Exploring the Potential for using Artificial Intelligence
... crime analysis (Chen et al. 2004). Nowhere are the data volume issues more evident than in the amount of police reports that were added each day in 2009. An average of 607 police reports were filed each day, totaling in 221 708 for the whole year, in the Västra Götaland region of Sweden alone1. The ...
... crime analysis (Chen et al. 2004). Nowhere are the data volume issues more evident than in the amount of police reports that were added each day in 2009. An average of 607 police reports were filed each day, totaling in 221 708 for the whole year, in the Västra Götaland region of Sweden alone1. The ...
Computational Intelligence: Neural Networks and
... learning, hybrid techniques, nonlinear dynamics and chaos, various soft computing technologies, bioinformatics and biomedicine, and engineering applications. IEEE International Conference on Systems Man and Cybernetics (SMC). Aims and scope are indicated next. SMC provides an international forum tha ...
... learning, hybrid techniques, nonlinear dynamics and chaos, various soft computing technologies, bioinformatics and biomedicine, and engineering applications. IEEE International Conference on Systems Man and Cybernetics (SMC). Aims and scope are indicated next. SMC provides an international forum tha ...
A Review of Class Imbalance Problem
... imbalanced classes. Section III, explain various evaluation metrics used in imbalanced classes. In Section IV, we explain various solutions introduced for dealing with imbalance class’s problem II. Feature Selection in Imbalance Problems Feature selection is another critical issue in machine learnin ...
... imbalanced classes. Section III, explain various evaluation metrics used in imbalanced classes. In Section IV, we explain various solutions introduced for dealing with imbalance class’s problem II. Feature Selection in Imbalance Problems Feature selection is another critical issue in machine learnin ...
proj02.doc
... 1. Before you start solving the problem, experiment with pow as described above to get a feel for how they work. That is, understand the tools before you begin trying to solve the problem. 2. Begin problem solving by using paper and pencil (and calculator) to solve the problem of calculating Hz val ...
... 1. Before you start solving the problem, experiment with pow as described above to get a feel for how they work. That is, understand the tools before you begin trying to solve the problem. 2. Begin problem solving by using paper and pencil (and calculator) to solve the problem of calculating Hz val ...
Particle Filters in Robotics, Sebastian Thrun
... still rely on gaussian-linear approximation advantages to pf's can be applied to any model that can be formulated using a Markov chain anytime comp time can be changed w number of particles, depending on resources easy to implement ...
... still rely on gaussian-linear approximation advantages to pf's can be applied to any model that can be formulated using a Markov chain anytime comp time can be changed w number of particles, depending on resources easy to implement ...
Probability and Equality: A Probabilistic Model of Identity Uncertainty
... have the same address and phone number. The probability that a single person lives in a house is 0.4. The probability that a person is living with a partner is 0.6. For a single person there is a 30% chance of having one child3 . The chances for a subsequent child is 10%. The probability that partne ...
... have the same address and phone number. The probability that a single person lives in a house is 0.4. The probability that a person is living with a partner is 0.6. For a single person there is a 30% chance of having one child3 . The chances for a subsequent child is 10%. The probability that partne ...
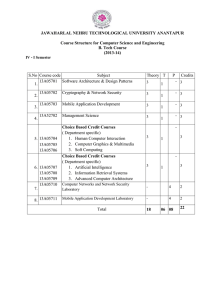
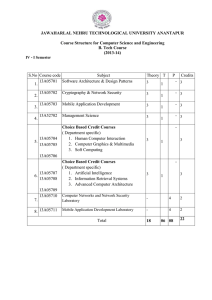
IV-I Sem R15 Syllabus for for the Academic Year 2016
... To introduce the Android technology and its application. Design & program real working education based mobile application projects. Become familiar with common mobile application technologies and platforms; open files, save files, create and program original material, integrate separate ...
... To introduce the Android technology and its application. Design & program real working education based mobile application projects. Become familiar with common mobile application technologies and platforms; open files, save files, create and program original material, integrate separate ...
pps
... Pr[Ij =1 | any execution history] ¸ 2/3 If we compare to ℓ independent coins with probability 2/3 where we take majority of answers For any prover* the interactive proof stochastically dominates ...
... Pr[Ij =1 | any execution history] ¸ 2/3 If we compare to ℓ independent coins with probability 2/3 where we take majority of answers For any prover* the interactive proof stochastically dominates ...
Table 4.2 The sample memberships and kernel set
... data and can take full advantage of much more detailed information for some ambiguity. However, certain challenging problems still remain open, such as: (1) Since hardly ever any disturbance or noise in the data set can be completely eliminated, therefore, for the case of interacting noise, the com ...
... data and can take full advantage of much more detailed information for some ambiguity. However, certain challenging problems still remain open, such as: (1) Since hardly ever any disturbance or noise in the data set can be completely eliminated, therefore, for the case of interacting noise, the com ...