attribute_selection
... selection is done using the learning algorithm as a black box. Ron Kohavi, George H. John (1997). Wrappers for feature subset selection. Artificial Intelligence. 97(1-2):273-324. N. Gagunashvili (UNAK & MPIK) ...
... selection is done using the learning algorithm as a black box. Ron Kohavi, George H. John (1997). Wrappers for feature subset selection. Artificial Intelligence. 97(1-2):273-324. N. Gagunashvili (UNAK & MPIK) ...
Document
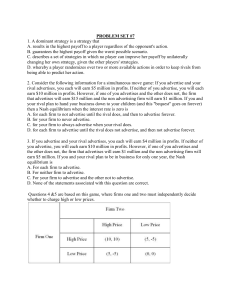
... Suppose an individual has $10,000 to invest between a stock and a bond. The stock is a financial asset which has a variable return that is uniformly distributed with an average return of 8.525% and a standard deviation of 3.767%. The bond returns 8.5% with certainty. Denote by 0 ≤ s ≤ 1 be the propo ...
... Suppose an individual has $10,000 to invest between a stock and a bond. The stock is a financial asset which has a variable return that is uniformly distributed with an average return of 8.525% and a standard deviation of 3.767%. The bond returns 8.5% with certainty. Denote by 0 ≤ s ≤ 1 be the propo ...
File
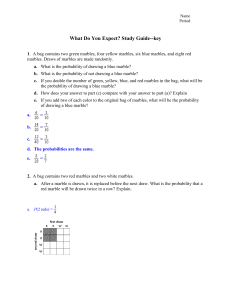
... 1. Temperature readings are taken at 20 weather stations throughout the UK. Readings are taken at each station 8 times in one day. a) Describe how a 2-D array could be used to store the temperatures for each station. b) Declare this array c) Write an algorithm that will count the number of occasions ...
... 1. Temperature readings are taken at 20 weather stations throughout the UK. Readings are taken at each station 8 times in one day. a) Describe how a 2-D array could be used to store the temperatures for each station. b) Declare this array c) Write an algorithm that will count the number of occasions ...
NECTAR: Nash Equilibrium Computation Algorithms
... player to play according to the prescribed strategy while others are playing according to the given strategy profile. In short, any player is not better off by unilateral deviation. Formally, the strategy profile s∗ = (s1∗, s2∗ , . . . , sn∗) is said to be a Nash equilibrium of G if, ui(si∗,s-i∗) ≥ ...
... player to play according to the prescribed strategy while others are playing according to the given strategy profile. In short, any player is not better off by unilateral deviation. Formally, the strategy profile s∗ = (s1∗, s2∗ , . . . , sn∗) is said to be a Nash equilibrium of G if, ui(si∗,s-i∗) ≥ ...
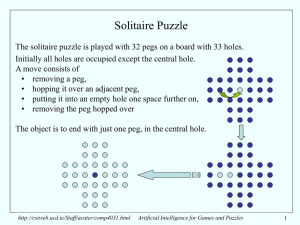
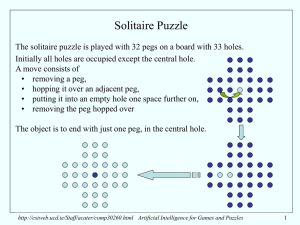
Artificial Intelligence Games- Outline Games vs. search problems
... • They illustrate several important points about AI • perfection is unattainable must approximate • good idea to think about what to think about ...
... • They illustrate several important points about AI • perfection is unattainable must approximate • good idea to think about what to think about ...