ppt-file
... Friedrich Schiller University Jena, Dept. of Bioinformatics Ernst-Abbe-Pl. 2, 07743 Jena email: (schuster, kamp)@minet.uni-jena.de ...
... Friedrich Schiller University Jena, Dept. of Bioinformatics Ernst-Abbe-Pl. 2, 07743 Jena email: (schuster, kamp)@minet.uni-jena.de ...
Overview of Metabolism - Chapter 4 - Formatted
... temperature, pressure, pH and many such parameters that we can blithely alter when we carry out reactions in test-tubes. To achieve this feat, biochemical evolution has produced enzymes, which are biocatalysts, ubiquitious in all prokaryotes and eukaryotes. You have learnt how enzymes facilitate rea ...
... temperature, pressure, pH and many such parameters that we can blithely alter when we carry out reactions in test-tubes. To achieve this feat, biochemical evolution has produced enzymes, which are biocatalysts, ubiquitious in all prokaryotes and eukaryotes. You have learnt how enzymes facilitate rea ...
(metabolic pathways) based on functional group
... In order to improve the understanding of disease process, many “omics ” sciences have been applied to provide useful biological information for researchers, including genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics and metabonomics. Among all “omics” sciences, metabonomics has been highlighted from the viewpo ...
... In order to improve the understanding of disease process, many “omics ” sciences have been applied to provide useful biological information for researchers, including genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics and metabonomics. Among all “omics” sciences, metabonomics has been highlighted from the viewpo ...
Powerpoint - Castle High School
... protein that requires the cofactor pyridoxal 5'-phosphate (PLP). Although heme is essential for activity inmammalian CBS, the chemistry is performed by PLP, and heme is not present in the enzyme of lower organisms. Why, then, has nature included a heme in the CBS of mammals? Our hypothesis is that t ...
... protein that requires the cofactor pyridoxal 5'-phosphate (PLP). Although heme is essential for activity inmammalian CBS, the chemistry is performed by PLP, and heme is not present in the enzyme of lower organisms. Why, then, has nature included a heme in the CBS of mammals? Our hypothesis is that t ...
L15 Gene Regulation Part1 Fa08
... – Gene that codes for a protein that controls the transcription of another gene or group of genes • Repressor – Protein that inhibits gene transcription – Binds to operator & prevents RNA polymerase from attaching to promoter ...
... – Gene that codes for a protein that controls the transcription of another gene or group of genes • Repressor – Protein that inhibits gene transcription – Binds to operator & prevents RNA polymerase from attaching to promoter ...
Chapter 4 - Cellular Metabolism 4.1 Introduction (p. 74) A. A living
... electricity, radiation, and by other causes. 4.4 Energy for Metabolic Reactions (p. 77) A. Energy is the capacity to do work. B. Common forms of energy include heat, light, and sound, and electrical, mechanical, and chemical energy. C. Release of Chemical Energy (p. 77) ...
... electricity, radiation, and by other causes. 4.4 Energy for Metabolic Reactions (p. 77) A. Energy is the capacity to do work. B. Common forms of energy include heat, light, and sound, and electrical, mechanical, and chemical energy. C. Release of Chemical Energy (p. 77) ...
Biological databases-Intro
... available is PubMed. But PubMed has only short abstracts. NO information about conditions, M&M etc We need to change this culture ...
... available is PubMed. But PubMed has only short abstracts. NO information about conditions, M&M etc We need to change this culture ...
Document
... ending with oxygen accepting electrons to water. Energy release is first used to pump protons (H+) across the membrane; a proton motive force (PMF) then drives ATP synthesis. Each NADH will make 3 ATP. Each FADH will make 2 ATP ...
... ending with oxygen accepting electrons to water. Energy release is first used to pump protons (H+) across the membrane; a proton motive force (PMF) then drives ATP synthesis. Each NADH will make 3 ATP. Each FADH will make 2 ATP ...
enzyme
... • What are enzymes? – Enzymes are proteins. Proteins are made from amino acids. Different combination of amino acids will create different structures of protein. The structure determines function of protein (enzyme) ...
... • What are enzymes? – Enzymes are proteins. Proteins are made from amino acids. Different combination of amino acids will create different structures of protein. The structure determines function of protein (enzyme) ...
Analysis of Binary Relations and Hierarchies of Enzymes in the
... found only for E. coli. Although E. coli genome sequencing has not yet been completed, the latter case may need further investigation because the functional assignments of H. in uenzae ORFs are mainly based on the homology search to other organisms, especially E. coli. In H. in uenzae, whose genomic ...
... found only for E. coli. Although E. coli genome sequencing has not yet been completed, the latter case may need further investigation because the functional assignments of H. in uenzae ORFs are mainly based on the homology search to other organisms, especially E. coli. In H. in uenzae, whose genomic ...
here - IMSS Biology 2014
... Changes basal metabolic rate Causes release of insulin which favors energy storage Alters hormonal control of appetite and satiety centers in the brain • Mechanisms • Direct gene activation • Epigenetic actions ...
... Changes basal metabolic rate Causes release of insulin which favors energy storage Alters hormonal control of appetite and satiety centers in the brain • Mechanisms • Direct gene activation • Epigenetic actions ...
Test Review Unit 1
... 8) What is metabolism (metabolic activity)? 9) What is homeostasis? Explain how the human body maintains homeostasis (one example). 10) What is asexual reproduction? What kind of offspring does it produce (compared to the parent)? 11) What is sexual reproduction? What kind of offspring does it prod ...
... 8) What is metabolism (metabolic activity)? 9) What is homeostasis? Explain how the human body maintains homeostasis (one example). 10) What is asexual reproduction? What kind of offspring does it produce (compared to the parent)? 11) What is sexual reproduction? What kind of offspring does it prod ...
Study Guide and Potential Essay Questions for Chapter 25
... hypothermia, Krebs’ cycle (TCA or citric acid cycle), lactic acid (lactate), metabolic rate, metabolic water, metabolism, minerals, mitochondrial matrix and inner membrane, NAD+/NADH + H+, nutrient, oxidation, oxidative phosphorylation, pyruvate-to-acetate step, reduction, substrate level phosphoryl ...
... hypothermia, Krebs’ cycle (TCA or citric acid cycle), lactic acid (lactate), metabolic rate, metabolic water, metabolism, minerals, mitochondrial matrix and inner membrane, NAD+/NADH + H+, nutrient, oxidation, oxidative phosphorylation, pyruvate-to-acetate step, reduction, substrate level phosphoryl ...
lecture notes-molecular biology-cell regulation
... When the cell has an energetically favorable carbon-energy source (e.g. glucose) available, ...
... When the cell has an energetically favorable carbon-energy source (e.g. glucose) available, ...
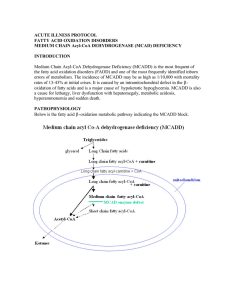
Fatty acid oxidation MCADdefici
... have become ill after severe exertion (e.g. jogging). The presentation is characterized by marked lethargy, often in association with vomiting after a period of fasting. This can progress to hypoglycemic seizures or coma within 1-2 hours of ONSET of symptoms. On occasion seizures or coma may be the ...
... have become ill after severe exertion (e.g. jogging). The presentation is characterized by marked lethargy, often in association with vomiting after a period of fasting. This can progress to hypoglycemic seizures or coma within 1-2 hours of ONSET of symptoms. On occasion seizures or coma may be the ...
Carbohydrate and sugar structure
... Metabolic pathways •Metabolic pathways are compartmentalized. •Oxidative phosphorylation occurs in mitochondria while glycolysis and fatty acid biosynthesis occur in the cytosol. •Gluconeogenesis occurs in liver to maintain constant level glucose in the circulation but adipose tissue specializes in ...
... Metabolic pathways •Metabolic pathways are compartmentalized. •Oxidative phosphorylation occurs in mitochondria while glycolysis and fatty acid biosynthesis occur in the cytosol. •Gluconeogenesis occurs in liver to maintain constant level glucose in the circulation but adipose tissue specializes in ...
D53 - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
... SPECT, fMRI – see D66 p. PET, SPECT - image function predominantly (anatomy to lesser degree) - most useful in: a) disease without easily identifiable anatomic correlates (e.g. Parkinson’s disease). b) diffuse brain disease (e.g. degenerative dementias - Alzheimer's disease, Pick disease). c) defini ...
... SPECT, fMRI – see D66 p. PET, SPECT - image function predominantly (anatomy to lesser degree) - most useful in: a) disease without easily identifiable anatomic correlates (e.g. Parkinson’s disease). b) diffuse brain disease (e.g. degenerative dementias - Alzheimer's disease, Pick disease). c) defini ...
... Due to the continuously increasing high energy demands of society and the finite nature of fossil fuels, alternative energy sources are becoming exceedingly important. Hydrogen is a promising alternative fuel because of its clean, renewable and high energy content of 122 kJ g – 1 which is 2.75 times ...
Metabolic network modelling

Metabolic network reconstruction and simulation allows for an in-depth insight into the molecular mechanisms of a particular organism. In particular, these models correlate the genome with molecular physiology. A reconstruction breaks down metabolic pathways (such as glycolysis and the Citric acid cycle) into their respective reactions and enzymes, and analyzes them within the perspective of the entire network. In simplified terms, a reconstruction collects all of the relevant metabolic information of an organism and compiles it in a mathematical model. Validation and analysis of reconstructions can allow identification of key features of metabolism such as growth yield, resource distribution, network robustness, and gene essentiality. This knowledge can then be applied to create novel biotechnology.In general, the process to build a reconstruction is as follows: Draft a reconstruction Refine the model Convert model into a mathematical/computational representation Evaluate and debug model through experimentation↑