins into smaller molecules, making the meat easier to chew.