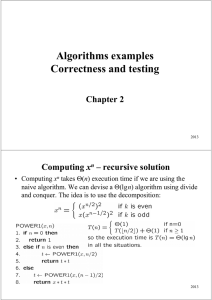
Beyond Classical Search
... input: population, a set of individuals FITNESS-FN, a function which determines the quality of the individual repeat new_population empty set loop for i from 1 to SIZE(population) do x RANDOM_SELECTION(population, FITNESS_FN) y RANDOM_SELECTION(population, FITNESS_FN) child REPRODUCE(x,y) if ...
... input: population, a set of individuals FITNESS-FN, a function which determines the quality of the individual repeat new_population empty set loop for i from 1 to SIZE(population) do x RANDOM_SELECTION(population, FITNESS_FN) y RANDOM_SELECTION(population, FITNESS_FN) child REPRODUCE(x,y) if ...
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
... • Local maxima: a local maximum, as opposed to a global maximum, is a peak that is lower than the highest peak in the state space. • Once on a local maximum, the algorithm will halt • even though the solution may be far from satisfactory. • Simple (often effective) solution – Multiple random restart ...
... • Local maxima: a local maximum, as opposed to a global maximum, is a peak that is lower than the highest peak in the state space. • Once on a local maximum, the algorithm will halt • even though the solution may be far from satisfactory. • Simple (often effective) solution – Multiple random restart ...
Research Paper
... has proven to be timely in not only its assessment of the arguments against the possibility of creating an intelligent computing machine, but also its answers to those arguments. The Turing Test concerns itself with measuring the performance of an allegedly intelligent machine against a human being. ...
... has proven to be timely in not only its assessment of the arguments against the possibility of creating an intelligent computing machine, but also its answers to those arguments. The Turing Test concerns itself with measuring the performance of an allegedly intelligent machine against a human being. ...
Guided Local Search Joins the Elite in Discrete Optimisation 1
... (b) an objective function: given any candidate solution, this function returns a numerical value. The problem is seen as an optimisation problem according to this objective function (which is to be minimized or maximized); (c) a neighbourhood function that maps every candidate solution x (often call ...
... (b) an objective function: given any candidate solution, this function returns a numerical value. The problem is seen as an optimisation problem according to this objective function (which is to be minimized or maximized); (c) a neighbourhood function that maps every candidate solution x (often call ...
Computational Intelligence
... to learn and/or to deal with new situations, such that the system is perceived to possess one or more attributes of reason, such as generalization, discovery, association and abstraction. Silicon-based computational intelligence systems usually comprise hybrids of paradigms such as artificial neural ...
... to learn and/or to deal with new situations, such that the system is perceived to possess one or more attributes of reason, such as generalization, discovery, association and abstraction. Silicon-based computational intelligence systems usually comprise hybrids of paradigms such as artificial neural ...
Design of Algorithms - Homework II (Solutions)
... That is, Xij is the indicator random variable for the event that the pair (i, j), with i < j, is inverted. Now, Pr{Xij = 1} is equal to 12 , because in any random permutation of distinct numbers, there are precisely two possibilities, viz., A[i] > A[j] and A[j] > A[i], with each of them having proba ...
... That is, Xij is the indicator random variable for the event that the pair (i, j), with i < j, is inverted. Now, Pr{Xij = 1} is equal to 12 , because in any random permutation of distinct numbers, there are precisely two possibilities, viz., A[i] > A[j] and A[j] > A[i], with each of them having proba ...
File
... When searching for the number 62, give the value of the middle, upper and lower variables after the second pass. ...
... When searching for the number 62, give the value of the middle, upper and lower variables after the second pass. ...
1 Review of Least Squares Solutions to Overdetermined Systems
... Note that any solution of the normal equations (3) is a correct solution to our least squares problem. Most likely, A0 A is nonsingular, so there is a unique solution. If A0 A is singular, still any solution to (3) is a correct solution to our problem. In this case, there will be infinitely many sol ...
... Note that any solution of the normal equations (3) is a correct solution to our least squares problem. Most likely, A0 A is nonsingular, so there is a unique solution. If A0 A is singular, still any solution to (3) is a correct solution to our problem. In this case, there will be infinitely many sol ...
Genetic algorithm

In the field of artificial intelligence, a genetic algorithm (GA) is a search heuristic that mimics the process of natural selection. This heuristic (also sometimes called a metaheuristic) is routinely used to generate useful solutions to optimization and search problems. Genetic algorithms belong to the larger class of evolutionary algorithms (EA), which generate solutions to optimization problems using techniques inspired by natural evolution, such as inheritance, mutation, selection, and crossover.