If multi-agent learning is the answer, what is the question?
... A final remark is in order. The reader may find some of the material in the next three sections basic or obvious; different readers will probably find different parts so. We don’t mean to insult anyone’s intelligence, but we err on the side of explicitness for two reasons. First, this article is add ...
... A final remark is in order. The reader may find some of the material in the next three sections basic or obvious; different readers will probably find different parts so. We don’t mean to insult anyone’s intelligence, but we err on the side of explicitness for two reasons. First, this article is add ...
A Planning Graph Heuristic for Forward-Chaining
... is not static. The exogenous dynamics can be caused by “nature” or by one or more other agents sharing the same environment. Other agents can behave neutrally (simply following their own independent agenda or otherwise acting unpredictably), adversarially, or cooperatively with respect to the protag ...
... is not static. The exogenous dynamics can be caused by “nature” or by one or more other agents sharing the same environment. Other agents can behave neutrally (simply following their own independent agenda or otherwise acting unpredictably), adversarially, or cooperatively with respect to the protag ...
maxmin
... Two kinds of "suspicious" points (for local max or min): f′(c) = 0 f′(c) does not exists ...
... Two kinds of "suspicious" points (for local max or min): f′(c) = 0 f′(c) does not exists ...
Evolutionary Game Theory: The Game of Life
... decision is called a strategy. A more formal definition is: A strategy is a complete contingent plan, or decision rule, that specifies how the player will act in every possible distinguishable circumstance in which she might be called upon to move.[1, pg.228] In the game we just defined, each player ...
... decision is called a strategy. A more formal definition is: A strategy is a complete contingent plan, or decision rule, that specifies how the player will act in every possible distinguishable circumstance in which she might be called upon to move.[1, pg.228] In the game we just defined, each player ...
Distributed Nash Equilibrium Seeking via the Alternating Direction
... in the context of finding an NE of a game. Here are the difficulties that we need to overcome: • A Nash game can be seen as a set of parallel optimization problems, each of them associated with the minimization of a player’s own cost function w.r.t. his variable. However, each optimization problem i ...
... in the context of finding an NE of a game. Here are the difficulties that we need to overcome: • A Nash game can be seen as a set of parallel optimization problems, each of them associated with the minimization of a player’s own cost function w.r.t. his variable. However, each optimization problem i ...
Approximate Solutions For Partially Observable Stochastic Games
... certainty and action selection is straightforward. But as this is not the case, each robot has uncertainty over the payoff. In the game theory literature, the private information held by an agent is called its type, and it encapsulates all non-commonly-known information to which the agent has access ...
... certainty and action selection is straightforward. But as this is not the case, each robot has uncertainty over the payoff. In the game theory literature, the private information held by an agent is called its type, and it encapsulates all non-commonly-known information to which the agent has access ...
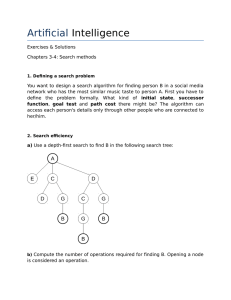
Artificial Intelligence
... root node, then expands all the successors of the root node, and then all their successors and so on. Breadth first search stops when first solution is found. ...
... root node, then expands all the successors of the root node, and then all their successors and so on. Breadth first search stops when first solution is found. ...
1 Bayesian Networks
... This blocked given D by the node E, since this is not one of the given nodes (i.e., is not D) and has both arrows on the path going into it. (ii) C − B − A − D − E − F . This path is also blocked by E (and D as well). So, D does d-separate C and F. (ii) Do D and E d-separate C and F ? The path C − B ...
... This blocked given D by the node E, since this is not one of the given nodes (i.e., is not D) and has both arrows on the path going into it. (ii) C − B − A − D − E − F . This path is also blocked by E (and D as well). So, D does d-separate C and F. (ii) Do D and E d-separate C and F ? The path C − B ...
Resources - CSE, IIT Bombay
... 1. Create a search graph G, consisting solely of the start node S; put S on a list called OPEN. 2. Create a list called CLOSED that is initially empty. 3. Loop: if OPEN is empty, exit with failure. 4. Select the first node on OPEN, remove from OPEN and put on CLOSED, call this node n. 5. if n is the ...
... 1. Create a search graph G, consisting solely of the start node S; put S on a list called OPEN. 2. Create a list called CLOSED that is initially empty. 3. Loop: if OPEN is empty, exit with failure. 4. Select the first node on OPEN, remove from OPEN and put on CLOSED, call this node n. 5. if n is the ...
A Well-Behaved Algorithm for Simulating Dependence Structures of
... Chu [2] designed an BN simulation algorithm also for testing learning algorithms. The algorithm takes three parameters as input: the number of nodes, the maximum in-degree d− , and the maximum out-degree d+ . For each node v, d− (v) (≤ d− ) is assigned first. Then d− (v) parent nodes are selected fr ...
... Chu [2] designed an BN simulation algorithm also for testing learning algorithms. The algorithm takes three parameters as input: the number of nodes, the maximum in-degree d− , and the maximum out-degree d+ . For each node v, d− (v) (≤ d− ) is assigned first. Then d− (v) parent nodes are selected fr ...