CMPS 470, Spring 2008 Syllabus
... an interesting topic, and our book covers a broad spectrum of concepts and algorithms. We will be studying a selection of them and write programs that apply these concepts and algorithms. Also, each student should get a USB thumb drive in order to save work and software that may be provided for the ...
... an interesting topic, and our book covers a broad spectrum of concepts and algorithms. We will be studying a selection of them and write programs that apply these concepts and algorithms. Also, each student should get a USB thumb drive in order to save work and software that may be provided for the ...
Machine Learning ICS 273A
... The gradient is an average over many data-points. If your parameters are very “bad”, every data-point will tell you to move in the same direction, so you need only a few data-points to find that direction. Towards convergence you need all the data-points. A small step-size effectively averages ...
... The gradient is an average over many data-points. If your parameters are very “bad”, every data-point will tell you to move in the same direction, so you need only a few data-points to find that direction. Towards convergence you need all the data-points. A small step-size effectively averages ...
Research Topics in Discovery and Artificial Intelligence
... primary interests are in the areas of artificial intelligence and machine learning/data mining, and my current research is focused upon: (1) dramatically increasing the autonomy and power of machine learning/data mining programs, (2) applying the discovery programs I develop to biomedical databases, ...
... primary interests are in the areas of artificial intelligence and machine learning/data mining, and my current research is focused upon: (1) dramatically increasing the autonomy and power of machine learning/data mining programs, (2) applying the discovery programs I develop to biomedical databases, ...
Dalle Molle Institute for Artificial Intelligence
... The monolithic approach to robotics, which assumes one unit to be able to perform all tasks, is put into question when robot missions require capabilities greater than those possessed by a single individual. A swarm-bot which is a collection of independent mobile robots is a possible answer. The sof ...
... The monolithic approach to robotics, which assumes one unit to be able to perform all tasks, is put into question when robot missions require capabilities greater than those possessed by a single individual. A swarm-bot which is a collection of independent mobile robots is a possible answer. The sof ...
ppt - UTK-EECS
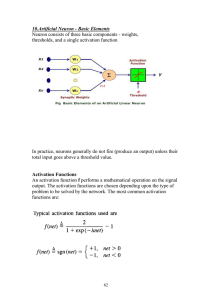
... According to Haykin, S. (1994), Neural Networks: A Comprehensive Foundation, NY: Macmillan, p. 2: ...
... According to Haykin, S. (1994), Neural Networks: A Comprehensive Foundation, NY: Macmillan, p. 2: ...
Data mining with
... tools. Interfaces to spreadsheet tools provide flexibility needed to work solutions as a team.” ...
... tools. Interfaces to spreadsheet tools provide flexibility needed to work solutions as a team.” ...
Machine Learning - Little Bee library
... Machine learning approaches are typically classified into three broad categories: Supervised learning: The computer is presented with example inputs and their desired outputs, given by a “teacher”, and the goal is to learn a general rule that maps inputs to outputs. The training process continues u ...
... Machine learning approaches are typically classified into three broad categories: Supervised learning: The computer is presented with example inputs and their desired outputs, given by a “teacher”, and the goal is to learn a general rule that maps inputs to outputs. The training process continues u ...
Machine Learning syl..
... Machine learning is an active and growing field that would require many courses to cover completely. This course aims at the middle of the theoretical versus practical spectrum. We will learn the concepts behind several machine learning algorithms without going deeply into the mathematics and gain p ...
... Machine learning is an active and growing field that would require many courses to cover completely. This course aims at the middle of the theoretical versus practical spectrum. We will learn the concepts behind several machine learning algorithms without going deeply into the mathematics and gain p ...