An Evolvable Hardware Tutorial - Department of Informatics
... An improvement of artificial evolution — called co-evolution, has been proposed [6]. In co-evolution, a part of the data which defines the problem co-evolves simultaneously with a population of individuals solving the problem. This could lead to a solution with a better generalization than a solutio ...
... An improvement of artificial evolution — called co-evolution, has been proposed [6]. In co-evolution, a part of the data which defines the problem co-evolves simultaneously with a population of individuals solving the problem. This could lead to a solution with a better generalization than a solutio ...
word - School of Computer Science
... how computers can learn to play chess [KEN01a], how evolutionary strategies can be used to predict macro-economic factors ([KEN01b], [KEN01c], KEN01d]) and how collective behaviour can emerge from seemingly simple organisms [WAR01]. In addition to the CNA grant, Dr Kendall has recently been awarded ...
... how computers can learn to play chess [KEN01a], how evolutionary strategies can be used to predict macro-economic factors ([KEN01b], [KEN01c], KEN01d]) and how collective behaviour can emerge from seemingly simple organisms [WAR01]. In addition to the CNA grant, Dr Kendall has recently been awarded ...
DEPARTMENT OF NON-METALLIC MATERIALS ENGINEERING
... x ≥ 0 are the constraints which specify a convex polytope over which the objective function is to be optimized. In this context, two vectors are comparable when they have the same dimensions. If every entry in the first is less-than or equal-to the corresponding entry in the second then we can say t ...
... x ≥ 0 are the constraints which specify a convex polytope over which the objective function is to be optimized. In this context, two vectors are comparable when they have the same dimensions. If every entry in the first is less-than or equal-to the corresponding entry in the second then we can say t ...
ORAL DEFENCE ANNOUNCEMENT Matching Market Design: From
... This thesis examines efficiency and fairness in matching markets. We first study a generalized many-tomany matching problem with ties. A natural solution concept is Pareto stability, which ensures both stability and Pareto efficiency. We show that a Pareto stable matching always exists by developing ...
... This thesis examines efficiency and fairness in matching markets. We first study a generalized many-tomany matching problem with ties. A natural solution concept is Pareto stability, which ensures both stability and Pareto efficiency. We show that a Pareto stable matching always exists by developing ...
The Robustness-Performance Tradeoff in Markov Decision Processes
... the real parameters, so that the performance of the solution under nominal parameters may provide important information for predicting the performance under the true parameters. Finally, there is a certain tradeoff relationship between the worst-case performance and the nominal performance, that is ...
... the real parameters, so that the performance of the solution under nominal parameters may provide important information for predicting the performance under the true parameters. Finally, there is a certain tradeoff relationship between the worst-case performance and the nominal performance, that is ...
the application of artificial intelligence methods in heat - QRC
... Genetic algorithms belong to the class of stochastic search methods. Whereas most stochastic search methods operate on a single solution to the problem at hand, genetic algorithms operate on a population of solutions. In genetic algorithm problem must be encoded in a structure that can be stored in ...
... Genetic algorithms belong to the class of stochastic search methods. Whereas most stochastic search methods operate on a single solution to the problem at hand, genetic algorithms operate on a population of solutions. In genetic algorithm problem must be encoded in a structure that can be stored in ...
Evolutionary Algorithm for Connection Weights in Artificial Neural
... One way to overcome gradient-descent-based training algorithms’ shortcomings is to adopt EANN’s, i.e., to formulate the training process as the evolution of connection weights in the environment determined by the architecture and the learning task. EA’s can then be used effectively in the evolution ...
... One way to overcome gradient-descent-based training algorithms’ shortcomings is to adopt EANN’s, i.e., to formulate the training process as the evolution of connection weights in the environment determined by the architecture and the learning task. EA’s can then be used effectively in the evolution ...
Solutions to Assignment 2.
... has half as many elements to compare. At the end only the global minimum will be left. This is n2 + n4 + n8 + . . . + 1 = n2 (2)(1 − n1 ) = n − 1 comparisons. Now, note that the second smallest element could only have been eliminated by the global minimum. Therefore, it must be one of the dlg ne ele ...
... has half as many elements to compare. At the end only the global minimum will be left. This is n2 + n4 + n8 + . . . + 1 = n2 (2)(1 − n1 ) = n − 1 comparisons. Now, note that the second smallest element could only have been eliminated by the global minimum. Therefore, it must be one of the dlg ne ele ...
April 4, 2014. WalkSat, part I
... then there are 2n many τ ’s to try. The runtime is ≈ |Γ| · 2n . The naive randomized algorithm for SAT is as follows. loop Choose τ at random if τ satisfies Γ then Output τ end if end loop Observe that if there are s satisfying assignments τ , then each loop can succeed with probability 2sn = p So t ...
... then there are 2n many τ ’s to try. The runtime is ≈ |Γ| · 2n . The naive randomized algorithm for SAT is as follows. loop Choose τ at random if τ satisfies Γ then Output τ end if end loop Observe that if there are s satisfying assignments τ , then each loop can succeed with probability 2sn = p So t ...
Reactiveness and Navigation in Computer Games: Different Needs
... Evolutionary algorithms can help to solve some of these problems, making them particularly suitable for certain game environments. Their stochastic nature, along with tunable high- or low-level representations, contribute to the discovery of non-obvious solutions, while their population-based nature ...
... Evolutionary algorithms can help to solve some of these problems, making them particularly suitable for certain game environments. Their stochastic nature, along with tunable high- or low-level representations, contribute to the discovery of non-obvious solutions, while their population-based nature ...
I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I
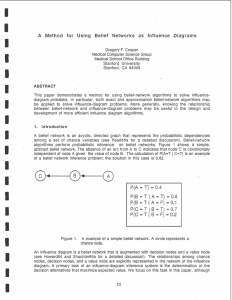
... singly connected [Pearl86a]. Those belief-network algorithms that are designed for performing probabilistic inference using multiply-connected belief networks can be used to perform expected-value decision making with multiply-connected influence diagrams. One example of an applicable multiply-conne ...
... singly connected [Pearl86a]. Those belief-network algorithms that are designed for performing probabilistic inference using multiply-connected belief networks can be used to perform expected-value decision making with multiply-connected influence diagrams. One example of an applicable multiply-conne ...
1 Divide and Conquer with Reduce
... You should realize, however, that this pattern does not work in general for divide-and-conquer algorithms. In particular, it does not work for algorithms that do more than a simple split that partition their input in two parts in the middle. For example, in the Euclidean Traveling Salesperson algori ...
... You should realize, however, that this pattern does not work in general for divide-and-conquer algorithms. In particular, it does not work for algorithms that do more than a simple split that partition their input in two parts in the middle. For example, in the Euclidean Traveling Salesperson algori ...
Genetic algorithm

In the field of artificial intelligence, a genetic algorithm (GA) is a search heuristic that mimics the process of natural selection. This heuristic (also sometimes called a metaheuristic) is routinely used to generate useful solutions to optimization and search problems. Genetic algorithms belong to the larger class of evolutionary algorithms (EA), which generate solutions to optimization problems using techniques inspired by natural evolution, such as inheritance, mutation, selection, and crossover.