Review Questions Chapter 9
... A) product differentiation increases the variety of products available to consumers. B) the benefits associated with a product exceed those accruing to people who consume it. C) a firm produces at the P = MC output. D) economic profits are zero in the long run. 5. A negative externality or spillover ...
... A) product differentiation increases the variety of products available to consumers. B) the benefits associated with a product exceed those accruing to people who consume it. C) a firm produces at the P = MC output. D) economic profits are zero in the long run. 5. A negative externality or spillover ...
No Slide Title
... Chapter 3- Individual Markets Objective – Students will be able to answer questions regarding supply and demand. ...
... Chapter 3- Individual Markets Objective – Students will be able to answer questions regarding supply and demand. ...
Degree Applicable - Glendale Community College
... 6. evaluate historical and contemporary use of fiscal and monetary policy; 7. organize and write a thesis-driven, organized essay which is at least three paragraphs in length; 8. interpret bar and line graphs; 9. use simple algebraic equations; 10. calculate elementary functions such as percentage c ...
... 6. evaluate historical and contemporary use of fiscal and monetary policy; 7. organize and write a thesis-driven, organized essay which is at least three paragraphs in length; 8. interpret bar and line graphs; 9. use simple algebraic equations; 10. calculate elementary functions such as percentage c ...
Theory of Markets
... demand curves. Market Demand - a schedule showing the amounts of a good consumers are willing and able to purchase in the market for a series of prices during a specified period in a given market. ...
... demand curves. Market Demand - a schedule showing the amounts of a good consumers are willing and able to purchase in the market for a series of prices during a specified period in a given market. ...
market failure
... If society does not produce at ( up to the market clearing equilibrium of 4 units of at $5, then we say that the market is not allocative efficient. When this happens market failure occurs ...
... If society does not produce at ( up to the market clearing equilibrium of 4 units of at $5, then we say that the market is not allocative efficient. When this happens market failure occurs ...
Market Efficiency and Market Failure
... intends only his own personal gain, and he is in this aim... led as if by an 'invisible hand' to promote an end which was no part of his intention" "By pursuing his own self-interest, the entrepreneur frequently promotes that of society more effectually than when he means to promote it" (from Adam S ...
... intends only his own personal gain, and he is in this aim... led as if by an 'invisible hand' to promote an end which was no part of his intention" "By pursuing his own self-interest, the entrepreneur frequently promotes that of society more effectually than when he means to promote it" (from Adam S ...
Econ 102 Fall 2004 –First Midterm
... Normative Economics – the benchmarking of how the economy should be. Reasons for market failure Externalities – a situation when the market fails to fully account for all benefits and/or costs (e.g., a firm pollutes and the cost of this pollution is not included in this firm’s cost of production: th ...
... Normative Economics – the benchmarking of how the economy should be. Reasons for market failure Externalities – a situation when the market fails to fully account for all benefits and/or costs (e.g., a firm pollutes and the cost of this pollution is not included in this firm’s cost of production: th ...
Unit 1 - Markets and Market Failure
... Economies and Diseconomies of Scale: Examples of economies of scale, recognising that they lead to lower unit costs and may underlie the development of monopolies. Also examples of diseconomies of scale and recognise they lead to higher average cost. ...
... Economies and Diseconomies of Scale: Examples of economies of scale, recognising that they lead to lower unit costs and may underlie the development of monopolies. Also examples of diseconomies of scale and recognise they lead to higher average cost. ...
Exam 2 Study Guide
... Marginal Social Cost Pigovian Tax Tradable Pollution Permits Coase Theorem Private market can solve externality problem if side payments can be made without cost ...
... Marginal Social Cost Pigovian Tax Tradable Pollution Permits Coase Theorem Private market can solve externality problem if side payments can be made without cost ...
Market Failures
... • An externality is present when the welfare of some economic agent depends directly on his/hers actions and the actions under the control of some other economic agent as well • Exclusivity is violated ...
... • An externality is present when the welfare of some economic agent depends directly on his/hers actions and the actions under the control of some other economic agent as well • Exclusivity is violated ...
Markets and Market Failure What makes markets efficient? • Welfare
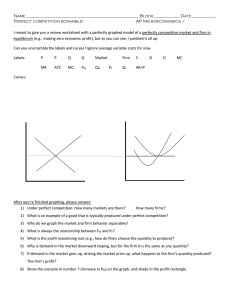
... – Each firm is a price taker Each firm produces perfect substitutes for the output of other firms. Perfect info. Equal access to technology. No barriers to entry and exit. No externalities. All costs and benefits priced. Accurate expression of individuals preferences. Low transaction costs. ...
... – Each firm is a price taker Each firm produces perfect substitutes for the output of other firms. Perfect info. Equal access to technology. No barriers to entry and exit. No externalities. All costs and benefits priced. Accurate expression of individuals preferences. Low transaction costs. ...