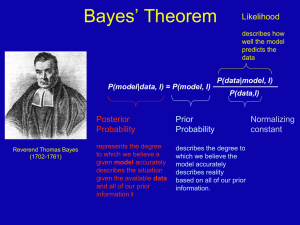
here - carrot!!!
... You can determine omega for the whole dataset; however, usually not all sites in a sequence are under selection all the time. PAML (and other programs) allow to either determine omega for each site over the whole tree, ...
... You can determine omega for the whole dataset; however, usually not all sites in a sequence are under selection all the time. PAML (and other programs) allow to either determine omega for each site over the whole tree, ...
Some critical remarks on the initial detection of lung ailments using clinical data & chest radiography
... involving symptoms and signs has been the centre of interest for diagnosing patients. Important decisions sometimes need to be made before the availability of the results of further tests. However, besides clinical data, the chest radiograph is also available. This study uses logistic regression mod ...
... involving symptoms and signs has been the centre of interest for diagnosing patients. Important decisions sometimes need to be made before the availability of the results of further tests. However, besides clinical data, the chest radiograph is also available. This study uses logistic regression mod ...
Full project report
... In order to achieve a neural network that is capable of classifying input, it needs to improve its initial edge weights. We do this through supervised learning. In this process we present the network with input from a training set. In each iteration of the learning process (or epoch), we iterate thr ...
... In order to achieve a neural network that is capable of classifying input, it needs to improve its initial edge weights. We do this through supervised learning. In this process we present the network with input from a training set. In each iteration of the learning process (or epoch), we iterate thr ...
6.S092: Visual Recognition through Machine Learning Competition
... • For every support vector xs the above inequality is an equality. After rescaling w and b by ρ/2 in the equality, we obtain that distance between each xs and the hyperplane is y s (wT x s + b) r= ...
... • For every support vector xs the above inequality is an equality. After rescaling w and b by ρ/2 in the equality, we obtain that distance between each xs and the hyperplane is y s (wT x s + b) r= ...
Mining Multi-label Data by Grigorios Tsoumakas, Ioannis Katakis
... Such data are called multi-label” (Tsoumakas et al). • Applications in ranking web pages. Web pages are often multi labeled. For example “cooking” and “food network” and “iron chef” might all apply to the same page. How do you rank and classify that along other pages that have some of the same label ...
... Such data are called multi-label” (Tsoumakas et al). • Applications in ranking web pages. Web pages are often multi labeled. For example “cooking” and “food network” and “iron chef” might all apply to the same page. How do you rank and classify that along other pages that have some of the same label ...
for machine learning on genomic data
... Project (phase 3) data by clustering 2,500 individuals with 80 million genomic variants each into their super-population groups achieving an ARI=0.82 (1 perfect and -1 random clustering). Aiming to further improve this performance and distinguish between the American and European populations, we sou ...
... Project (phase 3) data by clustering 2,500 individuals with 80 million genomic variants each into their super-population groups achieving an ARI=0.82 (1 perfect and -1 random clustering). Aiming to further improve this performance and distinguish between the American and European populations, we sou ...
Periodic table E
... A circle used to display data. The angle of each sector is proportional to the frequency ...
... A circle used to display data. The angle of each sector is proportional to the frequency ...
Project Description Student: Arvind Ravichandran Title: Examining
... Title: Examining the Mechanisms of the Human Brain with Computer Science Background: The object of all artificial intelligence studies is to simulate the capabilities of the Human brain. No project thus far has even been mildly successful in this endeavor. However, in this project, I seek to instead ...
... Title: Examining the Mechanisms of the Human Brain with Computer Science Background: The object of all artificial intelligence studies is to simulate the capabilities of the Human brain. No project thus far has even been mildly successful in this endeavor. However, in this project, I seek to instead ...