Best-First Heuristic Search for Multicore Machines Ethan Burns .
... One way to reduce contention during search is to access the closed list less frequently. A technique called delayed duplicate detection (DDD) (Korf, 2003), originally developed for externalmemory search, can be used to temporarily delay access to the a closed list. While several variations have been ...
... One way to reduce contention during search is to access the closed list less frequently. A technique called delayed duplicate detection (DDD) (Korf, 2003), originally developed for externalmemory search, can be used to temporarily delay access to the a closed list. While several variations have been ...
Ch 16. Artificial Intelligence
... First, link the node x6 with a randomly selected region (x,y) = (100,120) in the image (Fig. 16.4), then store this linkage in a table In order to confirm the linkage made, scan the periphery of the selected region in the image to find the five objects connected to x6 A search of the surrounding are ...
... First, link the node x6 with a randomly selected region (x,y) = (100,120) in the image (Fig. 16.4), then store this linkage in a table In order to confirm the linkage made, scan the periphery of the selected region in the image to find the five objects connected to x6 A search of the surrounding are ...
Using a Goal-Agenda and Committed Actions in Real
... A planning problem (A, s0 , g) is a triplet where A is the set of actions, s0 the initial state and g the set of goals. A plan π = ha1 , . . . , an i with a1 , . . . , an ∈ A is solution for a planning problem (A, s0 , g) if g ⊆ γ(s0 , π). The time allocated to action selection is upper-bounded by a ...
... A planning problem (A, s0 , g) is a triplet where A is the set of actions, s0 the initial state and g the set of goals. A plan π = ha1 , . . . , an i with a1 , . . . , an ∈ A is solution for a planning problem (A, s0 , g) if g ⊆ γ(s0 , π). The time allocated to action selection is upper-bounded by a ...
Automated Theorem Proving in a First
... Computer mathematics studies processing of mathematical knowledge with a computer. It explores questions of how to represent mathematical problems and their proofs in a computer, how to check correctness of proofs by a computer and even how to construct proofs automatically using a computer. The lat ...
... Computer mathematics studies processing of mathematical knowledge with a computer. It explores questions of how to represent mathematical problems and their proofs in a computer, how to check correctness of proofs by a computer and even how to construct proofs automatically using a computer. The lat ...
9200 front - Strategic
... Chapter 10 – Reduced Complexity and Management Costs __________________________________47 A Powerful and Open Systems Management Philosophy ..........................................................................47 HiCommand Allows Systems Management of Hitachi Storage and Software through the Ent ...
... Chapter 10 – Reduced Complexity and Management Costs __________________________________47 A Powerful and Open Systems Management Philosophy ..........................................................................47 HiCommand Allows Systems Management of Hitachi Storage and Software through the Ent ...
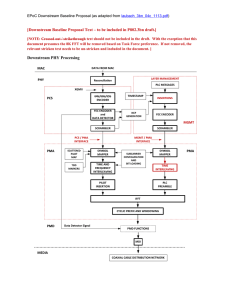
[Downstream Baseline Proposal Text – to be included in P802.3bn...
... The mapping of bits to QAM constellations is carried out in the Symbol Mapper. [Note to Editors: QAM constellation mapping as per prodan_3bn_02_1113.pdf as per TD#103. More text is likely needed.] Once FEC encoded codewords have been created, the codewords are placed into OFDM symbols. Because each ...
... The mapping of bits to QAM constellations is carried out in the Symbol Mapper. [Note to Editors: QAM constellation mapping as per prodan_3bn_02_1113.pdf as per TD#103. More text is likely needed.] Once FEC encoded codewords have been created, the codewords are placed into OFDM symbols. Because each ...
Heuristics - UCLA Cognitive Systems Laboratory
... trial begins with an “agent” at the start state sinit . The agent takes a sequence of actions where each action is selected greedily based on the current state evaluation function. The trial ends when the agent reaches a goal state. The algorithms are called “real-time” because they perform a limite ...
... trial begins with an “agent” at the start state sinit . The agent takes a sequence of actions where each action is selected greedily based on the current state evaluation function. The trial ends when the agent reaches a goal state. The algorithms are called “real-time” because they perform a limite ...
Strategies and Design for Interleaving Reasoning and Selection of Axioms
... important reasoning results to users. These strategies is aimed at satisfying a wide variety of user needs and removing the scalability barriers. Anytime algorithms are attractive for Web scale reasoning, because they allow a trade-off between the cost of the algorithm and the quality of the results ...
... important reasoning results to users. These strategies is aimed at satisfying a wide variety of user needs and removing the scalability barriers. Anytime algorithms are attractive for Web scale reasoning, because they allow a trade-off between the cost of the algorithm and the quality of the results ...
Functional Programming, Object-Oriented Programming and
... of code, but there is not The two systems related and share a lot of code, but In there is not any reuse of code are (in clearly a software engineering sense) between them. current ...
... of code, but there is not The two systems related and share a lot of code, but In there is not any reuse of code are (in clearly a software engineering sense) between them. current ...
Part I: Heuristics
... trial begins with an “agent” at the start state sinit . The agent takes a sequence of actions where each action is selected greedily based on the current state evaluation function. The trial ends when the agent reaches a goal state. The algorithms are called “real-time” because they perform a limite ...
... trial begins with an “agent” at the start state sinit . The agent takes a sequence of actions where each action is selected greedily based on the current state evaluation function. The trial ends when the agent reaches a goal state. The algorithms are called “real-time” because they perform a limite ...
Algorithms for Maximum Satisfiability
... path from S to G that does not pass a blocked square. Such a path will falsify one negative soft clause for every square it passes through. ...
... path from S to G that does not pass a blocked square. Such a path will falsify one negative soft clause for every square it passes through. ...
A Picture is Worth a Thousand Words
... If there is only one output for every input, you have a function. If not, you have a relation. Relations have more than one output for at least one input. The following table of values represents data collected by a student in a math class. ...
... If there is only one output for every input, you have a function. If not, you have a relation. Relations have more than one output for at least one input. The following table of values represents data collected by a student in a math class. ...
The complexity of planning - Dartmouth Computer Science
... be computationally much simpler, since in this case rewards cannot cancel each other out. We abstract the policy existence problems as follows: “Is there a policy with expected reward > 0?” We have chosen these decision problems because they can be used, along with binary search, to calculate the ex ...
... be computationally much simpler, since in this case rewards cannot cancel each other out. We abstract the policy existence problems as follows: “Is there a policy with expected reward > 0?” We have chosen these decision problems because they can be used, along with binary search, to calculate the ex ...
Stochastic Search and Surveillance Strategies for
... a symbiotic co-robot that facilitates efficient interaction of the human operator with the automaton. Given the complex interaction that can arise between the operator and the automaton, such a co-robotic partner will enable better interaction between the automaton and the operator by exploiting the ...
... a symbiotic co-robot that facilitates efficient interaction of the human operator with the automaton. Given the complex interaction that can arise between the operator and the automaton, such a co-robotic partner will enable better interaction between the automaton and the operator by exploiting the ...