... B14: (6 pts) Describe the role of hydrogen bonding in one of the following three situations. In the case of the first two choices your answer should include a description of the importance of this interaction in template directed polymer synthesis. In the case of the choice C, you should make a dist ...
ijbbaug
... D(-) Luciferin, interacts with different metal ions to produce colourless soluble salts with absorption spectra broader, intense and red shifted as compared to those of the parent compound. The equilibrium constants for the luciferin-metal ion system vary in the order, depository divalent transition ...
... D(-) Luciferin, interacts with different metal ions to produce colourless soluble salts with absorption spectra broader, intense and red shifted as compared to those of the parent compound. The equilibrium constants for the luciferin-metal ion system vary in the order, depository divalent transition ...
Oxidative stress induced by manganese (II) intoxication in Huh 7 cells
... stress [19]. This protective effect is likely to derive from the fact that Mn (II) can catalyze the dismutation of superoxide radical anion and H2O2 under physiological conditions. A number of studies have revealed that most organisms use MnSOD instead of Mn(II) to dismutate superoxide, possibly bec ...
... stress [19]. This protective effect is likely to derive from the fact that Mn (II) can catalyze the dismutation of superoxide radical anion and H2O2 under physiological conditions. A number of studies have revealed that most organisms use MnSOD instead of Mn(II) to dismutate superoxide, possibly bec ...
S1 Supplementary information.
... CD4-3200bp substrate. Examples of end-joining intermediates in C-NHEJ (left panel), which are KU/Lig4-dependant and A-EJ (right panel), which are KU/Lig4-independant. Upper panel: the structure of the I-SceI cleavage site (bold type indicates the four 3’-protruding nucleotides generated by I-SceI cl ...
... CD4-3200bp substrate. Examples of end-joining intermediates in C-NHEJ (left panel), which are KU/Lig4-dependant and A-EJ (right panel), which are KU/Lig4-independant. Upper panel: the structure of the I-SceI cleavage site (bold type indicates the four 3’-protruding nucleotides generated by I-SceI cl ...
CBS (EC 4.2.1.22). The rate equation for the CBS reaction
... In order to further simplify the model, we made additional general assumptions. Concentrations of ATP, adenosine, betaine, dimethylglycine, glycine, NADPH, and serine, as well as a total concentration of all intracellular folates (F0) are assumed to be constant. In this way, either there is no depen ...
... In order to further simplify the model, we made additional general assumptions. Concentrations of ATP, adenosine, betaine, dimethylglycine, glycine, NADPH, and serine, as well as a total concentration of all intracellular folates (F0) are assumed to be constant. In this way, either there is no depen ...
Rice HYDROPEROXIDE LYASES with Unique
... PCR-based amplification from rice genomic DNA, and their identity was confirmed by sequence analysis. OsHPL1 (1,533 bp) is predicted to encode a polypeptide of 511 amino acids with a calculated molecular mass of 55 kD. OsHPL2 (1,503 bp) is predicted to encode a polypeptide of 501 amino acids with a ...
... PCR-based amplification from rice genomic DNA, and their identity was confirmed by sequence analysis. OsHPL1 (1,533 bp) is predicted to encode a polypeptide of 511 amino acids with a calculated molecular mass of 55 kD. OsHPL2 (1,503 bp) is predicted to encode a polypeptide of 501 amino acids with a ...
ATPase - cloudfront.net
... Synthesis: accomplished through a process called translation. After DNA is transcribed into a messenger RNA molecule during transcription, the mRNA must be translated to produce a protein. http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/0/0f/Peptide_syn.png Every function in a living cell depends ...
... Synthesis: accomplished through a process called translation. After DNA is transcribed into a messenger RNA molecule during transcription, the mRNA must be translated to produce a protein. http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/0/0f/Peptide_syn.png Every function in a living cell depends ...
Principles of BIOCHEMISTRY
... • Catalyzes transfer of a phosphoryl group from ATP to the C-1 hydroxyl group of F6P to form fructose 1,6-bisphosphate (F1,6BP) • PFK-1 is metabolically irreversible and a critical regulatory point for glycolysis in most cells (PFK-1 is the first committed step of glycolysis) ...
... • Catalyzes transfer of a phosphoryl group from ATP to the C-1 hydroxyl group of F6P to form fructose 1,6-bisphosphate (F1,6BP) • PFK-1 is metabolically irreversible and a critical regulatory point for glycolysis in most cells (PFK-1 is the first committed step of glycolysis) ...
Tentative exam questions on Food Biochemistry part - e
... Interaction with formaldehyde. Application. Write the reaction. Interaction with ninhydrin. Application. Interaction with alcohols. Write the reaction. Lecture 2: Protein structure: primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary structure Describe the formation of a polypeptide chain. Peptide bond form ...
... Interaction with formaldehyde. Application. Write the reaction. Interaction with ninhydrin. Application. Interaction with alcohols. Write the reaction. Lecture 2: Protein structure: primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary structure Describe the formation of a polypeptide chain. Peptide bond form ...
Solutions to 7.012 Problem Set 2
... of Km is proportional to the affinity of the substrate for the enzyme and is thus of significant physiological relevance. c) The above graph only describes a specific enzymatic reaction at a single given concentration of the enzyme. Qualitatively, what would one expect to happen to Vmax if the amoun ...
... of Km is proportional to the affinity of the substrate for the enzyme and is thus of significant physiological relevance. c) The above graph only describes a specific enzymatic reaction at a single given concentration of the enzyme. Qualitatively, what would one expect to happen to Vmax if the amoun ...
BSC1010 Quiz 2 Answers - Palm Beach State College
... 33) Ancient prokaryotes are thought to have used glycolysis long before there was oxygen in the atmosphere, the reason for this is thought to be that ___________. A) Glycolysis is a very new process B) Very little O2 was available in the atmosphere until about 2.7 billion years ago, so early prokar ...
... 33) Ancient prokaryotes are thought to have used glycolysis long before there was oxygen in the atmosphere, the reason for this is thought to be that ___________. A) Glycolysis is a very new process B) Very little O2 was available in the atmosphere until about 2.7 billion years ago, so early prokar ...
Biochemistry_Written_Tests.doc
... to pyruvate (by LDH5) and used for gluconeogenesis, then the glucose formed is transported back to muscle for glycolysis. ...
... to pyruvate (by LDH5) and used for gluconeogenesis, then the glucose formed is transported back to muscle for glycolysis. ...
Controlling complexity and water penetration in functional de novo
... lower than those exhibited by natural proteins. Another similar method entails quantum mechanical calculation of the transition state followed by exposure of this hypothetical molecule to a set of protein crystal structures in silico [12– 14]. Once suitable structures have been identified, further m ...
... lower than those exhibited by natural proteins. Another similar method entails quantum mechanical calculation of the transition state followed by exposure of this hypothetical molecule to a set of protein crystal structures in silico [12– 14]. Once suitable structures have been identified, further m ...
Citric Acid Cycle: Central Role in Catabolism Entry of Pyruvate into
... dehydrogenase, cofactor TPP. (TPP, the coenzyme form of vitamin B1 facilitates decarboxylation reactions). Pyruvate gets complexed with TPP and looses a CO2 to become an alcohol. • Step 2. The substrate gets transferred from TPP to lipoamide forming a thioester linkage. In the process, the -C–OH is ...
... dehydrogenase, cofactor TPP. (TPP, the coenzyme form of vitamin B1 facilitates decarboxylation reactions). Pyruvate gets complexed with TPP and looses a CO2 to become an alcohol. • Step 2. The substrate gets transferred from TPP to lipoamide forming a thioester linkage. In the process, the -C–OH is ...
Inborn Errors of Amino Acid Metabolism
... Tyr will not be converted to catecholamine (neurotransmitter) Synthesis of catecholamines requires BH4 ...
... Tyr will not be converted to catecholamine (neurotransmitter) Synthesis of catecholamines requires BH4 ...
The Effect of Temperature on the Metabolism of
... found to differ in several respects (Table 2). The yield of organisms was greater at the lower growth temperature and slightly more nitrogen was utilized. In contrast, the ethanol production was less than half that observed with cultures grown at 38", despite the complete utilization of glucose. A f ...
... found to differ in several respects (Table 2). The yield of organisms was greater at the lower growth temperature and slightly more nitrogen was utilized. In contrast, the ethanol production was less than half that observed with cultures grown at 38", despite the complete utilization of glucose. A f ...
Fatty acid catabolism leture2-3
... In untreated diabetes, the concentration of ketone bodies (two of which are acids) in blood increases so much that it decreases the pH of blood. This condition is called “acidosis” which can lead to com or death. High concentration of ketone bodies in blood and urine is referred as “ketosis”. Due to ...
... In untreated diabetes, the concentration of ketone bodies (two of which are acids) in blood increases so much that it decreases the pH of blood. This condition is called “acidosis” which can lead to com or death. High concentration of ketone bodies in blood and urine is referred as “ketosis”. Due to ...
Anaerobic Respiration
... • Glycolysis is the only process that can function • The NAD that has been reduced (Hydrogen added) has to be re-oxidised (Hydrogen removed) so that it can keep accepting Hydrogens in glycolysis • There are two ways that NAD can be reoxidised • Fungi e.g. yeast use ethanol fermentation • Animals use ...
... • Glycolysis is the only process that can function • The NAD that has been reduced (Hydrogen added) has to be re-oxidised (Hydrogen removed) so that it can keep accepting Hydrogens in glycolysis • There are two ways that NAD can be reoxidised • Fungi e.g. yeast use ethanol fermentation • Animals use ...
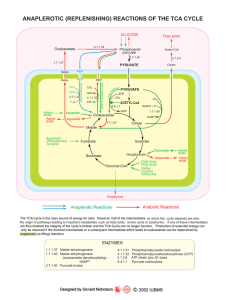
anaplerotic (replenishing) reactions of the tca cycle - Sigma
... The TCA Cycle is the main source of energy for cells. However, half of the intermediates on which the cycle depends are also the origin of pathways leading to important metabolites such as fatty acids , amino acids or porphyrins. If any of these intermediates are thus diverted the integrity of the c ...
... The TCA Cycle is the main source of energy for cells. However, half of the intermediates on which the cycle depends are also the origin of pathways leading to important metabolites such as fatty acids , amino acids or porphyrins. If any of these intermediates are thus diverted the integrity of the c ...
Enzyme

Enzymes /ˈɛnzaɪmz/ are macromolecular biological catalysts. Enzymes accelerate, or catalyze, chemical reactions. The molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates and the enzyme converts these into different molecules, called products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. The set of enzymes made in a cell determines which metabolic pathways occur in that cell. The study of enzymes is called enzymology.Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Most enzymes are proteins, although a few are catalytic RNA molecules. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures.Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by lowering its activation energy. Some enzymes can make their conversion of substrate to product occur many millions of times faster. An extreme example is orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase, which allows a reaction that would otherwise take millions of years to occur in milliseconds. Chemically, enzymes are like any catalyst and are not consumed in chemical reactions, nor do they alter the equilibrium of a reaction. Enzymes differ from most other catalysts by being much more specific. Enzyme activity can be affected by other molecules: inhibitors are molecules that decrease enzyme activity, and activators are molecules that increase activity. Many drugs and poisons are enzyme inhibitors. An enzyme's activity decreases markedly outside its optimal temperature and pH.Some enzymes are used commercially, for example, in the synthesis of antibiotics. Some household products use enzymes to speed up chemical reactions: enzymes in biological washing powders break down protein, starch or fat stains on clothes, and enzymes in meat tenderizer break down proteins into smaller molecules, making the meat easier to chew.